所有结构体定义均为
struct node{
int data;数据域
struct node *text;指针域
};
单链表的构造方法
一·头插法(带头节点)
struct node *tc(){
struct node *p,*head;
head=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
head->text=NULL;//构造一个头节点
int n=0,temp;
while(1){
scanf("%d",&temp);
if(temp==0) break;
p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->data=temp;
p->text=head->text;//将p插在头节点后面
head->text=p;
}
二.尾插法(不带头节点)
struct node *wc(){
struct node *head,*p,*p1;
int n=0,temp;
scanf("%d",&temp);
while(temp!=0){
p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->data=temp;
n++;
if(n==1) head=p1=p;
else{
p1->text=p;
p1=p;
}
scanf("%d",&temp);
}
if(head!=NULL) p->text=NULL;
return head;
}
单链表查找
查找某个值
void chazhao(struct node *head){
int t;
printf("输入要找的数字");
scanf("%d",&t);
getchar();
struct node *p=head;
while(p){
if(p->node==t){
printf("存在
");
return ;
}
p=p->next;
}
printf("不存在
");
}
查找第k个元素
与上面类似,加一个int的变量i来判断是第几个元素,若存在i==k输入并退出
删除等于x的结点
struct node *sc(struct node *head,int x){
struct node *p=head,*p1;
while(p->data!=x&& p){
p1=p;
p=p->next;
}
if(p->data==x){
if(p==head){
head=head->next;
free(p);
}
else{
p1->next=p->next;
free(p);
}
}
return head;
}
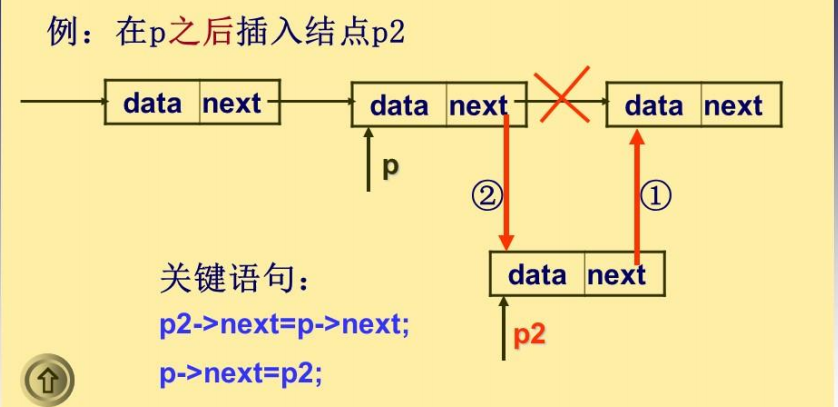
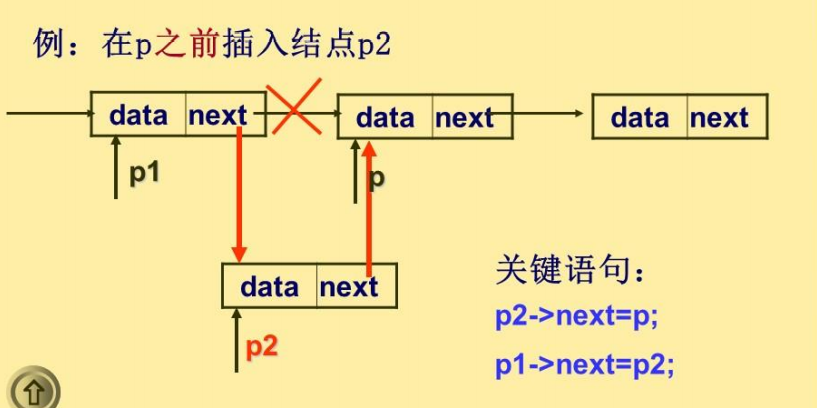
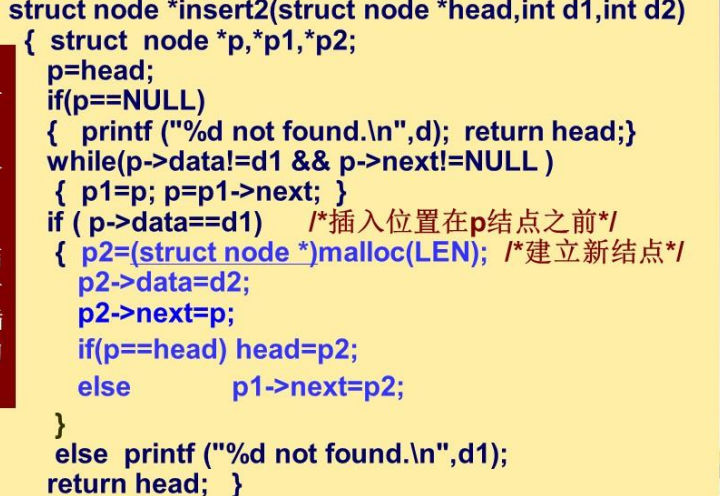
单链表的插入

单链表逆置
struct node *Reverse( struct node *head ){
struct node *p=head,*p1,*s=NULL;
while(p){
p1=p;
p=p->text;
p1->text=s;
s=p1;
}
return s;
}
单链表的排序(自己想的骚方法,效率低)
struct node *paixu(struct node *head,int n){
struct node *p=head;
int i,j,t,a[n];
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
a[i]=p->node;
p=p->next;
}
for(i=n-1;i>0;i--){
for(j=0;j<i;j++){
if(a[j]>a[j+1]){
t=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
}
}
p=head;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
p->node=a[i];
p=p->next;
}
return head;
}