cell 1 显示设置初始化
1 # A bit of setup 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from cs231n.classifiers.neural_net import TwoLayerNet 7 8 %matplotlib inline 9 plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 8.0) # set default size of plots 10 plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest' 11 plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray' 12 13 # for auto-reloading external modules 14 # see http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1907993/autoreload-of-modules-in-ipython 15 %load_ext autoreload 16 %autoreload 2 17 18 def rel_error(x, y): 19 """ returns relative error """ 20 return np.max(np.abs(x - y) / (np.maximum(1e-8, np.abs(x) + np.abs(y))))
cell 2 网络模型与数据初始化函数
1 # Create a small net and some toy data to check your implementations. 2 # Note that we set the random seed for repeatable experiments. 3 4 input_size = 4 5 hidden_size = 10 6 num_classes = 3 7 num_inputs = 5 8 9 def init_toy_model(): 10 np.random.seed(0) 11 return TwoLayerNet(input_size, hidden_size, num_classes, std=1e-1) 12 13 def init_toy_data(): 14 np.random.seed(1) 15 X = 10 * np.random.randn(num_inputs, input_size) 16 y = np.array([0, 1, 2, 2, 1]) 17 return X, y 18 19 net = init_toy_model() 20 X, y = init_toy_data()
通过末尾的调用,生成了NN类,并生成了测试数据。
类的初始化代码(cs231n/classifiers/neural_net.py):
1 def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, std=1e-4): 2 """ 3 Initialize the model. Weights are initialized to small random values and 4 biases are initialized to zero. Weights and biases are stored in the 5 variable self.params, which is a dictionary with the following keys: 6 7 W1: First layer weights; has shape (D, H) 8 b1: First layer biases; has shape (H,) 9 W2: Second layer weights; has shape (H, C) 10 b2: Second layer biases; has shape (C,) 11 12 Inputs: 13 - input_size: The dimension D of the input data. 14 - hidden_size: The number of neurons H in the hidden layer. 15 - output_size: The number of classes C. 16 """ 17 self.params = {} 18 self.params['W1'] = std * np.random.randn(input_size, hidden_size) 19 self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden_size) 20 self.params['W2'] = std * np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size) 21 self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output_size)
cell 3 前向传播计算loss,得到的结果与参考结果对比,证明模型的正确性:
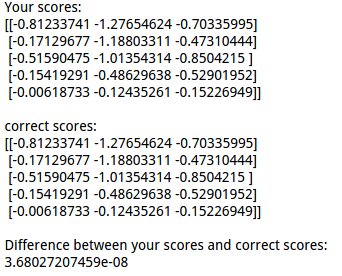
1 scores = net.loss(X) 2 print 'Your scores:' 3 print scores 4 print 5 print 'correct scores:' 6 correct_scores = np.asarray([ 7 [-0.81233741, -1.27654624, -0.70335995], 8 [-0.17129677, -1.18803311, -0.47310444], 9 [-0.51590475, -1.01354314, -0.8504215 ], 10 [-0.15419291, -0.48629638, -0.52901952], 11 [-0.00618733, -0.12435261, -0.15226949]]) 12 print correct_scores 13 14 # The difference should be very small. We get < 1e-7 15 print 'Difference between your scores and correct scores:' 16 print np.sum(np.abs(scores - correct_scores))
结果对比:
loss function 代码:
1 def loss(self, X, y=None, reg=0.0): 2 """ 3 Compute the loss and gradients for a two layer fully connected neural 4 network. 5 6 Inputs: 7 - X: Input data of shape (N, D). Each X[i] is a training sample. 8 - y: Vector of training labels. y[i] is the label for X[i], and each y[i] is 9 an integer in the range 0 <= y[i] < C. This parameter is optional; if it 10 is not passed then we only return scores, and if it is passed then we 11 instead return the loss and gradients. 12 - reg: Regularization strength. 13 14 Returns: 15 If y is None, return a matrix scores of shape (N, C) where scores[i, c] is 16 the score for class c on input X[i]. 17 18 If y is not None, instead return a tuple of: 19 - loss: Loss (data loss and regularization loss) for this batch of training 20 samples. 21 - grads: Dictionary mapping parameter names to gradients of those parameters 22 with respect to the loss function; has the same keys as self.params. 