滑动窗口
滑动窗口(sliding windows algorithm)这种方法,专门用于解决区间解的问题。它在运算的时候,将解集放在窗口中,结束的时候比对是否符合预期。在运算的过程中,会对窗口的左右边缘进行操作(扩大、缩小)。特别针对于线性输入解决,滑动窗口就很形象了。
30. Substring with Concatenation of All Words
You are given a string, s, and a list of words, words, that are all of the same length. Find all starting indices of substring(s) in s that is a concatenation of each word in words exactly once and without any intervening characters.
题意是从一串输入字符串s中,找到能全包含words数组的起点(数组元素等长),这个起点可能有多个,而且不需要关心顺序。
Input: s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"] Output: [0,9] Explanation: Substrings starting at index 0 and 9 are "barfoo" and "foobar" respectively. The output order does not matter, returning [9,0] is fine too.
比如这个例子,他在第0个位置和第9个位置可以包含words数组,也就是0位置和9位置各有一个长度为6的窗口可以囊括words数组。

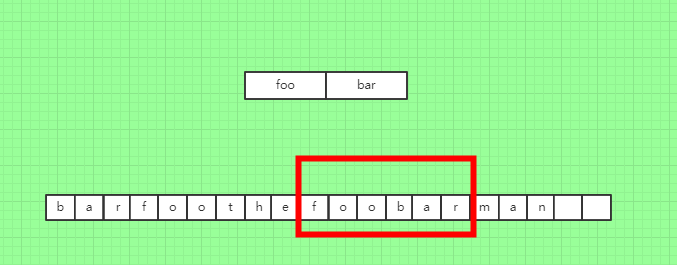
Template = "foo","bar" i=0 [b a r] f o o t h e f o o b a r m a n [b a r f o o] t h e f o o b a r m a n SAVE b a r f o o[] t h e f o o b a r m a n b a r f o o [t h e] f o o b a r m a n b a r f o o t h e [f o o] b a r m a n b a r f o o t h e [f o o b a r] m a n SAVE b a r f o o t h e f o o b a r[] m a n b a r f o o t h e f o o b a r [m a n] i=1 b [a r f] o o t h e f o o b a r m a n .... i=2 b a [r f o] o t h e f o o b a r m a n
....
每次扩展使用单词列表中的词长,如果扩展过程中不符合预期则清除窗口,窗口左端在当前词总数大于词组总数的时候,计算总数是单词的长度(因为s除以单词长度余数是0到单词长度之间,覆盖了余数就能覆盖整个场景)。
public class FindSubstring { public void test(){ // [0,9] String s1 = "barfoothefoobarman"; String[] words1 = {"foo","bar"}; System.out.println(findSubstring(s1,words1)); // [] String s2 = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword"; String[] words2 = {"word","good","best","word"}; System.out.println(findSubstring(s2,words2)); } /** * 单词等长 */ public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); if(s == null || words.length == 0){ return result; } int step = words[0].length(); Map<String,Integer> counter = new HashMap<>(); for(String word :words){ counter.merge(word, 1, (a, b) -> a + b); } for(int i=0;i<step;++i){ Map<String,Integer> window = new HashMap<>(); int left = i; int right = i; while (right <= s.length() - step && left <= s.length() - step*words.length){ String sub = s.substring(right,right + step); window.merge(sub,1,(a , b)->a + b); if(!counter.containsKey(sub)){ window.clear(); right += step; left = right; continue; } while (window.get(sub) > counter.get(sub)){ String drop = s.substring(left,left+step); Integer dec = window.get(drop); if(dec != null){ if(dec<=1){ window.remove(drop); }else { window.put(drop,dec-1); } } left += step; } right += step; if(right - left == step * words.length){ result.add(left); } } } return result; } }

76. Minimum Window Substring
Given a string S and a string T, find the minimum window in S which will contain all the characters in T in complexity O(n).
