实验十七 线程同步控制
实验时间 2018-12-10
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术;
多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案: 引入线 引入线 引入线 程同步机制 程同步机制 程同步机制 程同步机制 程同步机制 ,使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 使得另一线程要用该方法 ,就只 能等待 。
在Java 中解决多线程同步问题 的方法有两种: 的方法有两种: 的方法有两种: 的方法有两种: 的方法有两种: 的方法有两种: 的方法有两种:
-Java SE 5.0中引入 ReentrantLock ReentrantLock ReentrantLockReentrantLock ReentrantLock类(P 648648648页)。
-在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 在共享内存的类方法前加 synchronizedsynchronizedsynchronized synchronized synchronized synchronizedsynchronized修饰符 修饰符 修饰符 。
解决方案一:锁对象 与条件解决方案一:锁对象与条件
用ReentrantLock 保护代码块的基本结构如下:
myLock.lock myLock.lock myLock.lockmyLock.lock ();
try { try {try {try {
critical section critical section critical section critical section critical section }
finally{ finally{ finally{
myLock.unlock myLock.unlock myLock.unlockmyLock.unlock myLock.unlock (); (); (); (); }
有关锁对象和条件的键要点 有关锁对象和条件的键要点 :
锁用来保护代码片段 用来保护代码片段 用来保护代码片段 用来保护代码片段 用来保护代码片段 用来保护代码片段 用来保护代码片段 用来保护代码片段 ,保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 保证任何时刻只能有一 个线程执行被保护的代码 。
锁管理试图进入被保护代码段的线程 管理试图进入被保护代码段的线程 。
锁可拥有一个或多相关 条件对象 条件对象 条件对象 条件对象 。
每个 条件对象管理 条件对象管理 条件对象管理 条件对象管理 条件对象管理 条件对象管理 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 那些已经进入被保护的代码 段但还不能运行的线程 。
解决方案二: synchronized synchronized synchronized 关键字 关
synchronized 关键字作用:
某个类内方法用 某个类内方法用 某个类内方法用 某个类内方法用 某个类内方法用 某个类内方法用 某个类内方法用 synchronizedsynchronizedsynchronizedsynchronizedsynchronizedsynchronizedsynchronized synchronizedsynchronized synchronized修饰后 修饰后 修饰后 ,该方 法被称为同步方;
只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 只要某个线程正在访问同步方法 ,其他线程 其他线程 其他线程 其他线程 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞 ,直至线程从同 直至线程从同 直至线程从同 直至线程从同 直至线程从同 直至线程从同 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程 ,其他线程方 其他线程方 其他线程方 其他线程方 其他线程方 可能进入同步方法 。
在同步方法中使用 wait() wait()、notify notify notify 和notifyAll notifyAll notifyAllnotifyAll () 方法 (见教材 656 页
一个线程在使用的同步方法中时,可能根据问题 一个线程在使用的同步方法中时,可能根据问题 一个线程在使用的同步方法中时,可能根据问题 一个线程在使用的同步方法中时,可能根据问题 的需要,必须使用 wait() wait()方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 方法使本线程等待,暂 时让出 CPU 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 的使用权,并允许其它线程这个 同步方法。
线程如果用完同步方法,应当执行 线程如果用完同步方法,应当执行 notifyAll notifyAllnotifyAll () 方 法通知所有由于使用这个同步方而处等待的 法通知所有由于使用这个同步方而处等待的 法通知所有由于使用这个同步方而处等待的 法通知所有由于使用这个同步方而处等待的 线程结束等待。
(2) 线程综合编程练习
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材651页程序14-7,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握利用锁对象和条件对象实现的多线程同步技术。

1 package synch; 2 3 /** 4 * This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure. 5 * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class SynchBankTest 9 { 10 public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; 11 public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; 12 public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; 13 public static final int DELAY = 10; 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) 16 { 17 Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); 18 for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) 19 { 20 int fromAccount = i; 21 Runnable r = () -> { 22 try 23 { 24 while (true) 25 { 26 int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); 27 double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); 28 bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); 29 Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random())); 30 } 31 } 32 catch (InterruptedException e) 33 { 34 } 35 }; 36 Thread t = new Thread(r); 37 t.start(); 38 } 39 } 40 }

