MinkowskiPooling池化(下)
MinkowskiPoolingTranspose
class MinkowskiEngine.MinkowskiPoolingTranspose(kernel_size, stride, dilation=1, kernel_generator=None, dimension=None)
稀疏张量的池转置层。
展开功能,然后将其除以贡献的非零元素的数量。
__init__(kernel_size, stride, dilation=1, kernel_generator=None, dimension=None)
用于稀疏张量的高维解卷层。
Args:
kernel_size (int, optional): 输出张量中内核的大小。如果未提供,则region_offset应该是 RegionType.CUSTOM并且region_offset应该是具有大小的2D矩阵N×D 这样它列出了所有D维度的 N 偏移量。.
stride (int, or list, optional): stride size of the convolution layer. If non-identity is used, the output coordinates will be at least stride ×× tensor_stride away. When a list is given, the length must be D; each element will be used for stride size for the specific axis.
dilation (int, or list, optional): 卷积内核的扩展大小。给出列表时,长度必须为D,并且每个元素都是轴特定的膨胀。所有元素必须> 0。
kernel_generator (MinkowskiEngine.KernelGenerator, optional): 定义自定义内核形状。
dimension(int):定义所有输入和网络的空间的空间尺寸。例如,图像在2D空间中,网格和3D形状在3D空间中。
cpu() → T
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至CPU。
返回值:
模块:selfcuda(device: Optional[Union[int, torch.device]] = None) → T
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至GPU。
这也使关联的参数并缓冲不同的对象。因此,在构建优化程序之前,如果模块在优化过程中可以在GPU上运行,则应调用它。
参数:
设备(整数,可选):如果指定,则所有参数均为
复制到该设备
返回值:
模块:self
double() →T
将所有浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为double数据类型。
返回值:
模块:self
float() →T
将所有浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为float数据类型。
返回值:
模块:self
forward(input: SparseTensor.SparseTensor, coords: Union[torch.IntTensor, MinkowskiCoords.CoordsKey, SparseTensor.SparseTensor] = None)
input (MinkowskiEngine.SparseTensor): Input sparse tensor to apply a convolution on.
coords ((torch.IntTensor, MinkowskiEngine.CoordsKey, MinkowskiEngine.SparseTensor), optional): If provided, generate results on the provided coordinates. None by default.
to(*args, **kwargs)
Moves and/or casts the parameters and buffers.
This can be called as
to(device=None, dtype=None, non_blocking=False)
to(dtype, non_blocking=False)
to(tensor, non_blocking=False)
to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
其签名类似于torch.Tensor.to(),但仅接受所需dtype的浮点s。另外,此方法将仅将浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为dtype (如果给定的话)。device如果给定了整数参数和缓冲区 ,但dtype不变。当 non_blocking被设置时,它试图转换/如果可能异步相对于移动到主机,例如,移动CPU张量与固定内存到CUDA设备。
请参见下面的示例。
Args:
device (torch.device): the desired device of the parameters
and buffers in this module
dtype (torch.dtype): the desired floating point type of
the floating point parameters and buffers in this module
tensor (torch.Tensor): Tensor whose dtype and device are the desired
dtype and device for all parameters and buffers in this module
memory_format (torch.memory_format): the desired memory
format for 4D parameters and buffers in this module (keyword only argument)
Returns:
Module: self
Example:
>>> linear = nn.Linear(2, 2)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]])
>>> linear.to(torch.double)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> gpu1 = torch.device("cuda:1")
>>> linear.to(gpu1, dtype=torch.half, non_blocking=True)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16, device='cuda:1')
>>> cpu = torch.device("cpu")
>>> linear.to(cpu)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16)
type(dst_type: Union[torch.dtype, str]) → T
Casts all parameters and buffers to dst_type.
Arguments:
dst_type (type or string): the desired type
Returns:
Module: self
MinkowskiGlobalPooling
class MinkowskiEngine.MinkowskiGlobalPooling(average=True, mode=<GlobalPoolingMode.AUTO: 0>)
将所有输入功能集中到一个输出。
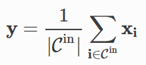
将稀疏坐标减少到原点,即将每个点云减少到原点,返回batch_size点的数量[[0,0,…,0],[0,0,…,1] ,, [0, 0,…,2]],其中坐标的最后一个元素是批处理索引。
Args:
average (bool): 当为True时,返回平均输出。如果不是,则返回所有输入要素的总和。
cpu() → T
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至CPU。
返回值:
模块:自我
Module: self
cuda(device: Optional[Union[int, torch.device]] = None) → T
将所有模型参数和缓冲区移至GPU。
这也使关联的参数并缓冲不同的对象。因此,在构建优化程序之前,如果模块在优化过程中可以在GPU上运行,则应调用它。
参数:
device (int, optional): if specified, all parameters will be
copied to that device
Returns:
Module: self
double() → T
将所有浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为double数据类型。
Returns:
Module: self
float() → T
将所有浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为float数据类型。
返回值:
模块:self
forward(input)
to(*args, **kwargs)
移动和/或强制转换参数和缓冲区。
这可以称为
to(device=None, dtype=None, non_blocking=False)
to(dtype, non_blocking=False)
to(tensor, non_blocking=False)
to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
其签名类似于torch.Tensor.to(),但仅接受所需dtype的浮点s。另外,此方法将仅将浮点参数和缓冲区强制转换为dtype (如果给定的话)。device如果给定了整数参数和缓冲区 ,dtype不变。当 non_blocking被设置时,它试图转换/如果可能异步相对于移动到主机,例如,移动CPU张量与固定内存到CUDA设备。
请参见下面的示例。
Args:
device (torch.device): the desired device of the parameters
and buffers in this module
dtype (torch.dtype): the desired floating point type of
the floating point parameters and buffers in this module
tensor (torch.Tensor): Tensor whose dtype and device are the desired
dtype and device for all parameters and buffers in this module
memory_format (torch.memory_format): the desired memory
format for 4D parameters and buffers in this module (keyword only argument)
Returns:
Module: self
Example:
>>> linear = nn.Linear(2, 2)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]])
>>> linear.to(torch.double)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1913, -0.3420],
[-0.5113, -0.2325]], dtype=torch.float64)
>>> gpu1 = torch.device("cuda:1")
>>> linear.to(gpu1, dtype=torch.half, non_blocking=True)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16, device='cuda:1')
>>> cpu = torch.device("cpu")
>>> linear.to(cpu)
Linear(in_features=2, out_features=2, bias=True)
>>> linear.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.1914, -0.3420],
[-0.5112, -0.2324]], dtype=torch.float16)
type(dst_type: Union[torch.dtype, str]) → T
Casts all parameters and buffers to dst_type.
Arguments:
dst_type (type or string): the desired type
Returns:
Module: self