Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
Example 1:
Input: [2,3,1,1,4] Output: true Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
Input: [3,2,1,0,4] Output: false Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
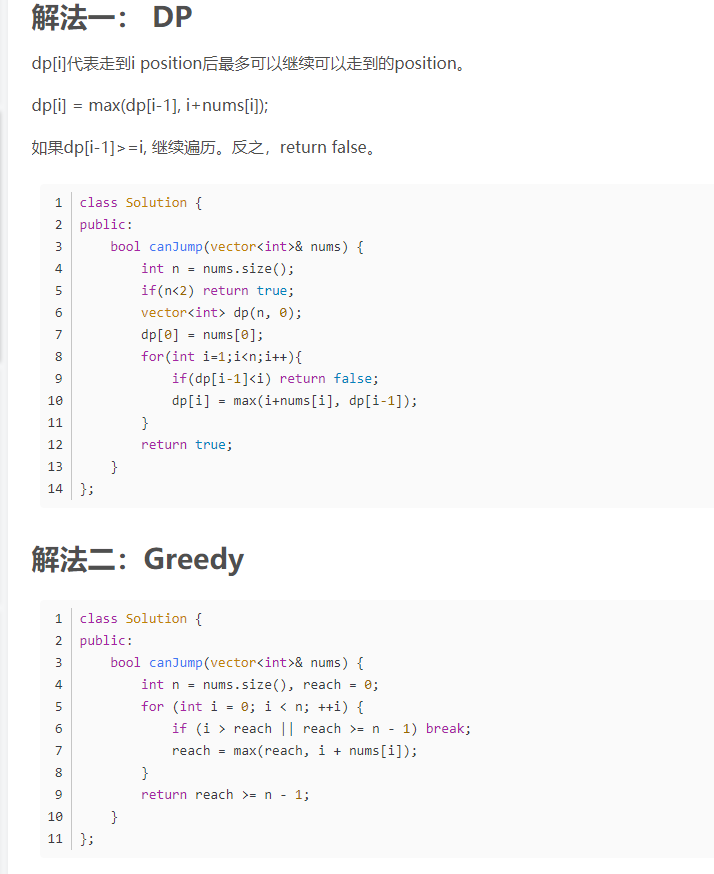
Greedy算法,从后往前
class Solution { public boolean canJump(int[] nums) { int lastposition = nums.length-1; for(int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--){ if(nums[i]+i >= lastposition){ lastposition = i; } } return lastposition==0; } }
从前到后,reach是能跳到的最大距离。
class Solution { public boolean canJump(int[] nums) { int n = nums.length; int reach = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (i > reach) break; reach = Math.max(reach, i + nums[i]); } return reach >= n - 1; } }