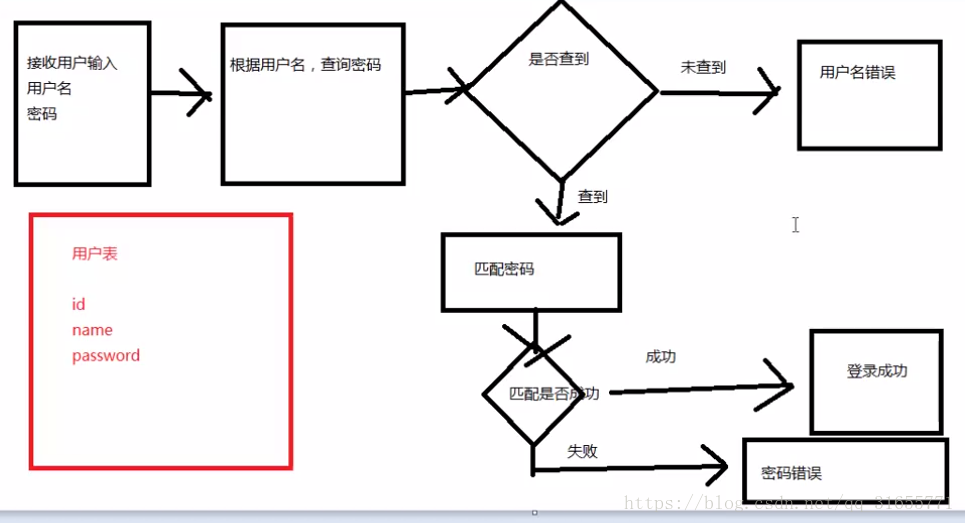
1.理解程序流程
2.创建用户表userinfos
表结构为:id、uname、upwd、isdelete
注意:需要对密码进行加密。如果使用md5加密,则密码包含32个字符;如果使用sha1加密,则密码包含40个字符,一般推荐使用这种加密方式。
create table userinfos(
id int primary key auto_increment,
uname varchar(20),
upwd char(40),
isdelete bit default 0
);3.加入测试数据
插入如下数据,用户名为123,密码为123,这是sha1加密后的值。
insert into userinfos values(0,'123','40bd001563085fc35165329ea1ff5c5ecbdbbeef',0);4.接收输入并验证
创建testLogin.py文件,引入hashlib模块(python自带)、MysqlHelper模块(自定义)。
根据用户名查询,如果未查到则提示用户名不存在;如果查到则匹配密码是否相等,如果相等则提示登录成功;如果不相等则提示密码错误。
#encoding=utf-8
from MysqlHelper import MysqlHelper
from hashlib import sha1
sname=input("请输入用户名:")
spwd=input("请输入密码:")
#对输入的密码spwd进行加密
s1=sha1()
s1.update(spwd)
spwdSha1=s1.hexdigest()
#通过get_one获取最新一行的值
sql="select upwd from userinfos where uname=%s"
params=[sname]
sqlhelper=MysqlHelper('localhost',3306,'test1','root','mysql')
userinfo=sqlhelper.get_one(sql,params)
#对获取到的值进行判别
if userinfo==None:
print('用户名错误')
elif userinfo[0]==spwdSha1:
print('登录成功')
else:
print('密码错误')