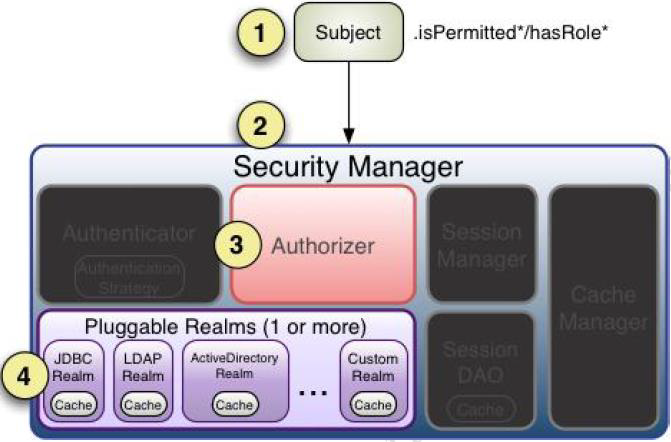
把 realms 配置给SecurityManager
在认证的时候单个realm是这样配置的:
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/> <!-- Single realm app. If you have multiple realms, use the 'realms' property instead. --> <!-- 配置session的管理方式 --> <!-- <property name="sessionMode" value="native"/> --> <property name="realm" ref="jdbcRealm"/> </property> </bean>
多个realm是这样配置的:
1).将多个realm配置给 authenticator
<!-- 配置多个Realm --> <bean id="authenticator" class="org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator"> <property name="realms"> <list> <ref bean="jdbcRealm"/> <ref bean="secondRealm"/> </list> </property> <property name="authenticationStrategy"> <bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AllSuccessfulStrategy"></bean> </property> </bean>
2).将 authenticator 配置给 SecurityManager
<!-- 1.配置SecurityManager! --> <bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/> <!-- Single realm app. If you have multiple realms, use the 'realms' property instead. --> <!-- 配置session的管理方式 --> <!-- <property name="sessionMode" value="native"/> --> <!-- <property name="realm" ref="jdbcRealm"/> --> <!-- 配置多个Realm --> <property name="authenticator" ref="authenticator"></property> </bean>
其实SecurityManager 中有一个 realms属性
<!-- 1.配置SecurityManager! --> <bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/> <!-- Single realm app. If you have multiple realms, use the 'realms' property instead. --> <!-- 配置session的管理方式 --> <!-- <property name="sessionMode" value="native"/> --> <!-- <property name="realm" ref="jdbcRealm"/> --> <!-- 配置多个Realm --> <property name="authenticator" ref="authenticator"></property> <property name="realms"></property> </bean>
那么直接在SecurityManager中配置 realms中是否可以呢,答案是可以的。
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/> <!-- Single realm app. If you have multiple realms, use the 'realms' property instead. --> <!-- 配置session的管理方式 --> <!-- <property name="sessionMode" value="native"/> --> <!-- <property name="realm" ref="jdbcRealm"/> --> <!-- 配置多个Realm --> <property name="authenticator" ref="authenticator"></property> <property name="realms"> <list> <ref bean="jdbcRealm"/> <ref bean="secondRealm"/> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置多个Realm --> <bean id="authenticator" class="org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator"> <property name="authenticationStrategy"> <bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AllSuccessfulStrategy"></bean> </property> </bean>
