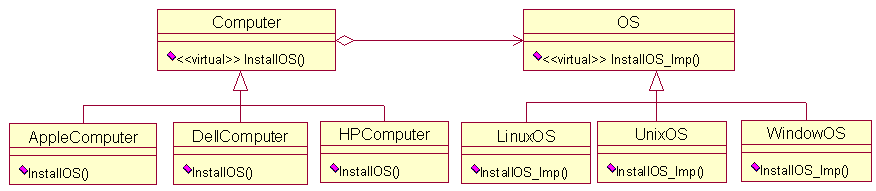
[DP]书上定义:将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化。考虑装操作系统,有多种配置的计算机,同样也有多款操作系统。如何运用桥接模式呢?可以将操作系统和计算机分别抽象出来,让它们各自发展,减少它们的耦合度。当然了,两者之间有标准的接口。这样设计,不论是对于计算机,还是操作系统都是非常有利的。下面给出这种设计的UML图,其实就是桥接模式的UML图。
UML图:
// Bridge.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class OS
{
public:
virtual void InstallOS_Imp(){}
};
{
public:
virtual void InstallOS_Imp(){}
};
class WindowOS:public OS
{
public:
virtual void InstallOS_Imp() override
{
cout<<"安装windows操作系统"<<endl;
}
};
class LinuxOS:public OS
{
public:
virtual void InstallOS_Imp() override
{
cout<<"安装Linux操作系统"<<endl;
}
};
{
public:
virtual void InstallOS_Imp() override
{
cout<<"安装windows操作系统"<<endl;
}
};
class LinuxOS:public OS
{
public:
virtual void InstallOS_Imp() override
{
cout<<"安装Linux操作系统"<<endl;
}
};
class UnixOS: public OS
{
public:
void InstallOS_Imp() { cout<<"安装Unix操作系统"<<endl; }
};
{
public:
void InstallOS_Imp() { cout<<"安装Unix操作系统"<<endl; }
};
class Computer
{
public:
virtual void InstallOS(OS *os) {}
};
{
public:
virtual void InstallOS(OS *os) {}
};
class DellComputer:public Computer
{
public:
DellComputer()
{
cout<<"Dell电脑"<<endl;
}
void InstallOS(OS *os) override
{
os->InstallOS_Imp();
}
};
{
public:
DellComputer()
{
cout<<"Dell电脑"<<endl;
}
void InstallOS(OS *os) override
{
os->InstallOS_Imp();
}
};
class AppleComputer:public Computer
{
public:
AppleComputer()
{
cout<<"苹果电脑"<<endl;
}
void InstallOS(OS *os) override
{
os->InstallOS_Imp();
}
};
{
public:
AppleComputer()
{
cout<<"苹果电脑"<<endl;
}
void InstallOS(OS *os) override
{
os->InstallOS_Imp();
}
};
class HPComputer:public Computer
{
public:
HPComputer()
{
cout<<"HP电脑"<<endl;
}
void InstallOS(OS *os) override
{
os->InstallOS_Imp();
}
};
{
public:
HPComputer()
{
cout<<"HP电脑"<<endl;
}
void InstallOS(OS *os) override
{
os->InstallOS_Imp();
}
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
cout<<"桥接模式"<<endl;
OS *os1 = new WindowOS();
OS *os2 = new LinuxOS();
Computer *computer1 = new AppleComputer();
computer1->InstallOS(os1);
computer1->InstallOS(os2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
{
cout<<"桥接模式"<<endl;
OS *os1 = new WindowOS();
OS *os2 = new LinuxOS();
Computer *computer1 = new AppleComputer();
computer1->InstallOS(os1);
computer1->InstallOS(os2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}