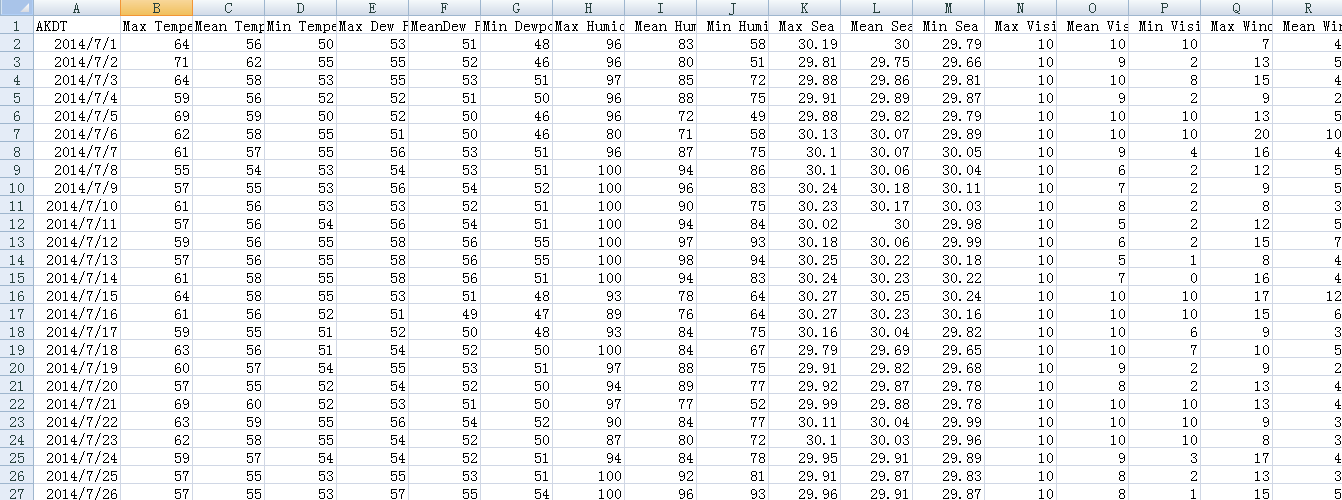
1.csv文件读取,csv文件是常用的数据存储格式之一,我们使用Python模块来处理csv文件,这是一个天气信息表
import csv from matplotlib import pyplot as plt filename = 'sitka_weather_07-2014.csv' with open(filename) as f: #从文件获取数据 reader = csv.reader(f) #获取数据的第一行也就是数据字段 header_row = next(reader) #print(header_row) #遍历读取到的第一行数据使用enumerate函数来获取每个元素的索引和值 # for index ,column_header in enumerate(header_row): # print(index,column_header) highs=[] #从文件获取到最高气温 for row in reader: highs.append(int(row[1])) print(highs) fig = plt.figure(dpi=128, figsize=(10, 6)) plt.plot(highs, c='red', alpha=0.5) #plt.plot(dates, lows, c='blue', alpha=0.5) #plt.fill_between(dates, highs, lows, facecolor='blue', alpha=0.1) title = "Daily high and low temperatures CA" plt.title(title, fontsize=20) plt.xlabel('', fontsize=16) fig.autofmt_xdate() plt.ylabel("Temperature (F)", fontsize=16) plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=16) plt.show()
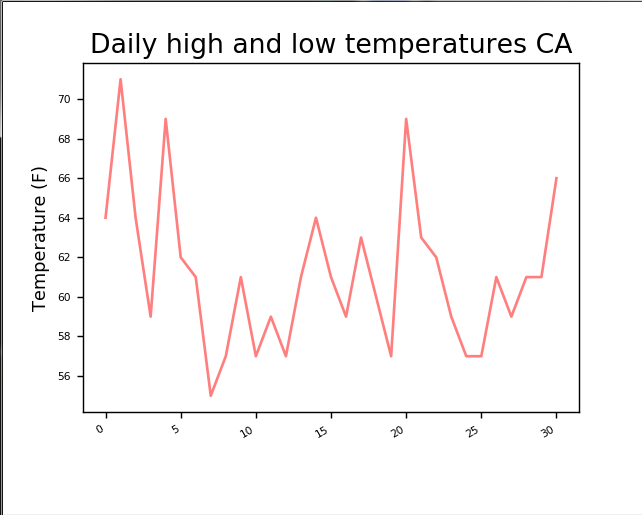
除了这样显示,我们还可以读取时间数据显示在x轴上,添加datetime模块
from datetime import datetime
读取时间数据
filename = 'sitka_weather_07-2014.csv' with open(filename) as f: #从文件获取数据 reader = csv.reader(f) #获取数据的第一行也就是数据字段 header_row = next(reader) #print(header_row) #遍历读取到的第一行数据使用enumerate函数来获取每个元素的索引和值 # for index ,column_header in enumerate(header_row): # print(index,column_header) highs,dates=[],[] #从文件获取到最高气温 for row in reader: #从文件获取日期 current_date=datetime.strptime(row[0],"%Y-%m-%d") dates.append(current_date) highs.append(int(row[1])) print(highs,dates) fig = plt.figure(dpi=128, figsize=(5, 4)) #添加日期 plt.plot(dates,highs, c='red', alpha=0.5)
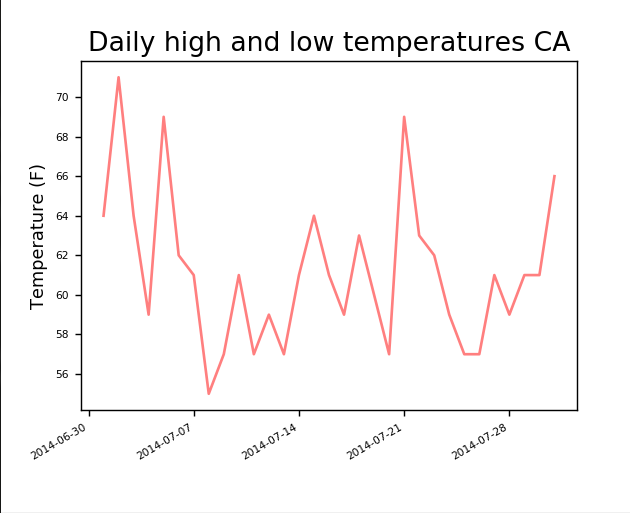
图中是一个月的天气温度情况
当然还可以读取整年的天气情况,只要有足够的数据
2.绘制一个数据系列,对比全年每个月的最高气温和最低气温
import csv from datetime import datetime from matplotlib import pyplot as plt filename = 'death_valley_2014.csv' with open(filename) as f: reader = csv.reader(f) header_row = next(reader) dates, highs, lows = [], [], [] for row in reader: #判断是否有时间信息 try: current_date = datetime.strptime(row[0], "%Y-%m-%d") high = int(row[1]) #读取最低温数据 low = int(row[3]) except ValueError: print(current_date, 'missing data') else: dates.append(current_date) highs.append(high) lows.append(low) #绘制图表. fig = plt.figure(dpi=128, figsize=(10, 9)) plt.plot(dates, highs, c='red', alpha=0.5) plt.plot(dates, lows, c='blue', alpha=0.5) #facecolor指定了填充区域的颜色 plt.fill_between(dates, highs, lows, facecolor='blue', alpha=0.1) title = "Daily high and low temperatures CA" plt.title(title, fontsize=10) plt.xlabel('', fontsize=6) fig.autofmt_xdate() plt.ylabel("Temperature (F)", fontsize=6) plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=6) plt.show()
