效果如下:
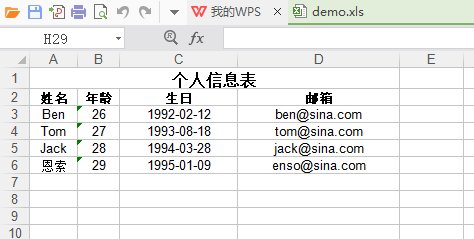
代码如下:
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFont; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellType; import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress; /** * 使用该类时,确定引入的poi相关的jar包 * Maven如下: * <!-- POI --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi</artifactId> <version>3.15</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId> <version>3.15</version> </dependency> * @author Mr.wang * @date 2018/06/14 * */ public class ExcelUtils { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { List<String> title = Arrays.asList("姓名", "年龄", "生日", "邮箱"); List<List<String>> personInfos = new ArrayList<List<String>>(); List<String> person01 = Arrays.asList("Ben", "26", "1992-02-12", "ben@sina.com"); List<String> person02 = Arrays.asList("Tom", "27", "1993-08-18", "tom@sina.com"); List<String> person03 = Arrays.asList("Jack", "28", "1994-03-28", "jack@sina.com"); List<String> person04 = Arrays.asList("恩索", "29", "1995-01-09", "enso@sina.com"); personInfos.add(person01); personInfos.add(person02); personInfos.add(person03); personInfos.add(person04); File file = new File("D:/demo.xls"); //createExcelFile(title, personInfos, file, null); createExcelFileWithHead(title, personInfos, file, null, "个人信息表"); } /** * 由生成流的方法进一步封装成生成excel(.xls)的文件 * @see #createExcelInStream(List, List, OutputStream, String) * @param title * @param listData * @param fileWithPathAndName * @param sheetName * @throws IOException */ public static void createExcelFile(List<String> title, List<List<String>> listData, File fileWithPathAndName, String sheetName) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileWithPathAndName); createExcelInStream(title, listData, fos, sheetName); if(fos!=null) { fos.close(); } } /** * 由生成流的方法进一步封装成生成excel(.xls)的文件 * @see #createExcelInStreamWithHead(List, List, OutputStream, String, String) * @param title * @param listData * @param fileWithPathAndName * @param sheetName * @param header * @throws IOException */ public static void createExcelFileWithHead(List<String> title, List<List<String>> listData, File fileWithPathAndName, String sheetName,String header) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileWithPathAndName); createExcelInStreamWithHead(title, listData, fos, sheetName, header); if(fos!=null) { fos.close(); } } /** * create by Mr.wang 2018/06/14 * * 生成excel流(不带表头)。以xls为后缀的文件,防止有些电脑不支持office07以上的 * * @param title * 标题 * @param listData * 数据内容 * @param outputStream * 输出的流 * @param sheetName * 创建的sheet(不是文件)的名称,如果有空,则采用sheet1作用默认的表名称 * @throws IOException * * * example: * * List<String> title = Arrays.asList("姓名", "年龄", "生日", "邮箱"); List<List<String>> personInfos = new ArrayList<List<String>>(); List<String> person01 = Arrays.asList("Ben", "26", "1992-02-12", "ben@sina.com"); List<String> person02 = Arrays.asList("Tom", "27", "1993-08-18", "tom@sina.com"); List<String> person03 = Arrays.asList("Jack", "28", "1994-03-28", "jack@sina.com"); List<String> person04 = Arrays.asList("恩索", "29", "1995-01-09", "enso@sina.com"); personInfos.add(person01); personInfos.add(person02); personInfos.add(person03); personInfos.add(person04); File file = new File("D:/demo.xls"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(file); createExcelFile(title, personInfos, fos, null); ... * */ @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public static void createExcelInStream(List<String> title, List<List<String>> listData, OutputStream outputStream, String sheetName) throws IOException { // 创建工作簿 HSSFWorkbook workBook = new HSSFWorkbook(); // 创建工作表 工作表的名字叫helloWorld if (sheetName == null || sheetName.length() == 0) { sheetName = "sheet1"; } HSSFSheet sheet = workBook.createSheet(sheetName); // 创建单元格,首先设置标题 HSSFFont fontTitle = workBook.createFont(); fontTitle.setBold(true); HSSFCellStyle titleStyle = workBook.createCellStyle(); titleStyle.