由上图可以看出来,插入和遍历的时间复杂度是不一样的。

这样不管游标在哪一个位置上,都可以通过后继或者前驱指针任意访问。
双向链表的继承层次:
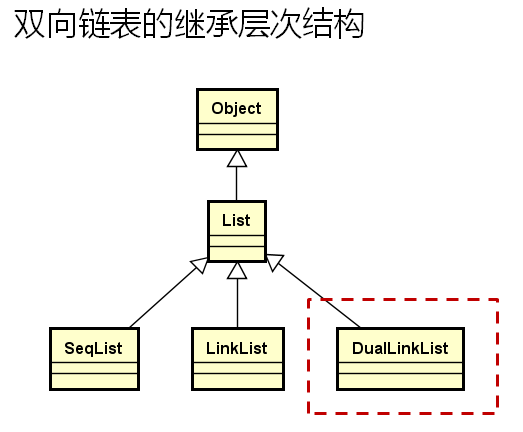
单链表和双向链表应该是兄弟关系,而不应该是继承关系,因为它们的内部机制是完全不同的了。

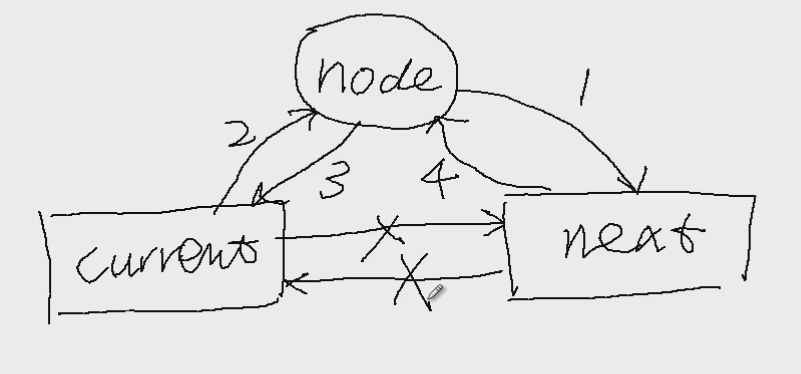
插入新节点图解:
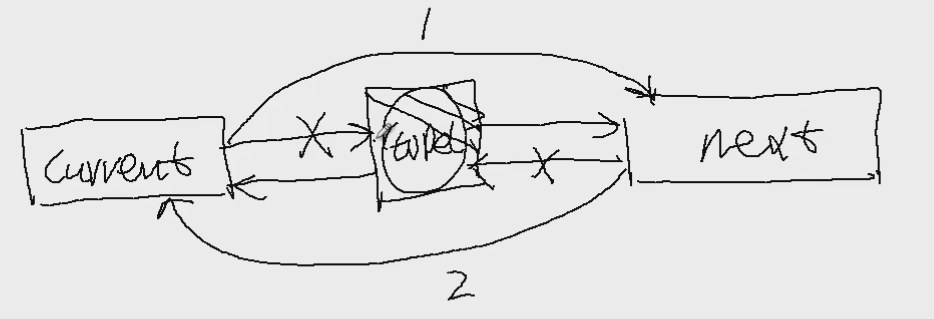
删除节点的步骤:
添加DualLinkList.h文件:
1 #ifndef DUALLINKLIST_H 2 #define DUALLINKLIST_H 3 4 #include "List.h" 5 #include "Exception.h" 6 7 namespace DTLib 8 { 9 10 template < typename T > 11 class DualLinkList : public List<T> 12 { 13 protected: 14 struct Node : public Object 15 { 16 T value; 17 Node* next; 18 Node* pre; 19 }; 20 21 mutable struct : public Object 22 { 23 char reserved[sizeof(T)]; 24 Node* next; 25 Node* pre; 26 }m_header; 27 28 int m_length; 29 int m_step; 30 Node* m_current; 31 32 Node* position(int i) const // O(n) 33 { 34 Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header); 35 36 for(int p = 0; p < i; p++) 37 { 38 ret = ret->next; 39 } 40 41 return ret; 42 } 43 44 virtual Node* create() 45 { 46 return new Node(); 47 } 48 49 virtual void destroy(Node* pn) 50 { 51 delete pn; 52 } 53 54 public: 55 DualLinkList() 56 { 57 m_header.next = NULL; 58 m_header.pre = NULL; 59 m_length = 0; 60 m_step = 1; 61 m_current = NULL; 62 } 63 64 bool insert(const T& e) 65 { 66 return insert(m_length, e); 67 } 68 69 bool insert(int i, const T& e) // O(n) 70 { 71 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length)); 72 73 if( ret ) 74 { 75 Node* node = create(); 76 77 if( node != NULL ) 78 { 79 Node* current = position(i); 80 Node* next = current->next; //即将插入的节点的后继节点 81 82 node->value = e; 83 84 node->next = next; //第1步 85 current->next = node; //第2步 86 87 if( current != reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header)) //判断是否是头结点 88 { 89 node->pre = current; // 第3步 90 } 91 else 92 { 93 node->pre = NULL; 94 } 95 96 if( next != NULL ) 97 { 98 next->pre = node; //第4步 99 } 100 101 m_length++; 102 } 103 else 104 { 105 THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memery to insert new element..."); 106 } 107 } 108 109 return ret; 110 } 111 112 bool remove(int i) // O(n) 113 { 114 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); 115 116 if( ret ) 117 { 118 Node* current = position(i); 119 Node* toDel = current->next; 120 Node* next = toDel->next; 121 122 if( m_current == toDel ) 123 { 124 m_current = next; 125 } 126 127 current->next = next; //第1步 128 129 if( next != NULL ) 130 { 131 next->pre = toDel->pre; //第2步 132 } 133 134 m_length--; 135 136 destroy(toDel); 137 138 } 139 140 return ret; 141 } 142 143 bool set(int i, const T& e) // O(n) 144 { 145 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); 146 147 if( ret ) 148 { 149 position(i)->next->value = e; 150 } 151 152 return ret; 153 } 154 155 virtual T get(int i) const // O(n) 156 { 157 T ret; 158 159 if( get(i, ret) ) 160 { 161 return ret; 162 } 163 else 164 { 165 THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid parameter i to get element ..."); 166 } 167 168 return ret; 169 } 170 171 bool get(int i, T& e) const // O(n) 172 { 173 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < m_length)); 174 175 if( ret ) 176 { 177 e = position(i)->next->value; 178 } 179 180 return ret; 181 } 182 183 int find(const T& e) const // O(n) 184 { 185 int ret = -1; 186 int i = 0; 187 188 Node* node = m_header.next; 189 190 while( node ) 191 { 192 if( node->value == e ) 193 { 194 ret = i; 195 break; 196 } 197 else 198 { 199 node = node->next; 200 i++; 201 } 202 } 203 204 return ret; 205 } 206 207 int length() const // O(1) 208 { 209 return m_length; 210 } 211 212 void clear() // O(n) 213 { 214 while( m_length > 0 ) 215 { 216 remove(0); 217 } 218 } 219 220 virtual bool move(int i, int step = 1) 221 { 222 bool ret = (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) && (step > 0); 223 224 if( ret ) 225 { 226 m_current = position(i)->next; 227 m_step = step; 228 } 229 230 return ret; 231 } 232 233 virtual bool end() 234 { 235 return (m_current == NULL); 236 } 237 238 virtual T current() 239 { 240 if( !end() ) 241 { 242 return m_current->value; 243 } 244 else 245 { 246 THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No value at current position ..."); 247 } 248 } 249 250 virtual bool next() //每次移动step步 251 { 252 int i = 0; 253 254 while((i < m_step) && !end()) 255 { 256 m_current = m_current->next; 257 i++; 258 } 259 260 return (i == m_step); 261 } 262 263 virtual bool pre() 264 { 265 int i = 0; 266 267 while((i < m_step) && !end()) 268 { 269 m_current = m_current->pre; 270 i++; 271 } 272 273 return (i == m_step); 274 } 275 276 ~DualLinkList() // O(n) 277 { 278 clear(); 279 } 280 }; 281 282 } 283 284 #endif // DUALLINKLIST_H
和LinkList的不同只在于Node的元素,我们新添加了pre成员。
insert函数和remove函数是改动最大的。
新增加了pre函数。
测试程序如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "DualLinkList.h" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 using namespace DTLib; 6 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 DualLinkList<int> dl; 11 12 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 13 { 14 dl.insert(0, i); 15 } 16 17 for(int i = 0; i < dl.length(); i++) 18 { 19 cout << dl.get(i) << endl; 20 } 21 22 cout << "begin" << endl; 23 24 for(dl.move(dl.length() - 1); !dl.end(); dl.pre()) 25 { 26 cout << dl.current() << endl; 27 } 28 29 cout << "end" << endl; 30 31 return 0; 32 }
第一个for循环时间复杂度是O(n*n),第二个for循环的时间复杂度是O(n)。
结果如下:

测试程序2:
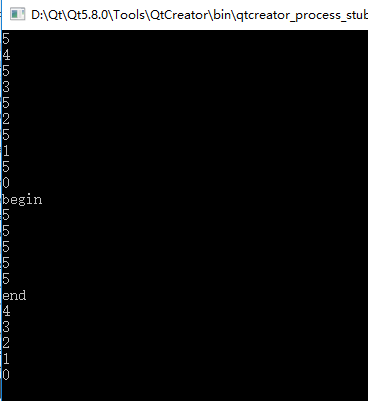
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "DualLinkList.h" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 using namespace DTLib; 6 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 DualLinkList<int> dl; 11 12 for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 13 { 14 dl.insert(0, i); 15 dl.insert(0, 5); 16 } 17 18 for(dl.move(0); !dl.end(); dl.next()) 19 { 20 cout << dl.current() << endl; 21 } 22 23 cout << "begin" << endl; 24 25 dl.move(dl.length() - 1); 26 27 while(!dl.end()) 28 { 29 if( dl.current() == 5 ) 30 { 31 cout << dl.current() << endl; 32 33 dl.remove(dl.find(dl.current())); 34 } 35 else 36 { 37 dl.pre(); 38 } 39 } 40 41 cout << "end" << endl; 42 43 for(dl.move(0); !dl.end(); dl.next()) 44 { 45 cout << dl.current() << endl; 46 } 47 48 return 0; 49 }
结果如下:
小结:


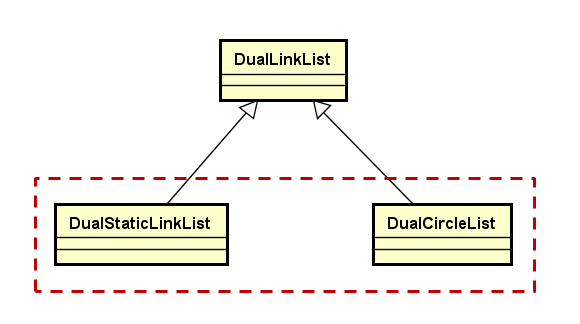
双向链表的子类: