Given a tree (i.e. a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 and exactly n - 1 edges. The root of the tree is the node 0, and each node of the tree has a label which is a lower-case character given in the string labels (i.e. The node with the number i has the label labels[i]).
The edges array is given on the form edges[i] = [ai, bi], which means there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return an array of size n where ans[i] is the number of nodes in the subtree of the ith node which have the same label as node i.
A subtree of a tree T is the tree consisting of a node in T and all of its descendant nodes.
Example 1:
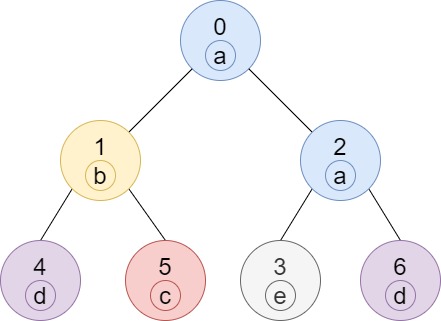
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], labels = "abaedcd" Output: [2,1,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: Node 0 has label 'a' and its sub-tree has node 2 with label 'a' as well, thus the answer is 2. Notice that any node is part of its sub-tree. Node 1 has a label 'b'. The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1,4 and 5, as nodes 4 and 5 have different labels than node 1, the answer is just 1 (the node itself).
Example 2:
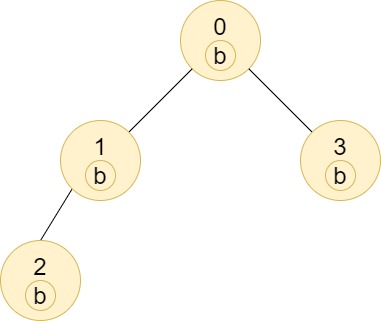
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,3]], labels = "bbbb" Output: [4,2,1,1] Explanation: The sub-tree of node 2 contains only node 2, so the answer is 1. The sub-tree of node 3 contains only node 3, so the answer is 1. The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1 and 2, both have label 'b', thus the answer is 2. The sub-tree of node 0 contains nodes 0, 1, 2 and 3, all with label 'b', thus the answer is 4.
Example 3:
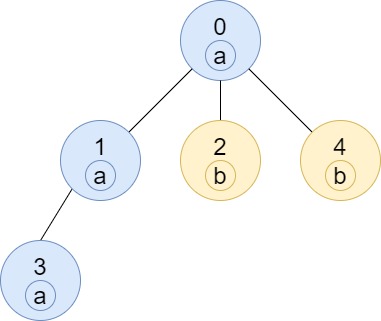
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[0,4]], labels = "aabab" Output: [3,2,1,1,1]
Example 4:
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[3,4],[4,5]], labels = "cbabaa" Output: [1,2,1,1,2,1]
Example 5:
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6]], labels = "aaabaaa" Output: [6,5,4,1,3,2,1]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bilabels.length == nlabelsis consisting of only of lower-case English letters.
class Solution { public int[] countSubTrees(int n, int[][] edges, String labels) { int[] ans = new int[n]; Set<Integer> used = new HashSet(); Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap(); for(int[] edge: edges) { map.computeIfAbsent(edge[0], l -> new ArrayList()).add(edge[1]); map.computeIfAbsent(edge[1], l -> new ArrayList()).add(edge[0]); } dfs(map, ans, labels, used, 0); return ans; } public int[] dfs(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map, int[] ans, String labels, Set<Integer> used, int root) { int[] count = new int[26]; if(used.add(root)) { char c = labels.charAt(root); for(int child: map.get(root)) { int[] cur = dfs(map, ans, labels, used, child); for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) { count[i] += cur[i]; } } count[c - 'a']++; ans[root] = count[c-'a']; } return count; } }
坑逼
用DFS的方法做,
因为这个edges里面会出现edge[0]是child,反而edge[1]是parent的奇葩情况,所以我们只能先把树做成图(双向连接),此外我们还需要一个used hashset来存放已经遍历过的root
既然只有26个字母,我们就计算每一个subtree所包含的字母,把它们存到array中,这使我们要用dfs往更深层递归。
然后要把每个根的child上的字母数加起来,才等于我们要求的。