为防止河蟹,“打”用“attack”代替
手玩一下发现他大概是可以贪心的
贪心的规则如下:
在求 maxans 时,分为以下情况:
环:siz - 1
自环:1
树:siz - 叶子数
基环树:siz - 叶子数
所以 maxans 就可以简化成 (n - 叶子数 - 非自环数)
在求 minans 时,分为以下情况:
环:(siz + 1) / 2
树:从叶子向上一层一层 attack
基环树:从叶子向上一层一层 attack
貌似这样就没问题了,可以拿一个很像拓扑排序的东西写了
多画几个图会发现,对于基环树求 minans时,
叶子的深度奇偶不同造成的情况也不同
下面讨论一下
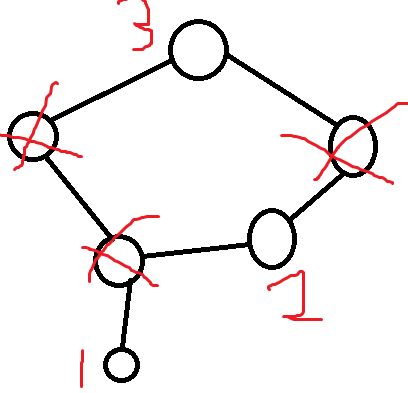
对于这样的一张图,直接从叶子开始按标号顺序 attack 是可以得到期望的最小答案的
那接下来考虑另一种情况,
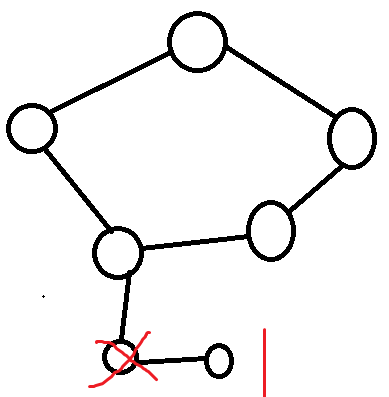
当环下的树的层数为偶数且没有处于奇数层的叶子时,
从叶子开始 attack ,中间某一步会剩下环,可以直接用上面对环讨论的情况做
如果是写 dfs 的话按照深度为奇数的情况做也是可以的...
下面简单证明一下求 minans 时基环树的贪心:
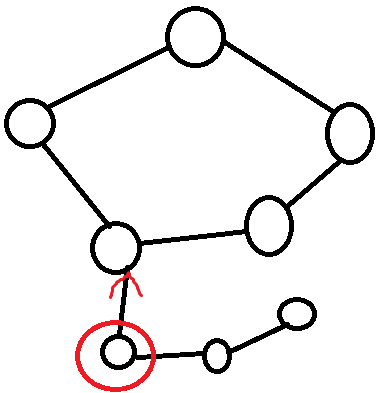
还拿这张图来说就行
考虑为什么要让圈中的点 attack 环上的点
显然,如果不让他 attack,他一定要被 attack
考虑两种情况的贡献,
首先即让他 attack 又让他被 attack 一定是不优的,因为求的是 minans
将当前树的答案设为 tans
若让他 attack,环的答案不变,tans 一定不变
若不让他 attack,环的答案不变,tans +1
为什么无论如何环的答案不会变呢?
回顾之前求环的答案的式子时,
它的 minans 其实就是从一个点开始顺着环的方向 attack
就是说你把环 attack 散了 和 保留完整的再求 minans 时都是一样的
所以这题就这么做就可以了
代码不写 dfs 实现起来比较恶心...
我是用并查集求的环,其他的代码里都有注释
反正都是中国式英语实在不懂机翻也是很准的= =...
代码:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1000005;
int n, top, minans, maxans;
int to[MAXN], fa[MAXN], siz[MAXN];
int ind[MAXN], stk[MAXN], len[MAXN];
int col[MAXN];
bool inc[MAXN], hascir[MAXN], GG[MAXN], chked[MAXN];
// 'stk' : storging circles' vertices
// 'len' : storging circles' length
// 'col' : marking that this vertice belongs to which circle
// 'inc' : vertice x is/isn't in a circle
// 'hascir' : the circle based on vertice x is/isn't a complete circle
// 'GG' : vertice x is/isn't alive
// 'chked' : whether vertice x has been checked
queue<int> q;
inline int rd() {
register int x = 0;
register char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
int findfa(int x) {
return ((fa[x] == x) ? (x) : (fa[x] = findfa(fa[x])));
}
inline bool link(int x, int y) {
register int fx = findfa(x), fy = findfa(y);
if (fx == fy) return false;
if (siz[fx] > siz[fy]) {
fa[fy] = fx;
siz[fx] += siz[fy];
} else {
fa[fx] = fy;
siz[fy] += siz[fx];
}
return true;
}
inline void markcir(int x) {
register int cur = to[x];
inc[x] = true;
len[x] = 1;
col[x] = x;
while (cur != x) {
inc[cur] = true;
col[cur] = x;
cur = to[cur];
++len[x];
}
if (len[x] == siz[findfa(x)] && len[x] != 1) {
--maxans;
}
return;
}
int main() {
n = maxans = rd();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
fa[i] = i;
siz[i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
to[i] = rd();
++ind[to[i]];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (!link(to[i], i)) {
hascir[i] = true;
stk[++top] = i; //count the circles and trees with circle
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= top ;++i) //mark all the circles
markcir(stk[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) if (!ind[i]) {
q.push(i);
--maxans;
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front(), y = to[x]; q.pop();
if (!chked[x]) --siz[findfa(x)];
chked[x] = true; //x has been checked
--ind[y];
if (!GG[x]) {
if (!GG[y]) {
GG[y] = true; //y has been slain
++minans;
q.push(y);
}
if (col[y]) {
hascir[col[y]] = false; //x broke the circle
}
} else { //if y is leagal for checking
if (!ind[y] && !GG[y] && !chked[y]) q.push(y);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= top; ++i) //if the circle is a complete circle
if (hascir[col[stk[i]]]) minans += (len[col[stk[i]]] + 1) / 2;
printf("%d %d
", minans, maxans);
return 0;
}