23 """ 24 # Unpack variables from the params dictionary 25 W1, b1 = self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'] 26 W2, b2 = self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'] 27 #5 *4 28 N, D = X.shape 29 num_train = N 30 # Compute the forward pass 31 scores = None 32 ############################################################################# 33 # TODO: Perform the forward pass, computing the class scores for the input. # 34 # Store the result in the scores variable, which should be an array of # 35 # shape (N, C). # 36 ############################################################################# 37 #5*4 * 4*10 >>>5*10 38 buf_H = np.dot(X,W1) + b1 39 #RELU 40 buf_H[buf_H<0] = 0 41 #5*10 * 10 *3 >>>5*3 42 buf_O=np.dot(buf_H,W2) + b2 43 scores = buf_O 44 ############################################################################# 45 # END OF YOUR CODE # 46 ############################################################################# 47 48 # If the targets are not given then jump out, we're done 49 if y is None: 50 return scores 51 52 # Compute the loss 53 loss = None 54 ############################################################################# 55 # TODO: Finish the forward pass, and compute the loss. This should include # 56 # both the data loss and L2 regularization for W1 and W2. Store the result # 57 # in the variable loss, which should be a scalar. Use the Softmax # 58 # classifier loss. So that your results match ours, multiply the # 59 # regularization loss by 0.5 # 60 ############################################################################# 61 scores = np.subtract( scores.T , np.max(scores , axis = 1) ).T 62 scores = np.exp(scores) 63 scores = np.divide( scores.T , np.sum(scores , axis = 1) ).T 64 loss = - np.sum(np.log ( scores[np.arange(num_train),y] ) ) / num_train 65 loss += 0.5 * reg * (np.sum(W1*W1) + np.sum(W2*W2) ) 66 ############################################################################# 67 # END OF YOUR CODE # 68 ############################################################################# 69 70 # Backward pass: compute gradients 71 grads = {} 72 ############################################################################# 73 # TODO: Compute the backward pass, computing the derivatives of the weights # 74 # and biases. Store the results in the grads dictionary. For example, # 75 # grads['W1'] should store the gradient on W1, and be a matrix of same size # 76 ############################################################################# 77 #get grad 78 scores[np.arange(num_train),y] -= 1 79 # 10 *5 * 5*3 >>>10*3 80 dW2 = np.dot(buf_H.T,scores)/num_train + reg*W2 81 # 82 db2 = np.sum(scores,axis =0)/num_train 83 #10 * 3 * 3 *5 >>10 * 5 84 buf_hide = np.dot(W2,scores.T) 85 #element > 0 86 buf_H[buf_H>0] = 1 87 #relu buf_hide 88 buf_relu = buf_hide.T * buf_H 89 #4*5 * 5*10 >>4*10 90 dW1 = np.dot(X.T,buf_relu) /num_train + reg*W1 91 # 92 db1 = np.sum(buf_relu,axis =0) /num_train 93 grads['W1'] = dW1 94 grads['W2'] = dW2 95 grads['b1'] = db1 96 grads['b2'] = db2 97 ############################################################################# 98 # END OF YOUR CODE # 99 ############################################################################# 100 101 return loss, grads
cell 4 计算包含正则的loss
1 loss, _ = net.loss(X, y, reg=0.1) 2 correct_loss = 1.30378789133 3 4 # should be very small, we get < 1e-12 5 print loss 6 print 'Difference between your loss and correct loss:' 7 print np.sum(np.abs(loss - correct_loss))
结果:
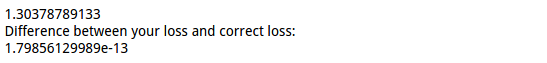
cell 5 反向传播,并用数值法来验证偏导的正确性》》注意使用链式法则:
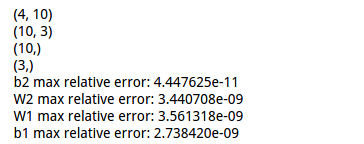
1 from cs231n.gradient_check import eval_numerical_gradient 2 3 # Use numeric gradient checking to check your implementation of the backward pass. 4 # If your implementation is correct, the difference between the numeric and 5 # analytic gradients should be less than 1e-8 for each of W1, W2, b1, and b2. 6 7 loss, grads = net.loss(X, y, reg=0.1) 8 print grads['W1'].shape 9 print grads['W2'].shape 10 print grads['b1'].shape 11 print grads['b2'].shape 12 # these should all be less than 1e-8 or so 13 for param_name in grads: 14 f = lambda W: net.loss(X, y, reg=0.1)[0] 15 param_grad_num = eval_numerical_gradient(f, net.params[param_name], verbose=False) 16 print '%s max relative error: %e' % (param_name, rel_error(param_grad_num, grads[param_name]))
显示解析法与数值法的结果差异:
cell 6 训练网络模型。在loss grad 计算无误的基础上,使用对应的函数方法来训练模型。
1 net = init_toy_model() 2 #two layers net 3 stats = net.train(X, y, X, y, 4 learning_rate=1e-1, reg=1e-5, 5 num_iters=100, verbose=False) 6 7 print 'Final training loss: ', stats['loss_history'][-1] 8 9 # plot the loss history 10 plt.plot(stats['loss_history']) 11 plt.xlabel('iteration') 12 plt.ylabel('training loss') 13 plt.title('Training Loss history') 14 plt.show()
训练函数代码:
1 def train(self, X, y, X_val, y_val, 2 learning_rate=1e-3, learning_rate_decay=0.95, 3 reg=1e-5, num_iters=100, 4 batch_size=200, verbose=False): 5 """ 6 Train this neural network using stochastic gradient descent. 7 8 Inputs: 9 - X: A numpy array of shape (N, D) giving training data. 10 - y: A numpy array f shape (N,) giving training labels; y[i] = c means that 11 X[i] has label c, where 0 <= c < C. 12 - X_val: A numpy array of shape (N_val, D) giving validation data. 13 - y_val: A numpy array of shape (N_val,) giving validation labels. 14 - learning_rate: Scalar giving learning rate for optimization. 15 - learning_rate_decay: Scalar giving factor used to decay the learning rate 16 after each epoch. 17 - reg: Scalar giving regularization strength. 18 - num_iters: Number of steps to take when optimizing. 19 - batch_size: Number of training examples to use per step. 20 - verbose: boolean; if true print progress during optimization. 21 """ 22 num_train = X.shape[0] 23 iterations_per_epoch = max(num_train / batch_size, 1) 24 25 # Use SGD to optimize the parameters in self.model 26 loss_history = [] 27 train_acc_history = [] 28 val_acc_history = [] 29 30 for it in xrange(num_iters): 31 X_batch = None 32 y_batch = None 33 34 ######################################################################### 35 # TODO: Create a random minibatch of training data and labels, storing # 36 # them in X_batch and y_batch respectively. # 37 ######################################################################### 38 if batch_size > num_train: 39 mask = np.random.choice(num_train, batch_size, replace=True) 40 else : 41 mask = np.random.choice(num_train, batch_size, replace=False) 42 X_batch = X[mask] 43 y_batch = y[mask] 44 ######################################################################### 45 # END OF YOUR CODE # 46 ######################################################################### 47 48 # Compute loss and gradients using the current minibatch 49 loss, grads = self.loss(X_batch, y=y_batch, reg=reg) 50 loss_history.append(loss) 51 52 ######################################################################### 53 # TODO: Use the gradients in the grads dictionary to update the # 54 # parameters of the network (stored in the dictionary self.params) # 55 # using stochastic gradient descent. You'll need to use the gradients # 56 # stored in the grads dictionary defined above. # 57 ######################################################################### 58 self.params['W1'] = self.params['W1'] - learning_rate * grads['W1'] 59 self.params['b1'] = self.params['b1'] - learning_rate * grads['b1'] 60 self.params['W2'] = self.params['W2'] - learning_rate * grads['W2'] 61 self.params['b2'] = self.params['b2'] - learning_rate * grads['b2'] 62 ######################################################################### 63 # END OF YOUR CODE # 64 ######################################################################### 65 66 if verbose and it % 100 == 0: 67 print 'iteration %d / %d: loss %f' % (it, num_iters, loss) 68 69 # Every epoch, check train and val accuracy and decay learning rate. 70 if it % iterations_per_epoch == 0: 71 # Check accuracy 72 train_acc = (self.predict(X_batch) == y_batch).mean() 73 val_acc = (self.predict(X_val) == y_val).mean() 74 train_acc_history.append(train_acc) 75 val_acc_history.append(val_acc) 76 77 # Decay learning rate 78 learning_rate *= learning_rate_decay 79 80 return { 81 'loss_history': loss_history, 82 'train_acc_history': train_acc_history, 83 'val_acc_history': val_acc_history, 84 }
显示最终的training loss以及绘制下降曲线:

之前都是使用比较简单的数据进行计算,接下来对cifar-10进行分类。
cell 7 载入训练和测试数据集,并显示各数据的维度:
1 from cs231n.data_utils import load_CIFAR10 2 3 def get_CIFAR10_data(num_training=49000, num_validation=1000, num_test=1000): 4 """ 5 Load the CIFAR-10 dataset from disk and perform preprocessing to prepare 6 it for the two-layer neural net classifier. These are the same steps as 7 we used for the SVM, but condensed to a single function. 8 """ 9 # Load the raw CIFAR-10 data 10 cifar10_dir = 'cs231n/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py' 11 X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir) 12 13 # Subsample the data 14 mask = range(num_training, num_training + num_validation) 15 X_val = X_train[mask] 16 y_val = y_train[mask] 17 mask = range(num_training) 18 X_train = X_train[mask] 19 y_train = y_train[mask] 20 mask = range(num_test) 21 X_test = X_test[mask] 22 y_test = y_test[mask] 23 24 # Normalize the data: subtract the mean image 25 mean_image = np.mean(X_train, axis=0) 26 X_train -= mean_image 27 X_val -= mean_image 28 X_test -= mean_image 29 30 # Reshape data to rows 31 X_train = X_train.reshape(num_training, -1) 32 X_val = X_val.reshape(num_validation, -1) 33 X_test = X_test.reshape(num_test, -1) 34 35 return X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, X_test, y_test 36 37 38 # Invoke the above function to get our data. 39 X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, X_test, y_test = get_CIFAR10_data() 40 print 'Train data shape: ', X_train.shape 41 print 'Train labels shape: ', y_train.shape 42 print 'Validation data shape: ', X_val.shape 43 print 'Validation labels shape: ', y_val.shape 44 print 'Test data shape: ', X_test.shape 45 print 'Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape
结果显示:

cell 8 初始化网络并进行训练:
1 input_size = 32 * 32 * 3 2 hidden_size = 50 3 num_classes = 10 4 net = TwoLayerNet(input_size, hidden_size, num_classes) 5 6 # Train the network 7 stats = net.train(X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, 8 num_iters=1000, batch_size=200, 9 learning_rate=1e-4, learning_rate_decay=0.95, 10 reg=0.5, verbose=True) 11 12 # Predict on the validation set 13 val_acc = (net.predict(X_val) == y_val).mean() 14 print 'Validation accuracy: ', val_acc
上述代码对验证集进行了预测,得到的准确率:

预测代码:
1 def predict(self, X): 2 """ 3 Use the trained weights of this two-layer network to predict labels for 4 data points. For each data point we predict scores for each of the C 5 classes, and assign each data point to the class with the highest score. 6 7 Inputs: 8 - X: A numpy array of shape (N, D) giving N D-dimensional data points to 9 classify. 10 11 Returns: 12 - y_pred: A numpy array of shape (N,) giving predicted labels for each of 13 the elements of X. For all i, y_pred[i] = c means that X[i] is predicted 14 to have class c, where 0 <= c < C. 15 """ 16 W1, b1 = self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'] 17 W2, b2 = self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'] 18 y_pred = None 19 20 #5*10 * 10 *3 >>>5*3 21 ########################################################################### 22 # TODO: Implement this function; it should be VERY simple! # 23 ########################################################################### 24 layer_hide = np.dot(X,W1) + b1 25 layer_hide[layer_hide<0] = 0 26 layer_soft = np.dot(layer_hide,W2) + b2 27 scores = np.subtract( layer_soft.T , np.max(layer_soft , axis = 1) ).T 28 scores = np.exp(scores) 29 scores = np.divide( scores.T , np.sum(scores , axis = 1) ).T 30 y_pred = np.argmax(scores , axis = 1) 31 ########################################################################### 32 # END OF YOUR CODE # 33 ########################################################################### 34 35 return y_pred
接下来,对网络模型进行一些调试,观察结果。
cell 9 绘制train集的loss以及train集的准确率与validation集的准确率:
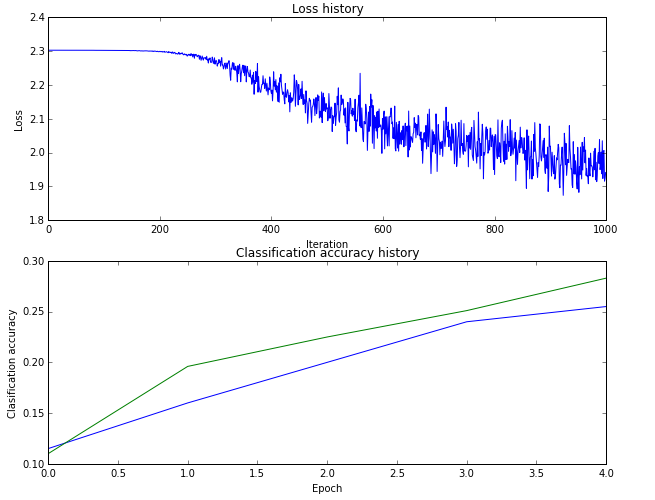
1 # Plot the loss function and train / validation accuracies 2 plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) 3 plt.plot(stats['loss_history']) 4 plt.title('Loss history') 5 plt.xlabel('Iteration') 6 plt.ylabel('Loss') 7 8 plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) 9 plt.plot(stats['train_acc_history'], label='train') 10 plt.plot(stats['val_acc_history'], label='val') 11 plt.title('Classification accuracy history') 12 plt.xlabel('Epoch') 13 plt.ylabel('Clasification accuracy') 14 plt.show()
绘制的图形曲线:
cell 10 对w的分量分别进行可视化:
1 from cs231n.vis_utils import visualize_grid 2 3 # Visualize the weights of the network 4 5 def show_net_weights(net): 6 W1 = net.params['W1'] 7 W1 = W1.reshape(32, 32, 3, -1).transpose(3, 0, 1, 2) 8 plt.imshow(visualize_grid(W1, padding=3).astype('uint8')) 9 plt.gca().axis('off') 10 plt.show() 11 12 show_net_weights(net)
结果:
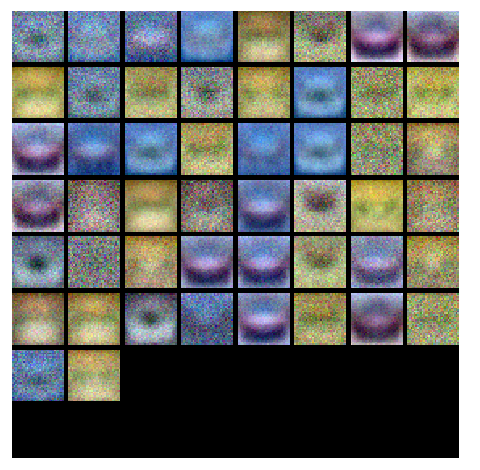
接着是通过验证的方式选取超参数,包括:隐藏层的结点数、学习率、正则化强度系数。
cell 11 选取超参数,没有对正则化强度系数及其衰减系数进行选取:
1 best_net = None # store the best model into this 2 best_val = 0 3 ################################################################################# 4 # TODO: Tune hyperparameters using the validation set. Store your best trained # 5 # model in best_net. # 6 # # 7 # To help debug your network, it may help to use visualizations similar to the # 8 # ones we used above; these visualizations will have significant qualitative # 9 # differences from the ones we saw above for the poorly tuned network. # 10 # # 11 # Tweaking hyperparameters by hand can be fun, but you might find it useful to # 12 # write code to sweep through possible combinations of hyperparameters # 13 # automatically like we did on the previous exercises. # 14 ################################################################################# 15 input_size = 32 * 32 * 3 16 Hidden_size = [50 ,64,128] 17 REG = [0.01,0.1,0.5] 18 num_classes = 10 19 for i in Hidden_size: 20 for j in REG : 21 net = TwoLayerNet(input_size, i, num_classes) 22 # Train the network 23 stats = net.train(X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, 24 num_iters=2000, batch_size=200, 25 learning_rate=1e-3, learning_rate_decay=0.95, 26 reg = j, verbose=False) 27 val_acc = (net.predict(X_val) == y_val).mean() 28 print 'Validation accuracy: ', val_acc 29 if best_val < val_acc: 30 best_val = val_acc 31 best_net = net 32 ################################################################################# 33 # END OF YOUR CODE # 34 #################################################################################
显示各个参数的验证集准确率结果:

cell 12 可视化最优参数对应模型的隐藏层结点对应的w的结果:
1 # visualize the weights of the best network 2 show_net_weights(best_net)
结果:

cell 13 使用最优参数模型对测试集进行预测:
1 test_acc = (best_net.predict(X_test) == y_test).mean() 2 print 'Test accuracy: ', test_acc
得到的结果:

附:通关CS231n企鹅群:578975100 validation:DL-CS231n