在授权中是需要将realms改为这样配置的
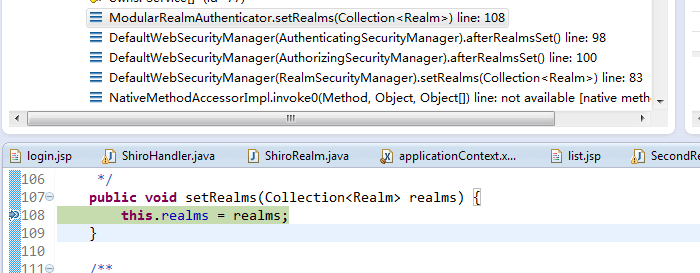
可以再 ModularRealmAuthenticator 的setRealms 中打个断点
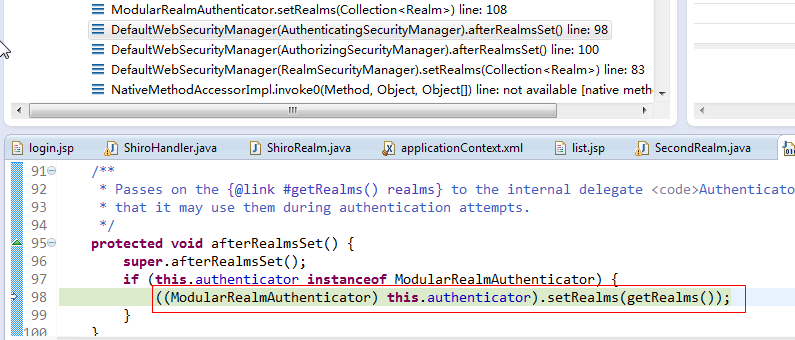
代码往前翻可以看到这里做了强制类型转换
授权:


默认拦截器:
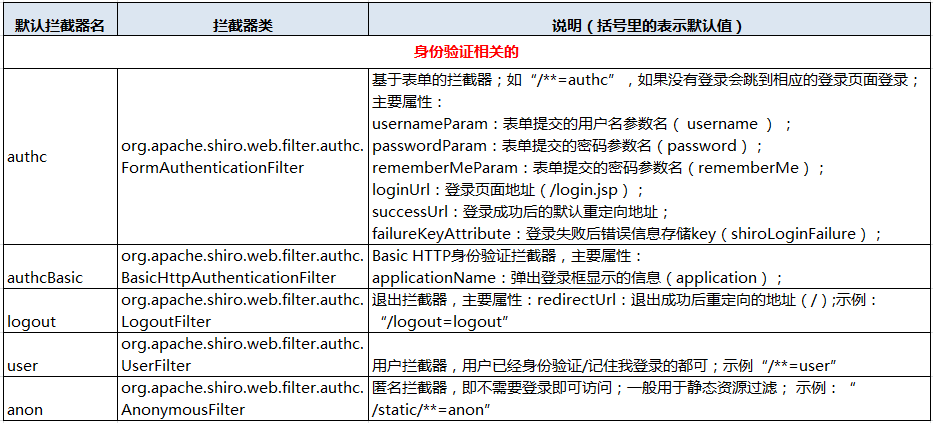
- Shiro内置了很多默认的拦截器,比如身份验证,授权等相关的。默认拦截器可以参考
public enum DefaultFilter { anon(AnonymousFilter.class), authc(FormAuthenticationFilter.class), authcBasic(BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter.class), logout(LogoutFilter.class), noSessionCreation(NoSessionCreationFilter.class), perms(PermissionsAuthorizationFilter.class), port(PortFilter.class), rest(HttpMethodPermissionFilter.class), roles(RolesAuthorizationFilter.class), ssl(SslFilter.class), user(UserFilter.class); private final Class<? extends Filter> filterClass; private DefaultFilter(Class<? extends Filter> filterClass) { this.filterClass = filterClass; } public Filter newInstance() { return (Filter) ClassUtils.newInstance(this.filterClass); } public Class<? extends Filter> getFilterClass() { return this.filterClass; } public static Map<String, Filter> createInstanceMap(FilterConfig config) { Map<String, Filter> filters = new LinkedHashMap<String, Filter>(values().length); for (DefaultFilter defaultFilter : values()) { Filter filter = defaultFilter.newInstance(); if (config != null) { try { filter.init(config); } catch (ServletException e) { String msg = "Unable to correctly init default filter instance of type " + filter.getClass().getName(); throw new IllegalStateException(msg, e); } } filters.put(defaultFilter.name(), filter); } return filters; } }
身份验证相关的有:
授权相关的:
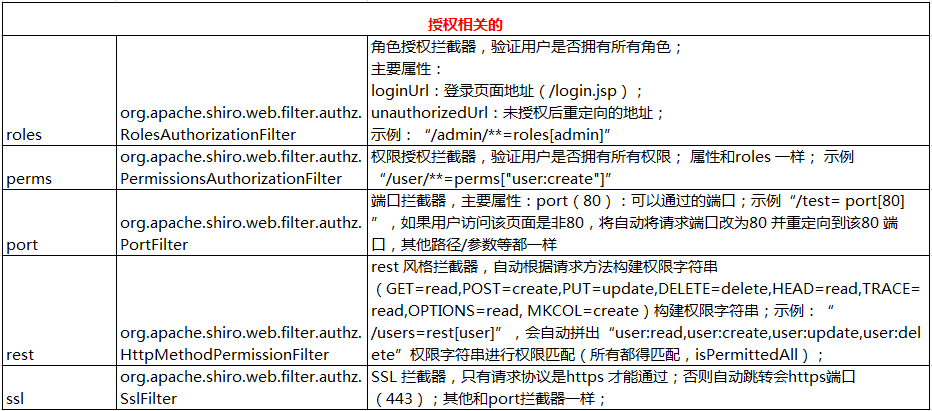
其他:

为访问路径配置权限:
1). 修改页面为 list.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h4>List Page</h4> <a href="admin.jsp">Admin Page</a> <br><br> <a href="user.jsp">User Page</a> <br><br> <a href="shiro/logout">Logout</a> </body> </html>
2). 在配置文件的过滤器中添加
<property name="filterChainDefinitions"> <value> /login.jsp= anon /shiro/login= anon /shiro/logout = logout /user.jsp = roles[user] /admin.jsp = roles[admin] # everything else requires authentication: /** = authc </value> </property>
3).授权需要继承 AuthorizingRealm 类,并实现其 doGetAuthorizationInfo 方法
AuthorizingRealm 类继承自 AuthorizingRealm , 但没有实现 AuthorizingRealm 中的 doGetAuthenticationInfo,
