工厂模式
工厂模式(Factory Pattern)是 Java 中最常用的设计模式之一。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
在工厂模式中,我们在创建对象时不会对客户端暴露创建逻辑,并且是通过使用一个共同的接口来指向新创建的对象。
实现
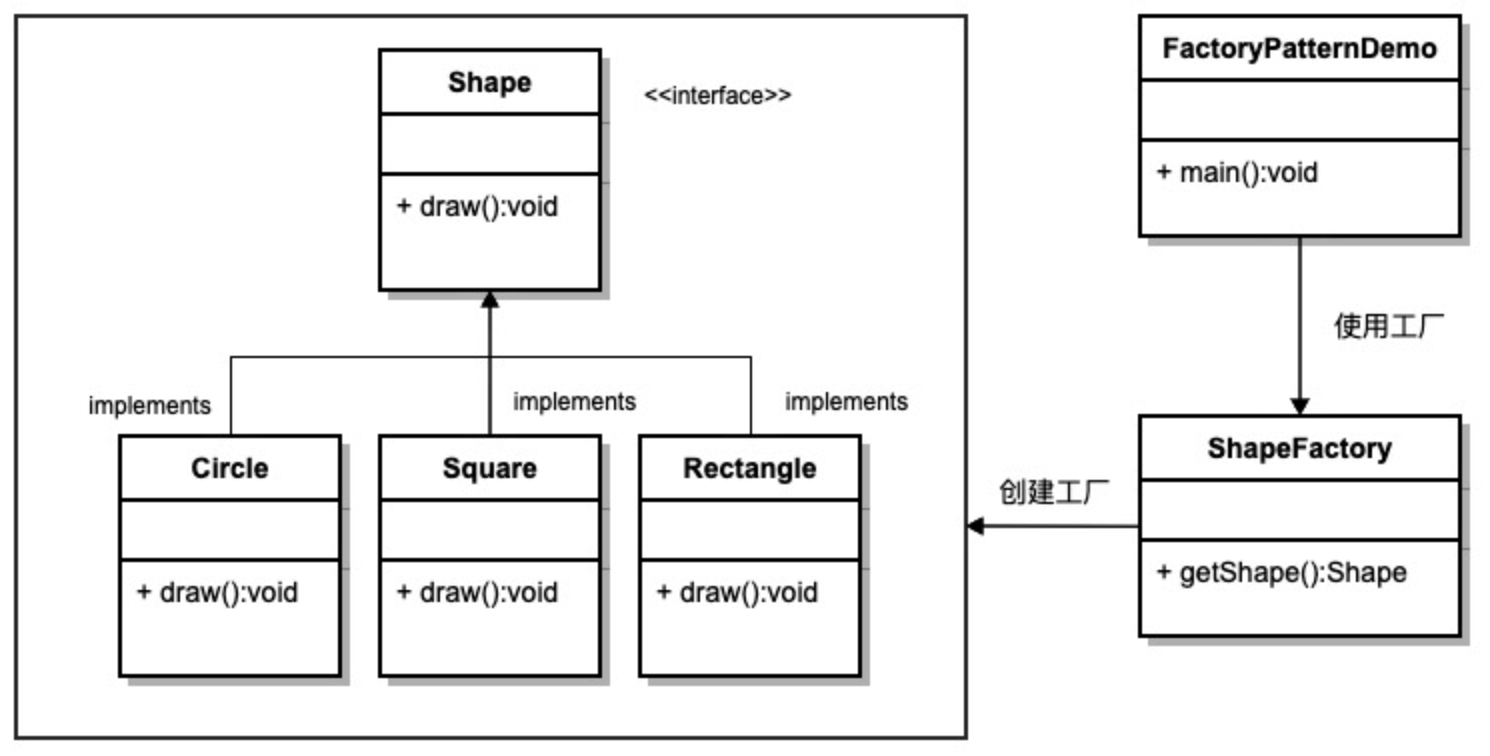
我们将创建一个 Shape 接口和实现 Shape 接口的实体类。下一步是定义工厂类 ShapeFactory。
FactoryPatternDemo,我们的演示类使用 ShapeFactory 来获取 Shape 对象。它将向 ShapeFactory 传递信息(CIRCLE / RECTANGLE / SQUARE),以便获取它所需对象的类型。
步骤 1
创建一个接口
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
步骤2
创建实现接口的实体类
public class Rectangle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建一个三角形");
}
}
public class Square implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建一个正方形");
}
}
public class Circle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建一个圆形");
}
}
步骤3
创建一个工厂,生成基于给定信息的实体类的对象。
public class ShapeFactory {
public Shape getShape(String shapeType)
{
if(shapeType==null)
return null;
if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("rectangle"))
return new Rectangle();
else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("square"))
return new Square();
else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("circle"))
return new Circle();
return null;
}
}
步骤4
使用该工厂,通过传递类型信息来获取实体类的对象。
public class FactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ShapeFactory shapefactory=new ShapeFactory();
Shape shape1=shapefactory.getShape("circle");
Shape shape2=shapefactory.getShape("square");
Shape shape3=shapefactory.getShape("rectangle");
shape1.draw();
shape2.draw();
shape3.draw();
}
}
步骤5
执行程序,输出结果:
创建一个圆形
创建一个正方形
创建一个三角形
抽象工厂模式
抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory Pattern)是围绕一个超级工厂创建其他工厂。该超级工厂又称为其他工厂的工厂。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
在抽象工厂模式中,接口是负责创建一个相关对象的工厂,不需要显式指定它们的类。每个生成的工厂都能按照工厂模式提供对象。
实现