Example:
Input: S = "ADOBECODEBANC", T = "ABC" Output: "BANC"
题意是将s子串中包含T的所有字母的最短子串找出来,例子中BANC是包含ABC的最短子串。
Template = "ABC" []A D O B E C O D E B A N C
[A] D O B E C O D E B A N C
[A D] O B E C O D E B A N C
[A D O] B E C O D E B A N C
[A D O B] E C O D E B A N C
[A D O B E] C O D E B A N C
[A D O B E C] O D E B A N C CONTAINS ABC mark substring A D O B E C ...
[A D O B E C O D E B] A N C B now 2 > 1 so moving left but A is compliance ...
[A D O B E C O D E B A] N C A 2 > 1 moving left
A D O [B E C O D E B A] N C B 2 > 1 moving left
A D O B E [C O D E B A] N C C O D E B A is not shorter than A D O B E C ...
A D O B E [C O D E B A N C] C 2 > 1 moving left
A D O B E C O D E [B A N C] B A N C is shorter than A D O B E C mark substring B A N C
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class MinimumWindowSubstring { public void test(){ String s1 = "ADOBECODEBANC"; String t1 = "ABC"; // BANC System.out.println(minWindow(s1,t1)); String s2 = "a"; String t2 = "aa"; // "" System.out.println(minWindow(s2,t2)); String s3 = "a"; String t3 = "b"; // "" System.out.println(minWindow(s3,t3)); String s4 = "a"; String t4 = "a"; // a System.out.println(minWindow(s4,t4)); String s5 = "ab"; String t5 = "b"; // b System.out.println(minWindow(s5,t5)); String s6 = "aa"; String t6 = "aa"; // aa System.out.println(minWindow(s6,t6)); String s7 = "acbbaca"; String t7 = "aba"; // baca System.out.println(minWindow(s7,t7)); String s8 = "aaaaaaaaaaaabbbbbcdd"; String t8 = "abcdd"; System.out.println(minWindow(s8,t8)); } public String minWindow(String s, String t) { if(s == null || t == null || s.isEmpty() || t.isEmpty() || s.length() < t.length()){ return ""; } Map<Character,Integer> counter = new HashMap<>(); char[] sArray = s.toCharArray(); for(char c :t.toCharArray()){ counter.merge(c,1,(a,b)->a+b); } int left = 0; int right ; int[] ans = {-1 , 0 , 0}; Map<Character,Integer> window = new HashMap<>(); for(int i=0;i<sArray.length;i++){ char c = sArray[i]; right = i; if(counter.containsKey(c)){ window.merge(c,1,(a,b)->a+b); if(window.keySet().size() == counter.keySet().size()){ while (true){ Integer dec = window.get(sArray[left]); Integer standard = counter.get(sArray[left]); if(dec != null && standard != null){ if(dec <= standard){ break; } if(dec > standard){ window.merge(sArray[left],-1,(a,b)->a+b); } } left ++; } boolean valid = true; for(char v : counter.keySet()){ if(window.get(v) < counter.get(v)){ valid = false; } } // mark if initial or shorter sequence if(valid && (ans[0] == -1 || right - left + 1 < ans[0])){ ans[0] = right - left + 1; ans[1] = left; ans[2] = right; } } } } return ans[0] == -1?"":s.substring(ans[1],ans[2]+1); } }
239. Sliding Window Maximum
Given an array nums, there is a sliding window of size k which is moving from the very left of the array to the very right. You can only see the k numbers in the window. Each time the sliding window moves right by one position. Return the max sliding window.
Input: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], and k = 3 Output: [3,3,5,5,6,7] Explanation: Window position Max --------------- ----- [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
class Solution { public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); if(nums == null || nums.length == 0){ return new int[]{}; } int left = 0; int windowMax = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ if(i - left + 1 > k){ int rv = nums[i]; int currentMax = windowMax; if(nums[left] == windowMax){ currentMax = nums[left+1]; for(int t = left+1 ; t <= i ; t ++){ currentMax = Math.max(nums[t],currentMax); } } windowMax = Math.max(currentMax,rv); result.add(windowMax); left ++ ; } else { windowMax = Math.max(nums[i],windowMax); if(i - left + 1 == k){ result.add(windowMax); } } } int[] copyRes = new int[result.size()]; for(int index = 0 ; index < result.size() ; index ++){ copyRes[index] = result.get(index); } return copyRes; } }