所以认证和授权 只需要继承 AuthorizingRealm就可以了,同时实现他们两个抽象方法。
package com.java.shiro.realms; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; public class TestRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { //授权需要实现的方法 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo( PrincipalCollection principals) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } //认证需要实现的方法 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo( AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } }
查看源码得到,多Realm授权中只要有一个通过就可以 ModularRealmAuthorizer
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principals, String roleIdentifier) { assertRealmsConfigured(); for (Realm realm : getRealms()) { if (!(realm instanceof Authorizer)) continue; if (((Authorizer) realm).hasRole(principals, roleIdentifier)) { return true; } } return false; }
授权Realm的实现
1). 在原先的ShiroRealm的基础上修改,修改其继承
package com.java.shiro.realms; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.LockedAccountException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.SimpleHash; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource; public class ShiroRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { /** * 用于认证的Realm保持不变 */ @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo( AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("[FirstRealm] doGetAuthenticationInfo " + token); // 1. 把AuthenticationToken 转换为UsernamePasswordToken UsernamePasswordToken up = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; // 2. 从UsernamePasswordToken 中来获取username String username = up.getUsername(); // 3. 调用数据库的方法,从数据库中查询username对应的用户记录 System.out.println("从数据库中获取userName :" + username + " 所对应的用户信息."); // 4. 若用户不存在,则可以抛出 UnknownAccoountException 异常 if ("unknown".equals(username)) { throw new UnknownAccountException("用户不存在"); } // 5. 根据用户信息的情况,决定是否需要抛出其他的AuthencationException 异常 假设用户被锁定 if ("monster".equals(username)) { throw new LockedAccountException("用户被锁定"); } // 6. 根据用户的情况,来构建AuthenticationInfo 对象并返回,通常使用的是 // SimpleAuthenticationInfo // 以下信息是从数据库获取的. Object principal = username; // principal 认证的实体信息. // 可以是username,也可以是数据表对应的用户的实体类对象 // String credentials = // "fc1709d0a95a6be30bc5926fdb7f22f4"; // // credentials:密码 String credentials = null; // credentials:密码 String realmName = getName(); AuthenticationInfo info = null;/* * new * SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, * credentials, realmName); */ if ("admin".equals(username)) { credentials = "038bdaf98f2037b31f1e75b5b4c9b26e"; } else if ("user".equals(username)) { credentials = "098d2c478e9c11555ce2823231e02ec1"; } ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(username);// 这里的参数要给个唯一的; info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, credentialsSalt, realmName); return info; } public static void main(String[] args) { String hashAlgorithmName = "MD5"; String credentials = "123456"; int hashIterations = 1024; ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes("user"); Object obj = new SimpleHash(hashAlgorithmName, credentials, credentialsSalt, hashIterations); System.out.println(obj); } /** * 这个是用于授权的Realm */ @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo( PrincipalCollection principals) { // 1. 从 PrincipalCollection 中获取来获取登录用户的信息 //由于我们配置了多个Realm 一个返回的是 seconde,一个返回的是认证实体,这两个Realm在配置认证的时候是有顺序地 /** * <property name="realms"> * <list> * <ref bean="jdbcRealm"/> * <ref bean="secondRealm"/> * </list> * </property> * * 当我们在获取Principal的时候也是有顺序的 */ Object principal = principals.getPrimaryPrincipal(); // 2. 利用登录用户的信息来判断当前用户的角色或权限(可能需要查询数据库) Set<String> roles = new HashSet<>(); roles.add("user"); // 这里无论登录的是user 还是 admin 都存放一个user角色 if ("admin".equals(principal)) { roles.add("admin"); // 如果是admin 授权一个admin角色 } AuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(roles); return info; } }
由于我们配置了多个Realm 一个返回的是 seconde,一个返回的是认证实体,这两个Realm在配置认证的时候是有顺序地
<property name="realms"> <list> <ref bean="jdbcRealm"/> <ref bean="secondRealm"/> </list> </property>
当我们在获取Principal的时候也是有顺序的
通过查看源代码
public Object getPrimaryPrincipal() { if (isEmpty()) { return null; } return iterator().next(); }
public Iterator iterator() { return asSet().iterator(); }
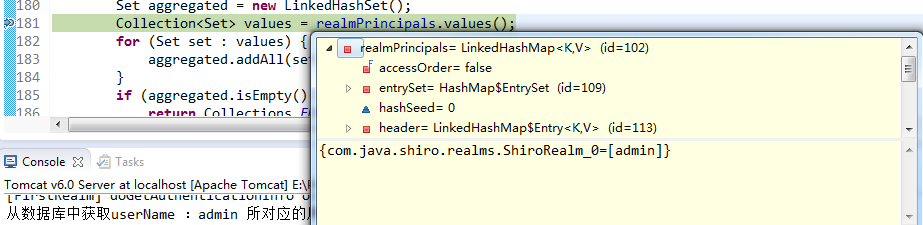
1 public Set asSet() { 2 if (realmPrincipals == null || realmPrincipals.isEmpty()) { 3 return Collections.EMPTY_SET; 4 } 5 Set aggregated = new LinkedHashSet(); 6 Collection<Set> values = realmPrincipals.values(); 7 for (Set set : values) { 8 aggregated.addAll(set); 9 } 10 if (aggregated.isEmpty()) { 11 return Collections.EMPTY_SET; 12 } 13 return Collections.unmodifiableSet(aggregated); 14 }
上述代码第6行得到 realmPrincipals 的类型 LinkedHashMap,只有这样才能保证我得到的是希望的那个值。
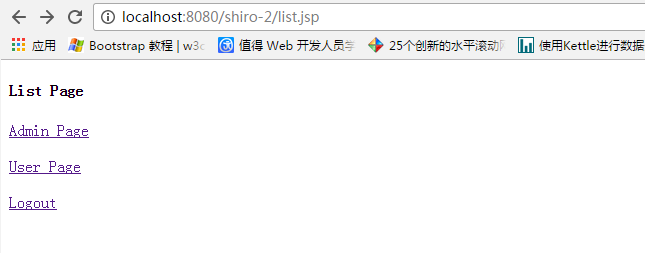
启动Tomcat
使用admin登录 可以访问两个页面,user登录只能访问一个页面
-
Permissions


-
授权流程