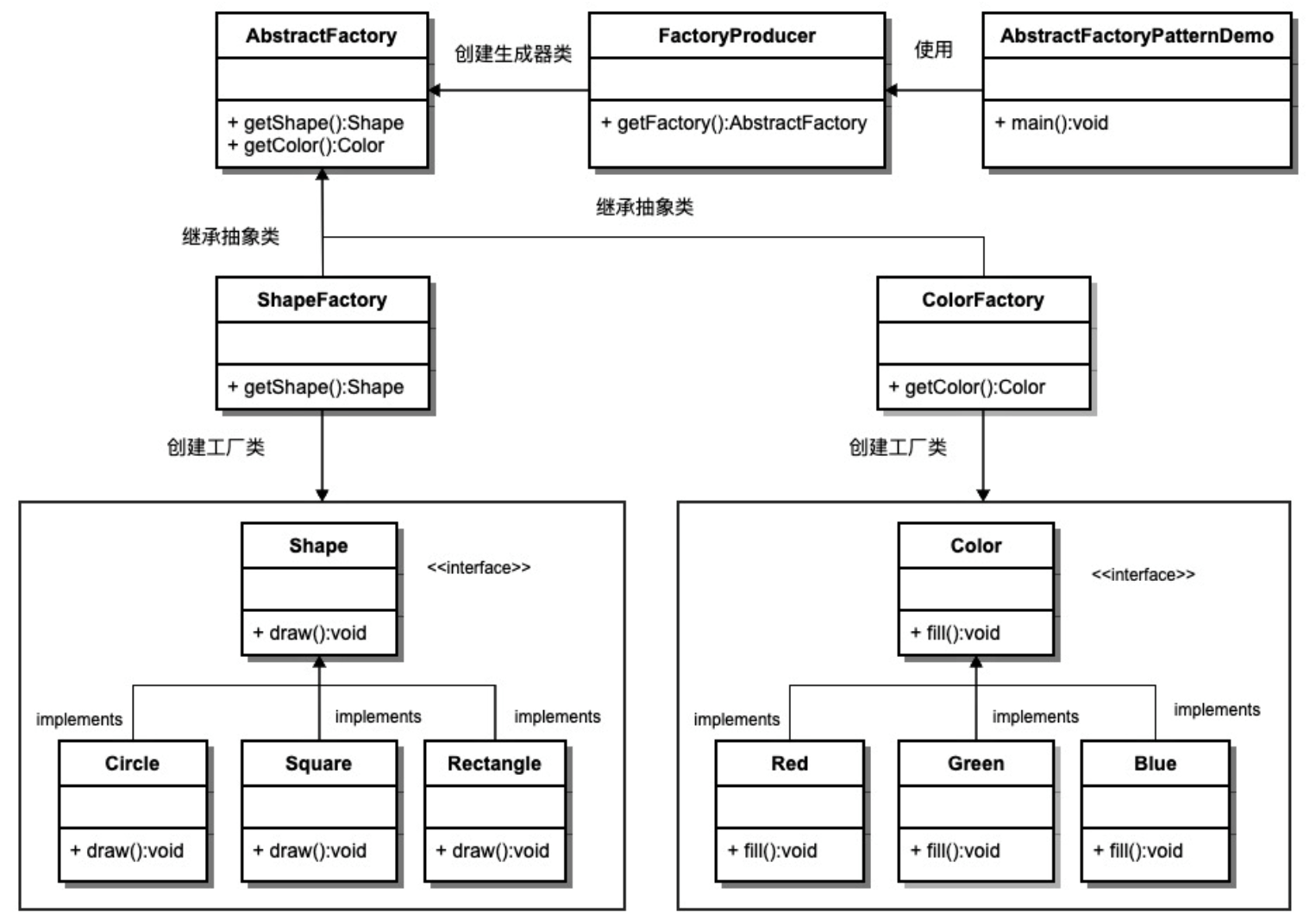
我们将创建 Shape 和 Color 接口和实现这些接口的实体类。下一步是创建抽象工厂类 AbstractFactory。接着定义工厂类 ShapeFactory 和 ColorFactory,这两个工厂类都是扩展了 AbstractFactory。然后创建一个工厂创造器/生成器类 FactoryProducer。
AbstractFactoryPatternDemo,我们的演示类使用 FactoryProducer 来获取 AbstractFactory 对象。它将向 AbstractFactory 传递形状信息 Shape(CIRCLE / RECTANGLE / SQUARE),以便获取它所需对象的类型。同时它还向 AbstractFactory 传递颜色信息 Color(RED / GREEN / BLUE),以便获取它所需对象的类型。
步骤1
为形状创建一个接口。
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
步骤2
创建实现接口的实体类。
public class Rectangle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建一个三角形");
}
}
public class Square implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建一个正方形");
}
}
public class Circle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建一个圆形");
}
}
步骤3
为颜色创建一个接口。
public interface Color {
void fill();
}
步骤4
创建实现接口的实体类。
public class Red implements Color{
@Override
public void fill() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建红色");
}
}
public class Green implements Color{
@Override
public void fill() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建绿色");
}
}
public class Blue implements Color{
@Override
public void fill() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("创建蓝色");
}
}
步骤5
为 Color 和 Shape 对象创建抽象类来获取工厂。
public abstract class AbstractFactory {
public abstract Shape getShape(String shapeType);
public abstract Color getColor(String colorType);
}
步骤6
创建扩展了 AbstractFactory 的工厂类,基于给定的信息生成实体类的对象。
public class ShapeFactory extends AbstractFactory{
public Shape getShape (String shapeType)
{
if(shapeType==null)
return null;
if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("rectangle"))
return new Rectangle();
else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("square"))
return new Square();
else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("circle"))
return new Circle();
return null;
}
@Override
public Color getColor(String colorType) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
}
public class ColorFactory extends AbstractFactory{
@Override
public Shape getShape(String shapeType) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public Color getColor(String colorType) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(colorType==null)
return null;
if(colorType.equalsIgnoreCase("red"))
return new Red();
else if(colorType.equalsIgnoreCase("green"))
return new Green();
else if(colorType.equalsIgnoreCase("blue"))
return new Blue();
return null;
}
}
步骤7
创建一个工厂创造器/生成器类,通过传递形状或颜色信息来获取工厂。
public class FactoryProducer {
public static AbstractFactory getFactory(String factoryType)
{
if(factoryType==null)
return null;
if(factoryType.equalsIgnoreCase("shape"))
return new ShapeFactory();
else if(factoryType.equalsIgnoreCase("color"))
return new ColorFactory();
return null;
}
}
步骤8
使用 FactoryProducer 来获取 AbstractFactory,通过传递类型信息来获取实体类的对象。
public class AbstractFactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
AbstractFactory shapeFactory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("SHAPE");
Shape shape1=shapeFactory.getShape("rectangle");
shape1.draw();
Shape shape2=shapeFactory.getShape("square");
shape2.draw();
Shape shape3=shapeFactory.getShape("circle");
shape3.draw();
AbstractFactory colorFactory=FactoryProducer.getFactory("color");
Color color1=colorFactory.getColor("red");
color1.fill();
Color color2=colorFactory.getColor("green");
color2.fill();
Color color3=colorFactory.getColor("blue");
color3.fill();
}
}
步骤9
执行程序,输出结果
创建一个三角形
创建一个正方形
创建一个圆形
创建红色
创建绿色
创建蓝色