MySQL数据管理
1. 外键(了解)
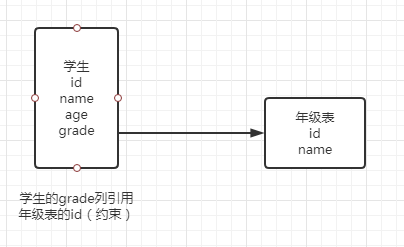
1. 方式1
在创建表的时候,增加约束(麻烦,比较复杂)
create table `grade` (
`gradeId` int(10) not null auto_increment comment '年级id',
`gradename` varchar(50) not null comment '年级名称',
primary key (`gradeId`)
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8
drop table if exists student
/*学生表的gradeId字段要去引用年级表的gradeId
定义外键key
给这个外键添加约束(执行引用)
fk = foreign key的简写
*/
create table if not exists `student` (
`id` int (4) not null auto_increment comment '学号',
`name` varchar (30) not null default '匿名' comment '姓名',
`pwd` varchar (20) not null default '123456' comment '密码',
`sex` varchar (2) not null default '女' comment '性别',
`birthdat` datetime default null comment '出生日期',
`gradeId` int(10) not null comment '学生的年级',
`address` varchar (100) default null comment '家庭住址',
`email` varchar (50) default null comment '邮箱',
primary key (`id`),
key `fk_gradeId` (`gradeId`),
constraint `fk_gradeId` foreign key (`gradeId`) references `grade` (`gradeId`)
) engine innodb default charset = utf8
删除有外键关系的表的时候,必须先删除应用别人的表(从表),再删除被应用的表(主表)
2. 方式2
创建表成功后,添加外键约束
/*创建表的时候,没有外键关系
alter table 表名
add constraint 约束名 foreign key(作为外键的列) references 引用到的表(引用到的表中的对应的列);
*/
create table if not exists `student` (
`id` int (4) not null auto_increment comment '学号',
`name` varchar (30) not null default '匿名' comment '姓名',
`pwd` varchar (20) not null default '123456' comment '密码',
`sex` varchar (2) not null default '女' comment '性别',
`birthdat` datetime default null comment '出生日期',
`gradeId` int(10) not null comment '学生的年级',
`address` varchar (100) default null comment '家庭住址',
`email` varchar (50) default null comment '邮箱',
primary key (`id`)
) engine innodb default charset = utf8
alter table `student`
add constraint `fk_gradeId` foreign key(`gradeId`) references `grade`(`gradeId`);
以上的操作都是物理外键,数据库级别的外键,不建议使用!(避免数据库过多造成困扰,这里了解即可)
最佳实现
-
数据库就是单纯的表,只用来存数据,只有行(数据)和列(字段)
-
我们想使用多张表的数据,想使用外键(程序去实现)
2. DML语言(全部记住)
数据库意义:数据存储,数据管理
DML语言:数据操作语言
- insert
- update
- delete
1. 添加
insert
/*插入语句(添加)
insert into 表名([字段1,字段2,字段3])values('值1'),('值2'),('值3'),......
*/
insert into `grade`(`gradename`) values('大四')
/*由于主键自增,我们可以省略主键
如果不写表的字段,它就会一一匹配
一般写插入语句,我们一定要数据和字段一一对应
*/
/*插入多个字段
values后面的字段用()包裹,并用,隔开
*/
insert into `grade`(`gradename`)
values('大二'),('大一')
insert into `student`(`name`) values('张三')
insert into `student`(`name`,`pwd`,`sex`) values('张三','aaaaaa','男')
insert into `student`(`name`,`pwd`,`sex`)
values('李四','bbbbbb','男'),('王五','cccccc','男')
语法
insert into 表名([字段1,字段2,字段3])values('值1'),('值2'),('值3'),......
注意事项
- 字段和字段之间使用英文逗号隔开
- 字段是可以省略的,但是后面的值必须一一对应,不能少
- 可以同时插入多条数据,values后面的值需要使用(),(),...隔开
2. 修改
update
/*修改学生的名字
*/
update `student` set `name`='wang' where id = 1
/*不指定条件的情况下,会改动所有表!
