sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博主亲自录制视频教程)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
https://www.pythonprogramming.net/part-of-speech-tagging-nltk-tutorial/?completed=/stemming-nltk-tutorial/
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Nov 13 09:14:13 2016
@author: daxiong
"""
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import state_union
from nltk.tokenize import PunktSentenceTokenizer
#训练数据
train_text=state_union.raw("2005-GWBush.txt")
#测试数据
sample_text=state_union.raw("2006-GWBush.txt")
'''
Punkt is designed to learn parameters (a list of abbreviations, etc.)
unsupervised from a corpus similar to the target domain.
The pre-packaged models may therefore be unsuitable:
use PunktSentenceTokenizer(text) to learn parameters from the given text
'''
#我们现在训练punkttokenizer(分句器)
custom_sent_tokenizer=PunktSentenceTokenizer(train_text)
#训练后,我们可以使用punkttokenizer(分句器)
tokenized=custom_sent_tokenizer.tokenize(sample_text)
'''
nltk.pos_tag(["fire"]) #pos_tag(列表)
Out[19]: [('fire', 'NN')]
'''
#文本词性标记函数
def process_content():
try:
for i in tokenized[0:5]:
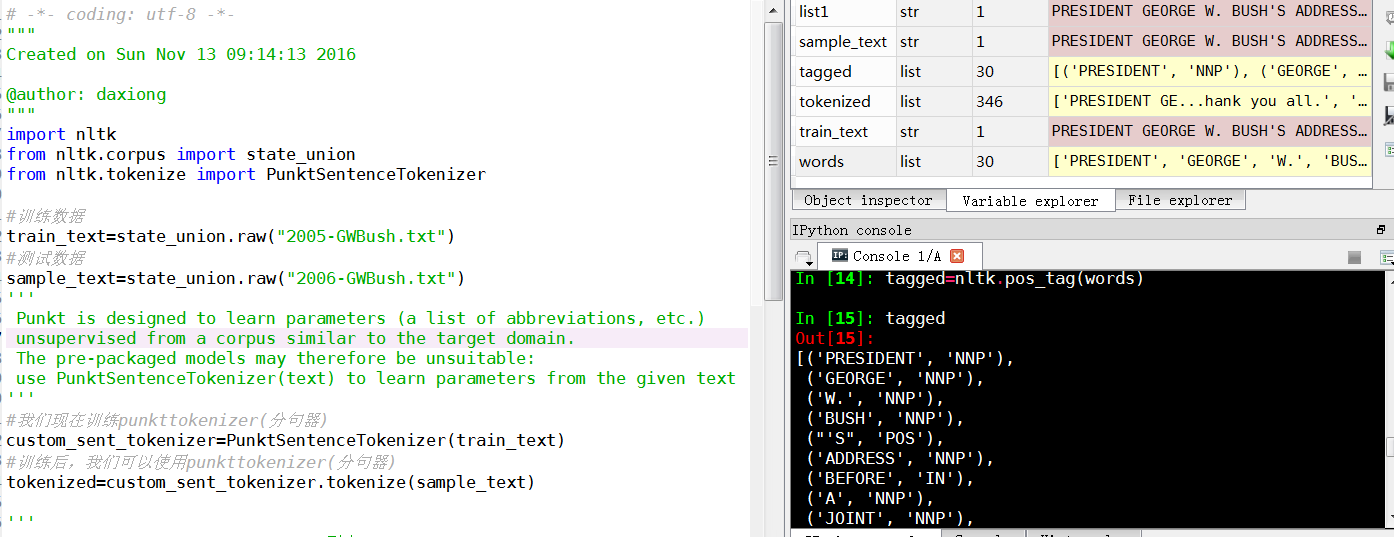
words=nltk.word_tokenize(i)
tagged=nltk.pos_tag(words)
print(tagged)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
process_content()
One of the more powerful aspects of the NLTK module is the Part of Speech tagging that it can do for you. This means labeling words in a sentence as nouns, adjectives, verbs...etc. Even more impressive, it also labels by tense, and more. Here's a list of the tags, what they mean, and some examples:
POS tag list:
CC coordinating conjunction
CD cardinal digit
DT determiner
EX existential there (like: "there is" ... think of it like "there exists")
FW foreign word
IN preposition/subordinating conjunction
JJ adjective 'big'
JJR adjective, comparative 'bigger'
JJS adjective, superlative 'biggest'
LS list marker 1)
MD modal could, will
NN noun, singular 'desk'
NNS noun plural 'desks'
NNP proper noun, singular 'Harrison'
NNPS proper noun, plural 'Americans'
PDT predeterminer 'all the kids'
POS possessive ending parent's
PRP personal pronoun I, he, she
PRP$ possessive pronoun my, his, hers
RB adverb very, silently,
RBR adverb, comparative better
RBS adverb, superlative best
RP particle give up
TO to go 'to' the store.