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); titleStyle.setFont(fontTitle); HSSFRow titleRow = sheet.createRow(0); for (int i = 0; i < title.size(); i++) { HSSFCell titleCol = titleRow.createCell(i, CellType.STRING); titleCol.setCellValue(title.get(i)); titleCol.setCellStyle(titleStyle); } sheet.autoSizeColumn(0); // 创建数据行 HSSFCellStyle dataStyle = workBook.createCellStyle(); dataStyle.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); for (int i = 0; i < listData.size(); i++) { HSSFRow dataRow = sheet.createRow(i + 1); List<String> rowData = listData.get(i); for (int j = 0; j < rowData.size(); j++) { HSSFCell dataCol = dataRow.createCell(j, CellType.STRING); dataCol.setCellValue(rowData.get(j)); dataCol.setCellStyle(dataStyle); } sheet.autoSizeColumn(i); } HSSFRow firstRow = sheet.getRow(0); int lastCellNum = firstRow.getLastCellNum(); //为了美观,把所有的cell扩大1/2 for(int i=0;i<lastCellNum;i++) { int columnWidth = sheet.getColumnWidth(i); sheet.setColumnWidth(i, columnWidth+columnWidth*1/2); } workBook.write(outputStream); workBook.close();// 最后记得关闭工作簿 } /** * create by Mr.wang 2018/06/14 * * 生成excel流(带表头)。以xls为后缀的文件,防止有些电脑不支持office07以上的 * * @param title * 标题 * @param listData * 数据内容 * @param outputStream * 输出的流 * @param sheetName * 创建的sheet(不是文件)的名称,如果有空,则采用sheet1作用默认的表名称 * @param header * 表的表头 * @throws IOException * * * example: * * List<String> title = Arrays.asList("姓名", "年龄", "生日", "邮箱"); List<List<String>> personInfos = new ArrayList<List<String>>(); List<String> person01 = Arrays.asList("Ben", "26", "1992-02-12", "ben@sina.com"); List<String> person02 = Arrays.asList("Tom", "27", "1993-08-18", "tom@sina.com"); List<String> person03 = Arrays.asList("Jack", "28", "1994-03-28", "jack@sina.com"); List<String> person04 = Arrays.asList("恩索", "29", "1995-01-09", "enso@sina.com"); personInfos.add(person01); personInfos.add(person02); personInfos.add(person03); personInfos.add(person04); File file = new File("D:/demo.xls"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(file); createExcelFileWithHead(title, personInfos, fos, null, "个人信息表"); ... * */ @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public static void createExcelInStreamWithHead(List<String> title, List<List<String>> listData, OutputStream outputStream, String sheetName,String header) throws IOException { // 创建工作簿 HSSFWorkbook workBook = new HSSFWorkbook(); // 创建工作表 工作表的名字叫helloWorld if (sheetName == null || sheetName.length() == 0) { sheetName = "sheet1"; } HSSFSheet sheet = workBook.createSheet(sheetName); //设置表头 //参数说明:1:开始行 2:结束行 3:开始列 4:结束列 //比如我要合并 第二行到第四行的 第六列到第八列 sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(1,3,5,7)); sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0,0,0,title.size()-1)); HSSFRow headerRow = sheet.createRow(0); HSSFCell headerCell = headerRow.createCell(0); // 创建单元格,首先设置标题 HSSFFont font = workBook.createFont(); short fontHeightInPoints = font.getFontHeightInPoints(); font.setFontHeightInPoints((short)(fontHeightInPoints+2)); font.setBold(true); HSSFCellStyle cellHeaderStyle = workBook.createCellStyle(); cellHeaderStyle.setFont(font); cellHeaderStyle.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); headerCell.setCellStyle(cellHeaderStyle);//可表头加粗,居中 headerCell.setCellValue(header); //cellStyle.setAlignment(alignmentEnum);//还原,标题不居中 HSSFFont fontTitle = workBook.createFont(); fontTitle.setBold(true); HSSFCellStyle titleStyle = workBook.createCellStyle(); titleStyle.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); titleStyle.setFont(fontTitle); HSSFRow titleRow = sheet.createRow(1); for (int i = 0; i < title.size(); i++) { HSSFCell titleCol = titleRow.createCell(i, CellType.STRING); titleCol.setCellValue(title.get(i)); titleCol.setCellStyle(titleStyle); } sheet.autoSizeColumn(1); // 创建数据行 HSSFCellStyle dataStyle = workBook.createCellStyle(); dataStyle.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); for (int i = 0; i < listData.size(); i++) { HSSFRow dataRow = sheet.createRow(i + 2); List<String> rowData = listData.get(i); for (int j = 0; j < rowData.size(); j++) { HSSFCell dataCol = dataRow.createCell(j, CellType.STRING); dataCol.setCellValue(rowData.get(j)); dataCol.setCellStyle(dataStyle); } sheet.autoSizeColumn(i); } HSSFRow firstRow = sheet.getRow(1); int lastCellNum = firstRow.getLastCellNum(); //为了美观,把所有的cell扩大1/2 for(int i=0;i<lastCellNum;i++) { int columnWidth = sheet.getColumnWidth(i); sheet.setColumnWidth(i, columnWidth+columnWidth*1/2); } workBook.write(outputStream); workBook.close();// 最后记得关闭工作簿 } }