1 package synch; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.*; 5 6 /** 7 * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses locks for serializing access. 8 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 9 * @author Cay Horstmann 10 */ 11 public class Bank 12 { 13 private final double[] accounts; 14 private Lock bankLock; 15 private Condition sufficientFunds; 16 17 /** 18 * Constructs the bank. 19 * @param n the number of accounts 20 * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account 21 */ 22 public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) 23 { 24 accounts = new double[n]; 25 Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); 26 bankLock = new ReentrantLock(); 27 sufficientFunds = bankLock.newCondition(); 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * Transfers money from one account to another. 32 * @param from the account to transfer from 33 * @param to the account to transfer to 34 * @param amount the amount to transfer 35 */ 36 public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException 37 { 38 bankLock.lock(); 39 try 40 { 41 while (accounts[from] < amount) 42 sufficientFunds.await(); 43 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); 44 accounts[from] -= amount; 45 System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); 46 accounts[to] += amount; 47 System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); 48 sufficientFunds.signalAll(); 49 } 50 finally 51 { 52 bankLock.unlock(); 53 } 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * Gets the sum of all account balances. 58 * @return the total balance 59 */ 60 public double getTotalBalance() 61 { 62 bankLock.lock(); 63 try 64 { 65 double sum = 0; 66 67 for (double a : accounts) 68 sum += a; 69 70 return sum; 71 } 72 finally 73 { 74 bankLock.unlock(); 75 } 76 } 77 78 /** 79 * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. 80 * @return the number of accounts 81 */ 82 public int size() 83 { 84 return accounts.length; 85 } 86 }

测试程序2:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材655页程序14-8,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握synchronized在多线程同步中的应用。

1 package synch2; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses synchronization primitives. 7 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class Bank 11 { 12 private final double[] accounts; 13 14 /** 15 * Constructs the bank. 16 * @param n the number of accounts 17 * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account 18 */ 19 public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) 20 { 21 accounts = new double[n]; 22 Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Transfers money from one account to another. 27 * @param from the account to transfer from 28 * @param to the account to transfer to 29 * @param amount the amount to transfer 30 */ 31 public synchronized void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException 32 { 33 while (accounts[from] < amount) 34 wait(); 35 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); 36 accounts[from] -= amount; 37 System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); 38 accounts[to] += amount; 39 System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); 40 notifyAll(); 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * Gets the sum of all account balances. 45 * @return the total balance 46 */ 47 public synchronized double getTotalBalance() 48 { 49 double sum = 0; 50 51 for (double a : accounts) 52 sum += a; 53 54 return sum; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. 59 * @return the number of accounts 60 */ 61 public int size() 62 { 63 return accounts.length; 64 } 65 }

1 package synch2; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses synchronization primitives. 7 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class Bank 11 { 12 private final double[] accounts; 13 14 /** 15 * Constructs the bank. 16 * @param n the number of accounts 17 * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account 18 */ 19 public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) 20 { 21 accounts = new double[n]; 22 Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Transfers money from one account to another. 27 * @param from the account to transfer from 28 * @param to the account to transfer to 29 * @param amount the amount to transfer 30 */ 31 public synchronized void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException 32 { 33 while (accounts[from] < amount) 34 wait(); 35 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); 36 accounts[from] -= amount; 37 System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); 38 accounts[to] += amount; 39 System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); 40 notifyAll(); 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * Gets the sum of all account balances. 45 * @return the total balance 46 */ 47 public synchronized double getTotalBalance() 48 { 49 double sum = 0; 50 51 for (double a : accounts) 52 sum += a; 53 54 return sum; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. 59 * @return the number of accounts 60 */ 61 public int size() 62 { 63 return accounts.length; 64 } 65 }
测试程序3:
l 在Elipse环境下运行以下程序,结合程序运行结果分析程序存在问题;
l 尝试解决程序中存在问题。
|
class Cbank { private static int s=2000; public static void sub(int m) { int temp=s; temp=temp-m; try { Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } s=temp; System.out.println("s="+s); } } class Customer extends Thread { public void run() { for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) Cbank.sub(100); } } public class Thread3 { public static void main(String args[]) { Customer customer1 = new Customer(); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer1.start(); customer2.start(); } } |


1 package synch3; 2 class Cbank 3 { 4 private static int s=2000; 5 public synchronized static void sub(int m) 6 { 7 int temp=s; 8 temp=temp-m; 9 try { 10 Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); 11 } 12 catch (InterruptedException e) { } 13 s=temp; 14 System.out.println("s="+s); 15 } 16 } 17 class Customer extends Thread 18 { 19 public void run() 20 { 21 for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) 22 Cbank.sub(100); 23 } 24 } 25 public class Thread3 26 { 27 public static void main(String args[]) 28 { 29 Customer customer1 = new Customer(); 30 Customer customer2 = new Customer(); 31 customer1.start(); 32 customer2.start(); 33 } 34 }