UH interjection errrrrrrrm
VB verb, base form take
VBD verb, past tense took
VBG verb, gerund/present participle taking
VBN verb, past participle taken
VBP verb, sing. present, non-3d take
VBZ verb, 3rd person sing. present takes
WDT wh-determiner which
WP wh-pronoun who, what
WP$ possessive wh-pronoun whose
WRB wh-abverb where, when
How might we use this? While we're at it, we're going to cover a new sentence tokenizer, called the PunktSentenceTokenizer. This tokenizer is capable of unsupervised machine learning, so you can actually train it on any body of text that you use. First, let's get some imports out of the way that we're going to use:
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import state_union
from nltk.tokenize import PunktSentenceTokenizer
Now, let's create our training and testing data:
train_text = state_union.raw("2005-GWBush.txt")
sample_text = state_union.raw("2006-GWBush.txt")
One is a State of the Union address from 2005, and the other is from 2006 from past President George W. Bush.
Next, we can train the Punkt tokenizer like:
custom_sent_tokenizer = PunktSentenceTokenizer(train_text)
Then we can actually tokenize, using:
tokenized = custom_sent_tokenizer.tokenize(sample_text)
Now we can finish up this part of speech tagging script by creating a function that will run through and tag all of the parts of speech per sentence like so:
def process_content():
try:
for i in tokenized[:5]:
words = nltk.word_tokenize(i)
tagged = nltk.pos_tag(words)
print(tagged)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
process_content()
The output should be a list of tuples, where the first element in the tuple is the word, and the second is the part of speech tag. It should look like:
[('PRESIDENT', 'NNP'), ('GEORGE', 'NNP'), ('W.', 'NNP'), ('BUSH', 'NNP'), ("'S", 'POS'), ('ADDRESS', 'NNP'), ('BEFORE', 'NNP'), ('A', 'NNP'), ('JOINT', 'NNP'), ('SESSION', 'NNP'), ('OF', 'NNP'), ('THE', 'NNP'), ('CONGRESS', 'NNP'), ('ON', 'NNP'), ('THE', 'NNP'), ('STATE', 'NNP'), ('OF', 'NNP'), ('THE', 'NNP'), ('UNION', 'NNP'), ('January', 'NNP'), ('31', 'CD'), (',', ','), ('2006', 'CD'), ('THE', 'DT'), ('PRESIDENT', 'NNP'), (':', ':'), ('Thank', 'NNP'), ('you', 'PRP'), ('all', 'DT'), ('.', '.')] [('Mr.', 'NNP'), ('Speaker', 'NNP'), (',', ','), ('Vice', 'NNP'), ('President', 'NNP'), ('Cheney', 'NNP'), (',', ','), ('members', 'NNS'), ('of', 'IN'), ('Congress', 'NNP'), (',', ','), ('members', 'NNS'), ('of', 'IN'), ('the', 'DT'), ('Supreme', 'NNP'), ('Court', 'NNP'), ('and', 'CC'), ('diplomatic', 'JJ'), ('corps', 'NNS'), (',', ','), ('distinguished', 'VBD'), ('guests', 'NNS'), (',', ','), ('and', 'CC'), ('fellow', 'JJ'), ('citizens', 'NNS'), (':', ':'), ('Today', 'NN'), ('our', 'PRP$'), ('nation', 'NN'), ('lost', 'VBD'), ('a', 'DT'), ('beloved', 'VBN'), (',', ','), ('graceful', 'JJ'), (',', ','), ('courageous', 'JJ'), ('woman', 'NN'), ('who', 'WP'), ('called', 'VBN'), ('America', 'NNP'), ('to', 'TO'), ('its', 'PRP$'), ('founding', 'NN'), ('ideals', 'NNS'), ('and', 'CC'), ('carried', 'VBD'), ('on', 'IN'), ('a', 'DT'), ('noble', 'JJ'), ('dream', 'NN'), ('.', '.')] [('Tonight', 'NNP'), ('we', 'PRP'), ('are', 'VBP'), ('comforted', 'VBN'), ('by', 'IN'), ('the', 'DT'), ('hope', 'NN'), ('of', 'IN'), ('a', 'DT'), ('glad', 'NN'), ('reunion', 'NN'), ('with', 'IN'), ('the', 'DT'), ('husband', 'NN'), ('who', 'WP'), ('was', 'VBD'), ('taken', 'VBN'), ('so', 'RB'), ('long', 'RB'), ('ago', 'RB'), (',', ','), ('and', 'CC'), ('we', 'PRP'), ('are', 'VBP'), ('grateful', 'JJ'), ('for', 'IN'), ('the', 'DT'), ('good', 'NN'), ('life', 'NN'), ('of', 'IN'), ('Coretta', 'NNP'), ('Scott', 'NNP'), ('King', 'NNP'), ('.', '.')] [('(', 'NN'), ('Applause', 'NNP'), ('.', '.'), (')', ':')] [('President', 'NNP'), ('George', 'NNP'), ('W.', 'NNP'), ('Bush', 'NNP'), ('reacts', 'VBZ'), ('to', 'TO'), ('applause', 'VB'), ('during', 'IN'), ('his', 'PRP$'), ('State', 'NNP'), ('of', 'IN'), ('the', 'DT'), ('Union', 'NNP'), ('Address', 'NNP'), ('at', 'IN'), ('the', 'DT'), ('Capitol', 'NNP'), (',', ','), ('Tuesday', 'NNP'), (',', ','), ('Jan', 'NNP'), ('.', '.')]
At this point, we can begin to derive meaning, but there is still some work to do. The next topic that we're going to cover is chunking, which is where we group words, based on their parts of speech, into hopefully meaningful groups.