1、fork之后父子进程共享文件:文件引用计数的值改变,共享偏移。
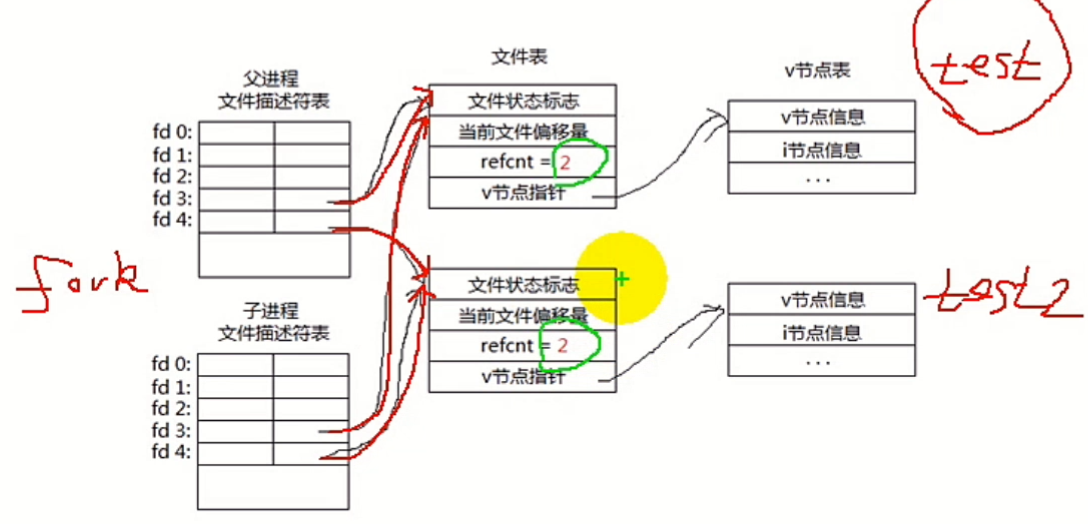
在下面的例子中test.txt为parentchil。如果子进程没有睡眠,两个进程交叉执行,内容不可预测。
1 #include<unistd.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include <sys/stat.h> 4 #include <fcntl.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<stdio.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 #include<string.h> 9 #include<signal.h> 10 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 11 do 12 { 13 perror(m); 14 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 15 }while(0) //宏要求一条语句 16 17 int main() 18 { 19 signal(SIGCHLD,SIG_IGN);//避免僵死进程。父进程忽略子进程退出信号SIGCHLD 20 printf("before fork pid=%d ",getpid()); 21 int fd; 22 fd=open("test.txt",O_WRONLY); 23 if(fd==-1) 24 ERR_EXIT("open error"); 25 26 pid_t pid; 27 pid=fork(); 28 if(pid==-1) 29 ERR_EXIT("fork error"); 30 if(pid>0) 31 { 32 printf("parent "); 33 write(fd,"parent",6); 34 } 35 36 else if(pid==0) 37 { 38 sleep(1); 39 printf("child "); 40 write(fd,"child",5);//偏移6,child在parent之后。 41 } 42 43 return 0; 44 }
2、fork与vfork:
在fork还没有实现copy on write之前,UNIX设计者很关心fork之后立刻执行exec所造成的地址空间浪费,所以引入了vfork系统调用。vfork有个限制,子进程必须立刻
执行_exit或者exec函数。即使fork实现了copy on write,效率也没有vfork高,但是我们不推荐使用vfork,因为几乎每一个vfork的实现,都或多或少存在一定的问题。
vfork+exec:创建一个进程+exec vfork不会复制父进程地址空间,共享地址空间,直接替换进程,大大提高了效率。
1 #include<unistd.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include <sys/stat.h> 4 #include <fcntl.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<stdio.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 #include<string.h> 9 #include<signal.h> 10 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 11 do 12 { 13 perror(m); 14 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 15 }while(0) //宏要求一条语句 16 int gval=100; 17 int main() 18 { 19 signal(SIGCHLD,SIG_IGN);//避免僵死进程 20 printf("before fork pid=%d ",getpid()); 21 22 pid_t pid; 23 //pid=fork();//copy on write机制。数据改变时,子进程才拷贝。gval=100(p),gval=101(child) 24 pid=vfork();//gval=101(p) gval=101(c)在exec之前子进程是没有独立的地址空间的。且会有一个段错误vfork有个限制,子进程必须立刻执行_exit或者exec函数。 25 if(pid==-1) 26 ERR_EXIT("fork error"); 27 if(pid>0) 28 { 29 sleep(1); 30 printf("parent,gval=%d ",gval);//100 31 } 32 33 else if(pid==0) 34 { 35 gval++; 36 printf("child,gval=%d ",gval);//101 37 _exit(0);//如果没有会有段错误。 38 } 39 40 return 0; 41 }
3、exit与_exit:
a、_exit是一个系统调用,exit是一个C库函数。
b、调用_exit直接陷入内核,进程终止;调用exit会先调用终止处理程序(终止处理程序是程序结束时调用的代码段,需要安装),然后清除I/O缓冲,接下来和_exit一样的操作。
4、atexit:
atexit可以注册终止处理程序,ANSI C规定最多只能注册32个终止处理程序。终止处理程序的调用与注册相反。
#include <stdlib.h>
int atexit(void (*function)(void));
1 #include<unistd.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<stdio.h> 5 #include<errno.h> 6 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 7 do 8 { 9 perror(m); 10 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 11 }while(0) //宏要求一条语句 12 void my_exit1(void) 13 { 14 printf("my exit1... "); 15 } 16 void my_exit2(void) 17 { 18 printf("my exit2... "); 19 } 20 int main() 21 { 22 23 atexit(my_exit1); 24 atexit(my_exit2); 25 exit(0); 26 //my exit2... 27 //my exit1... 28 }