实验2 编程练习
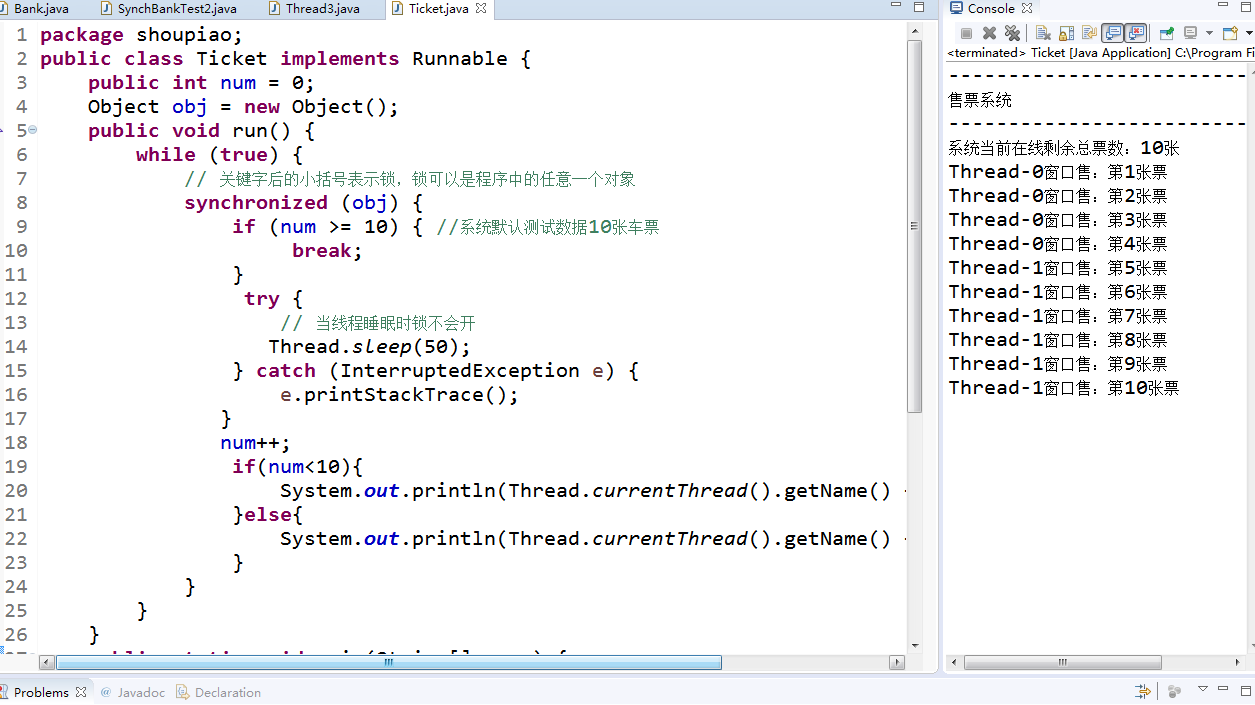
利用多线程及同步方法,编写一个程序模拟火车票售票系统,共3个窗口,卖10张票,程序输出结果类似(程序输出不唯一,可以是其他类似结果)。
Thread-0窗口售:第1张票
Thread-0窗口售:第2张票
Thread-1窗口售:第3张票
Thread-2窗口售:第4张票
Thread-2窗口售:第5张票
Thread-1窗口售:第6张票
Thread-0窗口售:第7张票
Thread-2窗口售:第8张票
Thread-1窗口售:第9张票
Thread-0窗口售:第10张票

1 package shoupiao; 2 public class Ticket implements Runnable { 3 public int num = 0; 4 Object obj = new Object(); 5 public void run() { 6 while (true) { 7 // 关键字后的小括号表示锁,锁可以是程序中的任意一个对象 8 synchronized (obj) { 9 if (num >= 10) { //系统默认测试数据10张车票 10 break; 11 } 12 try { 13 // 当线程睡眠时锁不会开 14 Thread.sleep(50); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 num++; 19 if(num<10){ 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "第"+num+"张票" ); 21 }else{ 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "第"+num+"张票" ); 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 public static void main(String[] args) { 28 Ticket ticket = new Ticket(); 29 //1.创建购票线程 30 Thread t1 = new Thread(ticket, "Thread-0窗口售:"); 31 Thread t2 = new Thread(ticket, "Thread-1窗口售:"); 32 Thread t3 = new Thread(ticket, "Thread-2窗口售:"); 33 //2.开启购票点(模拟3个线程)测试购票 34 System.out.println("---------------------------------"); 35 System.out.println("售票系统"); 36 System.out.println("---------------------------------"); 37 System.out.println("系统当前在线剩余总票数:10张"); 38 t1.start(); 39 t2.start(); 40 t3.start(); 41 } 42 }
实验总结:通过对多线程的进一步学习,理解了线程中各种状态代表的含义,以及如何调用,运行的原理,理解和掌握了线程的优先级属性及调度方法,线程同步的概念及实现技术。通过多线程的运用,实现了多个程序同步运行,以及各个程序在运行期间各种状态如何合理有序的切换
