聚合函数
count 返回查询结果的条数
max 返回查询结果的最大值
min 返回查询结果的最小值
sum 返回查询结果的和
avg 返回查询结果的平均值
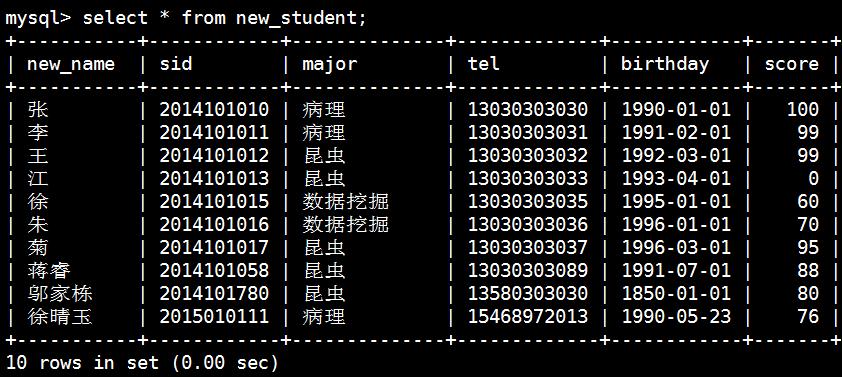
统计分数大于等于90的人数:
mysql> select count(*) from new_student
-> where score >="90";
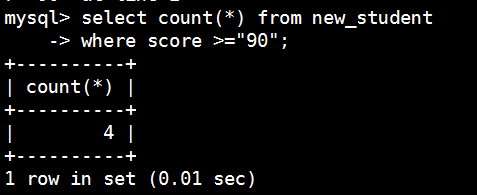
使用distinct剔除字段值重复的条数
mysql> select count(distinct score) from new_student
-> where score >="90";
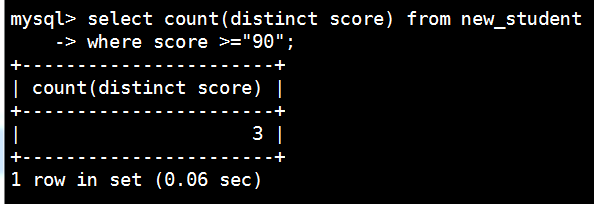
统计最高分-max
mysql> select max(score) from new_student;
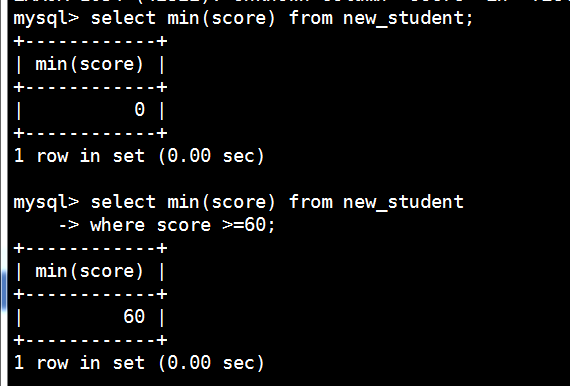
统计最低分-min
mysql> select min(score) from new_student;
mysql> select min(score) from new_student
-> where score >=60;
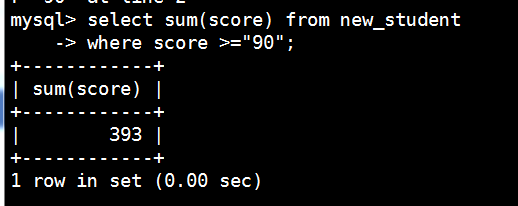
统计分数大于等于90的分数的和-sum
mysql> select sum(score) from new_student
-> where score >="90";
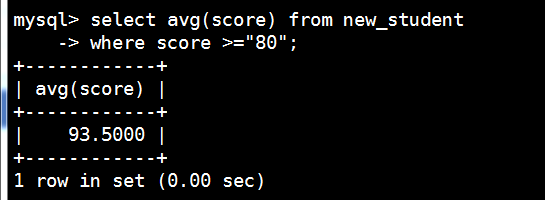
统计平均数-avg
mysql> select avg(score) from new_student
-> where score >="80";
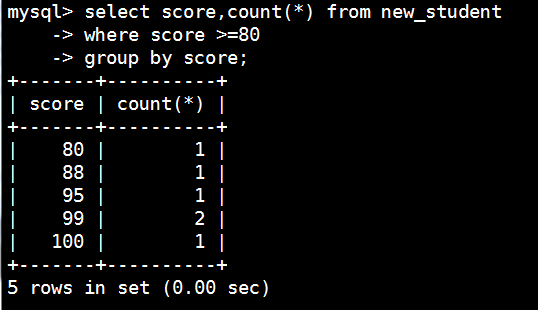
分组查询
语法格式;
select [聚合函数] 字段名 from 表名
where 查询条件
group by 字段名
having 过滤条件
mysql> select score,count(*) from new_student
-> where score >=80
-> group by score;
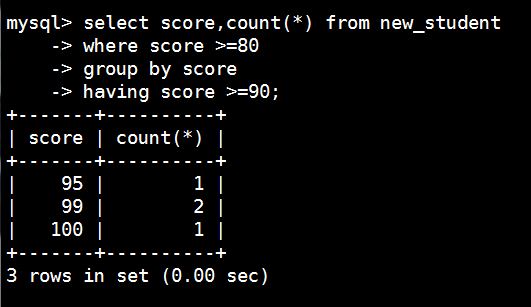
mysql> select score,count(*) from new_student
-> where score >=80
-> group by score
-> having score >=90;
注:having子语句与where子语句区别:前者在分组后对记录进行过滤,后者在分组前对记录进行过滤
mysql> select score,count(*) from new_student
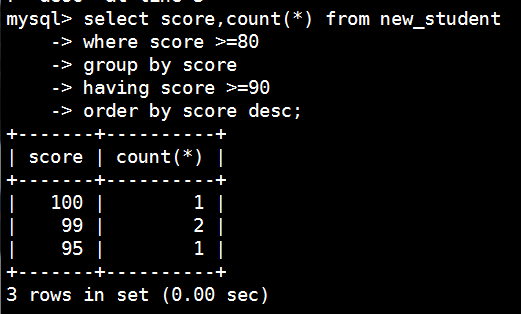
-> where score >=80
-> group by score
-> having score >=90
-> order by score desc;

联合查询
语法格式
select 语句
union [all]
select 语句
...
注:联合查询结果使用第一个select语句中的字段名
mysql> select * from test_wl
-> union
-> select * from test_wu;