相关工具方法
/** * create by Mr.wang 2018/06/14 * * 将简单的对象(读取不到父类的属性)转化成List<String> * * @param o 对象 * @param convertMap 转换器 指定对象属性中某一个属性值如何转化为String。如果不需要,可以设置成null即可 * @param args 指定要输出的属性,一般用于属性选择和排序 ,如果不需要,则不设置.如果要查找父类的属性,则自身及父类的属性全部定义在此处,不再自动搜索自身的属性 * 这里注意如果同样的属性要利用两次,可以使用field&alias的格式来指定转换器 * 例如:code,code&1---->code&1可以设定与之对应的转换器 * @return * @throws IllegalArgumentException * @throws IllegalAccessException * @throws NoSuchFieldException * @throws SecurityException * * example: * { * "name":"jack", * "age":26, * "birthday":new Date() * } * 转成 * ["jack","26","2018-06-14 16:02:20"] */ public static List<String> convertSimpleObj2StringList(Object o,Map<String,FieldConvert> convertMap,String... args) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException{ List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>(); Class<? extends Object> objClas = o.getClass(); if(args.length==0) { Field[] declaredFields = objClas.getDeclaredFields(); for(Field f : declaredFields) { f.setAccessible(true); String fileName = f.getName(); Object obj=f.get(o);//对应的属性没值,则设置为“/” processFieldValue(convertMap, list, fileName, obj); } }else { for(String ag : args) { String fieldKey=null; String convertKey=ag; if(ag.contains("&")) { String[] split = ag.split("&"); fieldKey=split[0]; }else { fieldKey=ag; } Object fieldValue = getFieldValue(o, fieldKey); processFieldValue(convertMap, list, convertKey, fieldValue); } } return list; } private static void processFieldValue(Map<String, FieldConvert> convertMap, List<String> list, String ag, Object fieldValue) { if(fieldValue==null) { list.add("/"); return; }else { if(convertMap!=null&&convertMap.containsKey(ag)){ FieldConvert filedConvert = convertMap.get(ag); String s = filedConvert.covertFiledValueToString(fieldValue); if(s!=null){ list.add(s); }else{ list.add("/"); } }else{ list.add(fieldValue.toString()); } } } /** * create by Mr.wang 2018/06/14 * @see #convertSimpleObj2StringList * @param objs * @param convertMap * @param args * @return * @throws IllegalArgumentException * @throws IllegalAccessException * @throws NoSuchFieldException * @throws SecurityException */ public static <T> List<List<String>> convertSimpleObjList2StringList(List<T> objs,Map<String,FieldConvert> convertMap,String... args) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException{ List<List<String>> list=new ArrayList<List<String>>(); for(T obj : objs) { list.add(convertSimpleObj2StringList(obj,convertMap,args)); } return list; } /** * create by Mr.wang 2018/06/14 * 通过反射,向上(父类)一直获取对象的属性,如果一直获取不到则抛 NoSuchFieldException 异常 * @param obj 要操作的操作 * @param fieldName 要获取的属性名称 * @return * @throws NoSuchFieldException * @throws SecurityException * @throws IllegalArgumentException * @throws IllegalAccessException */ public static Object getFieldValue(Object obj,String fieldName) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException { Class<? extends Object> class1 = obj.getClass(); Field declaredField=null; try { declaredField = class1.getDeclaredField(fieldName); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { declaredField=null; } while(declaredField==null) { class1=class1.getSuperclass(); if(class1==null) { throw new NoSuchFieldException(); } try { declaredField = class1.getDeclaredField(fieldName); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { declaredField=null; } } declaredField.setAccessible(true); return declaredField.get(obj); }
FieldConvert.java
public interface FieldConvert { String covertFiledValueToString(Object filedValue); }