*/
update `student` set `name`='wang'
/*修改多个属性,用逗号隔开*/
update `student` set `name` = 'wang', `email` = 'xxxxx@qq.com' where id = 1
/*通过多个条件,定位数据*/
update `student` set `name` = '这是一个名字' where `name` = 'wang' or `sex` = '女'
语法
update 表名 set column_name = value, [column_name = value,...] where [条件] --column列字段
条件:where子句 运算符
| 操作符 | 含义 | 范围 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | 等于 | 5=6 | false |
| <>或!= | 不等于 | 5<>6 | true |
| > | 大于 | 5>6 | false |
| < | 小于 | 5<6 | true |
| <= | 小于等于 | 5<=6 | true |
| >= | 大于等于 | 5>=6 | false |
| between...and... | 在某个范围内,闭合区间 | [2,5] | |
| and | &&和 | 5>1 and 1>2 | false |
| or | ||或 | 5>1 or 1>2 | true |
注意:
- column_name 是数据库的列,尽量带上``
- 条件,筛选的条件,如果没有指定,则会修改所有的列
- value可以是一个具体的值,也可以是一个变量
3. 删除
1. delete命令
语法
delete from 表名 [where 条件]
/*删除数据(避免这样写,会全部删除)*/
delete from `student`
/*删除指定数据*/
delete from `student` where id = 1
2. truncate命令
作用:完全清空一个数据库表,表的索引和约束条件不会变!
/*清空student表*/
truncate `student`
3. delete和truncate的区别
- 相同点:都能删除数据,都不会删除表结构
- 不同点:
- truncate 能重新设置自增列,计数器会归零
- truncate 不会影响事务
4. delete删除的问题
重启数据库,现象:
- INNODB:自增列会从1开始(数据存在内存当中,断电即失)
- MYISAM:继续从上一个自增量开始(数据存在文件中,不会丢失)
3. DQL语言(最重点)
查询数据
1.DQL
Data Query Language:数据查询语言
- 所有的查询操作都用它 Select
- 简单的查询,复杂的查询它都能做
- 数据库最核心的语言,最重要的语句
- 使用频率最高的语言
select完整的语法
select [all | distinct]
{* | table.* | [table.field1[as alias1][,table.field2[as alias]][,...]]}
from table_name [as table_alias]
[left | right | inner join table_name2] -- 联合查询
[where ...] -- 等值查询,指定结果需要满足的条件
[group by ...] -- 指定结果按照哪几个字段来分组
[having] -- 过滤分组的记录必须满足的次要条件
[order by ...] -- 排序,指定查询记录按照一个或者多个条件排序
[limit {[offset,]row_count | row_countoffset offsets}]; -- 分页,指定查询的记录从哪条至哪条
注意:[ ]代表可选的,{ }代表必选的
2. 指定查询字段
-- 查询全部的学生 select 字段 from 表名
select * from `student`
-- 查询指定字段
select `studentno`, `studentname` from `student`
-- 别名,给结果起一个名字 as
-- 可以给字段起别名,也可以给表起别名
select `studentno` as 学号, `studentname` as 学生姓名 from `student` as s
-- 函数 concat(a,b)
-- 作用:将多个字符串合连接为一个字符串
select concat ('姓名:',`studentname`) as 新名字 from `student`
语法
select 字段1,... from 表
有的时候,列的名字不是那么的见名知意,此时我们可以起别名 用as
字段名 as 别名
表名 as 别名
1. 去重
-- 查询一下有哪些同学参加了考试(有成绩)
select * from `result` -- 查询全部的考试成绩
-- 查询有哪些同学参加了考试
select `studentno` from `result`
-- 发现重复数据,去重
select distinct `studentno` from `result`
作用:去除select查询出来的结果中重复的数据,重复的数据只显示一条
2. 数据库的列(表达式)
-- 查询系统版本(函数)
select version()
-- 用来计算(表达式)
select 100*3-1 as 计算结果
-- 查询自增的步长(变量)
select @@auto_increment_increment
-- 学生考试成绩+1分查看
select `studentno`,`studentresult`+1 as 提分后 from result
数据库中的表达式:文本值,列,Null,函数,计算表达式,系统变量...
语法
select 表达式 from 表
3. where条件子句
作用:检索数据中符合条件的值
搜索的条件由一个或多个表达式组成,返回结果为布尔值
1. 逻辑运算符
| 运算符 | 语法 | 结果描述 |
|---|---|---|
| and && | a and b a&&b | 逻辑与 |
| or || | a or b a||b | 逻辑或 |
| not ! | not a !a | 逻辑非 |
尽量使用英文字母
-- ================== where ===================
select `studentno`,`studentresult` from result
-- 查询考试成绩在95~100分之间的
select `studentno`,`studentresult` from result
where `studentresult` >=95 and `studentresult` <=100
-- 模糊查询(区间)
select `studentno`,`studentresult` from result
where `studentresult` between 95 and 100
-- 除了1000号学生之外的同学的成绩 not !
-- 注意not的位置!
-- 不加not:where `studentno`=1000,因此not放在 where之后对取值取非
select `studentno`,`studentresult` from result
where not `studentno`=1000
select `studentno`,`studentresult` from result
where `studentno` != 1000
2. 模糊查询
比较运算符
| 运算符 | 语法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| is null | a is null | 如果操作符为null,则结果为true |
| is not null | a is not null | 如果操作符为not null,则结果为true |
| between...and... | a between b and c | 若a在b和c之间,则结果为true |
| like | a like b | SQL匹配,如果a匹配b,则结果为true(可以使用通配符) |
| in | a in (a1,a2,a3,...) | 假设a在a1,或者a2...其中的某一个值中,结果为true(不能使用通配符) |
-- ================== 模糊查询 ===================
-- ================== like ===================
-- 查询姓张的同学
-- like结合 %(代表0到任意个字符) _(一个字符)
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `studentname` like '张%'
-- 查询姓张的同学,名字后面只有一个字的
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `studentname` like '张_'
-- 查询姓张的同学,名字后面只有两个个字的
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `studentname` like '张__'
-- 查询名字中有伟的同学 %伟%
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `studentname` like '%伟%'
-- ================== in ===================
-- in是具体的一个或多个值,不可以用通配符
-- 查询1000,1001号学员信息
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `studentno` in (1000,1001)
-- 查询在北京的学生
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `address` in ('北京朝阳')
-- ================== null not null ===================
-- 查询地址为空的学生 null或者''
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `address`='' or `address` is null
-- 查询有出生日期的同学=不为空
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `borndate` is not null
-- 查询没有出生日期的同学=为空
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `borndate` is null
4. 联表查询
1. join对比
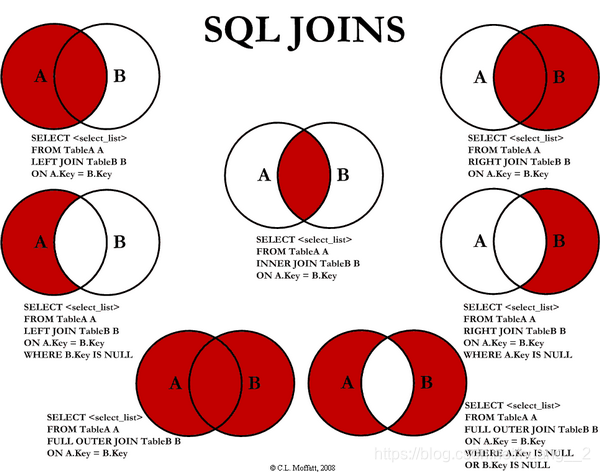
-- ================== 联表查询 join ===================
-- 查询参加了考试的同学(学号,学号,科目编号,分数)
select * from student
select * from result
/*思路
1.分析需求,分析查询的字段来自哪些表(超过一张表采用连接查询)
2.确定使用哪种连接查询?
确定交叉点(这两个表中哪个数据是相同的)
判断的条件:学生表中的studentno = 成绩表studentno
表的别名.字段:表示要查询的字段来源于哪个表
*/
select s.`studentno`,`studentname`,`subjectno`,`studentresult`
from `student` as s
inner join `result` as r
on s.`studentno` = r.`studentno`
-- Right Join
select s.`studentno`,`studentname`,`subjectno`,`studentresult`
from `student` as s
right join `result` as r
on s.`studentno` = r.`studentno`
-- Left Join
select s.`studentno`,`studentname`,`subjectno`,`studentresult`
from `student` as s
left join `result` as r
on s.`studentno` = r.`studentno`
-- 查询缺考的同学
select s.`studentno`,`studentname`,`subjectno`,`studentresult`
from `student` as s
left join `result` as r
on s.`studentno` = r.`studentno`
where `studentresult` is null
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| inner join | 如果表中至少有一个匹配,就返回行 |
| left join | 会从左表中返回所有的值,即使右表中没有匹配 |
| right join | 会从右表中返回所有的值,即使左表中没有匹配 |
join on 和where
join (连接的表) on (判断的条件) 连接查询(多张表)
where 等值查询(一张表)
查询多张表
-- 查询了参加考试的同学信息:学号,学生姓名,科目名称,分数
/*思路
1.分析需求,分析查询的字段来自哪些表:student,result,subject
2.确定使用哪种连接查询?
确定交叉点(这两个表中哪个数据是相同的)
左表为学生表,右表为成绩表时,使用右连,这样可以将所有参加了考试的学生number输出
on条件为学号相等,即可筛选出参加了考试的学生
查询科目,将结果表与科目表inner join,on的条件为相同的subjectno,这样就能查出对应的subjectname
判断的条件:学生表中的studentno = 成绩表studentno
表的别名.字段:表示要查询的字段来源于哪个表
*/
select s.`studentno`,`studentname`,`subjectname`,`studentresult`
from `student` as s
right join `result` as r
on r.`studentno`=s.`studentno`
inner join `subject` as sub
on sub.`subjectno`=r.`subjectno`
/*
我要查询哪些数据 select ...
从哪几个表中查 from 表 XXX join 连接的报表 on 交叉条件
假设存在多张表查询,慢慢来,先查询两张表然后再慢慢增加
a left join b on XXX :以a表位基准(左连接)
a right join b on XXX :以b表位基准(右连接)
*/
2. 自连接
自己的表和自己的表连接,核心:一张表拆为两张一样的表即可
父类
| categoryId | categoryName |
|---|---|
| 2 | 信息技术 |
| 3 | 软件开发 |
| 5 | 美术设计 |
子类
| pid | categoryId | categoryName |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 数据库 |
| 2 | 8 | 办公技术 |
| 3 | 6 | web开发 |
| 5 | 7 | ps技术 |
操作:查询父类对应的子类关系
| 父类 | 子类 |
|---|---|
| 信息技术 | 办公信息 |
| 软件开发 | 数据库 |
| 软件开发 | web开发 |
| 美术设计 | ps技术 |
-- 查询父子信息
select a.`categoryname` as '父栏目',b.`categoryname` as '子栏目'
-- 将一张表看为两个一模一样的表
from `category` as a,`category` as b
where a.`categoryid`=b.`pid`
5. 分页和排序
1. 排序
-- ================ 排序 order by ===============
-- 排序:升序 ASC,降序 DESC
-- 语法:order by 通过哪个字段排序,怎么排
-- 查询的结果根据 成绩降序 排序
select s.studentno,studentname,subjectname,studentresult
from student as s
inner join result as r
on s.studentno = r.studentno
inner join `subject` sub
on r.subjectno = sub.subjectno
where sub.subjectname = '高等数学-4'
-- 对成绩进行降序排序
order by studentresult desc
2. 分页
-- ================ 分页 limit ===============
-- 100万
-- 为什么要分页?
-- 缓解数据库压力,给人的体验更好
-- 分页,每页只显示五条数据
-- 语法:limit 起始值,页面的大小
-- limit 0,5 1~5条数据
-- limit 1,5 2~6条数据
select s.studentno,studentname,subjectname,studentresult
from student as s
inner join result as r
on s.studentno = r.studentno
inner join `subject` sub
on r.subjectno = sub.subjectno
where sub.subjectname = '高等数学-4'
order by studentresult desc
limit 0,1
-- 第一页 limit 0,5
-- 第二页 limit 5,5
-- 第三页 limit 10,5
-- 第n页 limit (n-1) * pageSize, pageSize
-- pageSize:页面大小
-- (n-1) * pageSize起始值
-- n:当前页
-- 数据总数/页面大小 = 总页数(向上取整,有余数时总页数+1)
语法
-- 语法:limit 起始值,页面的大小
6. 子查询
where (这个值是计算出来的)
本质:在where语句中嵌套一个子查询语句
-- =========================== where ======================
-- 1.查询 高等数学-4 的所有考试结果(学号,科目,成绩),降序排列
-- 方式1:使用连接查询
select `studentno`,`subjectname`,`studentresult`
from `result` as r
inner join `subject` as sub
on r.`subjectno` = sub.`subjectno`
where `subjectname`='高等数学-4'
order by `studentresult` desc
-- 方式二:使用子查询(由里及外)
select `studentno`,`subjectno`,`studentresult`
from `result`
where `subjectno`=(
select `subjectno` from `subject`
where `subjectname`='高等数学-4'
)
order by studentresult desc
-- 分数不小于80分的学生的学号和姓名
select distinct s.`studentno`,`studentname`
from `student` as s
inner join `result` as r
on r.`studentno`=s.`studentno`
where r.`studentresult` >= 80
-- 在这个基础上增加一个科目,高等数学-2
select distinct s.`studentno`,`studentname`
from `student` as s
inner join `result` as r
on r.`studentno`=s.`studentno`
where r.`studentresult` >= 80 and `subjectno`=(
select `subjectno` from `subject`
where `subjectname`='高等数学-2'
)
-- 查询课程为 高等数学-2 且分数不小于 80 的同学的学号和姓名
-- 由里及外
select `studentno`,`studentname`
from `student` where `studentno` in (
select `studentno` from `result`
where `studentresult` >= 80 and `subjectno` = (
select `subjectno` from `subject`
where `subjectname` = '高等数学-2'
)
)
7. 分组和过滤
分组的语法
group by 用于分组的字段
过滤的语法
having 过滤的条件
-- 注意:having 位于 group by之后!
-- 查询不同课程的平均分,最高分,最低分,平均分大于80
-- 核心:根据不同的课程分组
select `subjectname` as 科目,avg(`studentresult`) as 平均分,max(`studentresult`) as 最高分,min(`studentresult`) as 最低分
from `result` as r
inner join `subject` as sub
on r.`subjectno` = sub.`subjectno`
-- 通过什么字段来分组
group by r.`subjectno`
-- 利用having对分组后的结果进行过滤(此处不能用where是因为where不支持聚合函数),可以使用别名
having 平均分 >= 80
4. MySQL函数
官网:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/sql-function-reference.html
1. 常用函数
-- ======================== 常用函数 ==========================
-- 数学运算
select abs(-8) -- 绝对值
select ceiling(9.4) -- 向上取整
select floor(9.4) -- 向下取整
select rand() -- 返回一个0~1之间的随机数
select sign(-9) -- 判断一个数的符号 0返回0,负数返回-1,正数返回1
-- 字符串函数
select char_length('这是一段字符串') -- 字符串长度
select concat('这','是','一句话') -- 拼接字符串
select insert('替换失败',3,2,'成功') -- 查询,从某个位置开始替换某个长度的字符串,此处的开始位置从1开始计算
select lower('ABCdefg') -- 转小写字母
select upper('ABCdefg') -- 转大写字母
select instr('blue_sky','e') -- 返回第一次出现的子串的索引
select replace('这是原来的字符串','原来','替换后') -- 替换出现的指定字符串
select substr('这是原来的字符串',4,2) -- 返回指定的子字符串(源字符串,截取的位置,截取的长度)
select reverse('这是原来的字符串') -- 反转字符串
-- 查询姓 将姓赵的同学的姓替换为兆
select replace(`studentname`,'赵','兆') from `student`
where `studentname` like '赵%'
-- 时间和日期函数(重要)
select current_date() -- 获取当前日期
select curdate() -- 获取当前日期
select now() -- 获取当前的时间
select localtime() -- 获取本地时间
select sysdate() -- 获取系统时间
select year(now())
select month(now())
select day(now())
select hour(now())
select minute(now())
select second(now())
-- 系统
select system_user() -- 获取系统的用户
select user() -- 获取系统的用户
select version() -- 获取系统的版本
2. 聚合函数(常用)
| 函数名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| count() | 计数 |
| sum() | 求和 |
| avg() | 平均值 |
| max() | 最大值 |
| min() | 最小值 |
| ... |
-- ====================== 聚合函数 ====================
-- 都能够统计 表中的数据(想查询表中有多少个记录,就用count())
select count(`studentname`) from `student` -- count(字段),会忽略所有的null值
select count(*) from `student` -- count(*),不会忽略null值,本质:计算行数
select count(1) from `student` -- count(1),不会忽略null值,本质:计算行数
select sum(`studentresult`) as 总和 from `result`
select avg(`studentresult`) as 平均分 from `result`
select max(`studentresult`) as 最高分 from `result`
select min(`studentresult`) as 最低分 from `result`
3. 数据库级别的MD5加密(扩展)
什么是MD5?
主要是增强算法复杂度和不可逆性
MD5不可逆,具体的值MD5是一样的
MD5破解网站的原理:背后有一个字典,MD5加密后的值 加密前的值
-- ==================== 测试MD5 加密 ====================
create table `testMD5` (
`id` int(4) not null,
`name` varchar(20) not null,
`pwd` varchar(50) not null,
primary key(`id`)
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8
-- 明文密码
insert into `testMD5` (`id`,`name`,`pwd`) values
(1,'张三','123456'),
(2,'李四','123456'),
(3,'王五','123456')
-- 加密全部的密码,使用函数md5()
update `testMD5` set pwd=md5(pwd)
-- 插入的时候加密
insert into `testMD5` (`id`,`name`,`pwd`) values
(4,'小明',md5('123456'))
-- 如何校验:将用户传递进来的密码进行MD5加密,然后比对加密后的值
select * from `testMD5` where `name` = '小明' and pwd = md5('123456')