第一种:
主要是利用 树结点类型的数组、二叉树结点序号之间的关系 来创建:
父结点序号为 i 则,左儿子结点序号为 2*i ,右儿子序号为 2*i+1.
//用层次遍历的方法来创建二叉树 #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; //二叉链表的结构类型定义 const int maxsize=1024; typedef char datatype; typedef struct node { datatype data; struct node *lchild,*rchild; }bitree; bitree*creattree(); void PreOrder(bitree*); //TestCase: ebfad.g..c# void main() { bitree* pb = creattree(); PreOrder(pb); cout<<endl; system("pause"); } //层次遍历建立二叉树 1 bitree* creattree() { char ch; int front = 1,rear = 0; bitree *root, *s; root = NULL; bitree *Q[maxsize]; //front是用来指向父结点下标的。 printf("按层次输入二叉树,虚结点输入'.',以'#'结束输入: "); while( (ch=getchar()) != '#' ) { s = NULL; if(ch!='.') { //为结点分配空间和设置数据域,指针域 s=(bitree*)malloc(sizeof(bitree)); s->data = ch; s->lchild = NULL; s->rchild = NULL; } //输入一个结点就放到数组里 rear ++; Q[rear] = s; //根结点: if(rear == 1) root = s; else { //如果是虚结点,则申请不到s就不必考虑怎么挂结点s if( s && Q[front]) { //下标为偶数的话就挂在左子树上 if( rear%2== 0) Q[front]-> lchild = s; //下标为奇数就挂在右边 else Q[front]-> rchild = s; } //放好两个结点之后就要改变父结点的下标了 if(rear%2 == 1) front++; } } return root; } //先序遍历输出 void Visit(bitree* T) { if(T->data != '#') { printf("%c ",T->data); } } void PreOrder(bitree* T){ if(T != NULL){ Visit(T); PreOrder(T->lchild); PreOrder(T->rchild); } }
第二种:
用队列来辅助完成二叉树的层次创建。
(1)第一步很特殊,首先是树根
Binary_node* pNode=A.front();
A.pop();
B.push(pNode);
A:bfad.g..c
B:e
树:

(2)后面的每一步都是从A中取出两个队首,放入B队列尾部(如果为NULL则不放)。从B中取出队首,队列A中取出的元素正好是B中取出元素的小孩子
Binary_node* pfather= B.front();
B.pop();
Binary_node* pLchild= A.front();//先出来的是左孩子
A.pop();
Binary_node* pRchild= A.front();
A.pop();
pfather->left=pLchild;
pfather->right=pRchild;
//先放入左孩子
if(pLchild!=NULL)
{
B.push(pLchild);
}
if(pRchild!=NULL)
{
B.push(pRchild);
}
A:ad.g..c
B:bf
树:

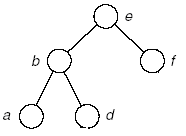
(3)
A:.g..c
B:fad
树:
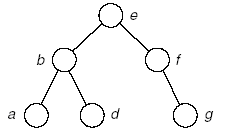
(4)
A:..c
B:adg
树:
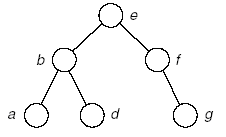
(5)
A:c
B:dg
树:
(6)
A:空(当队列A为空的时候整个算法结束,树构造成功)
B:g
树:

完成。
buildTree(Binary_node * &root) { char nodeData;//结点中的数据 queue<char> treeDataQueue; queue< Binary_node * > treeNodeQueue;// queue<Binary_node * > treeFatherQueue;// Binary_node *pTreeNode;//从树结点队列中弹出的结点 Binary_node *pfather ; Binary_node *pLchild; Binary_node *pRchild; while(!treeDataQueue.empty()){ nodeData = treeDataQueue.front(); treeDataQueue.pop(); if(nodeData!='.') pTreeNode = new Binary_node(nodeData); else pTreeNode = NULL; treeNodeQueue.push(pTreeNode); } //根结点 pTreeNode = treeNodeQueue.front(); treeNodeQueue.pop(); root = pTreeNode; treeFatherQueue.push(pTreeNode); while(!treeNodeQueue.empty()){ pfather = treeFatherQueue.front(); treeFatherQueue.pop(); pLchild = treeNodeQueue.front(); treeNodeQueue.pop(); if(pLchild!=NULL){ pfather->left = pLchild; treeFatherQueue.push(pLchild); } if(!treeNodeQueue.empty()){ pRchild = treeNodeQueue.front(); treeNodeQueue.pop(); if(pRchild!=NULL){ pfather->right = pRchild; treeFatherQueue.push(pRchild); }//end if(pRchild!=NULL) }//end if(!treeNodeQueue.empty()) }//end while(!treeNodeQueue.empty()) }