原文链接:http://tecdat.cn/?p=6454
聚类方法用于识别从营销,生物医学和地理空间等领域收集的多变量数据集中的相似对象。它们是不同类型的聚类方法,包括:
- 划分方法
- 分层聚类
- 模糊聚类
- 基于密度的聚类
- 基于模型的聚类
数据准备
- 演示数据集:名为USArrest的内置R数据集
- 删除丢失的数据
- 缩放变量以使它们具有可比性
# Load and prepare the data
my_data <- USArrests %>%
na.omit() %>% # Remove missing values (NA)
scale() # Scale variables
# View the firt 3 rows
head(my_data, n = 3)距离
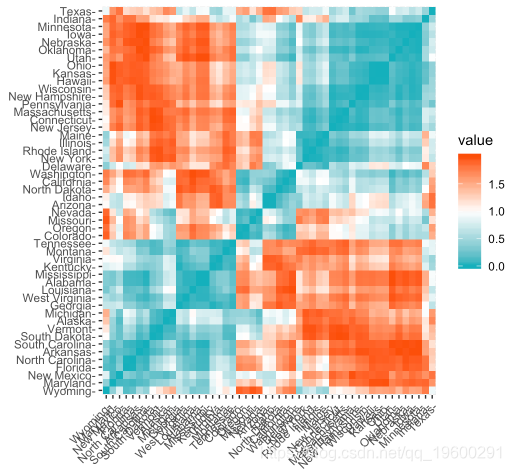
get_dist():用于计算数据矩阵的行之间的距离矩阵。与标准dist()功能相比,它支持基于相关的距离测量,包括“皮尔逊”,“肯德尔”和“斯皮尔曼”方法。fviz_dist():用于可视化距离矩阵
res.dist <- get_dist(U
gradient = list(low = "#00AFBB", mid = "white", high = "#FC4E07"))
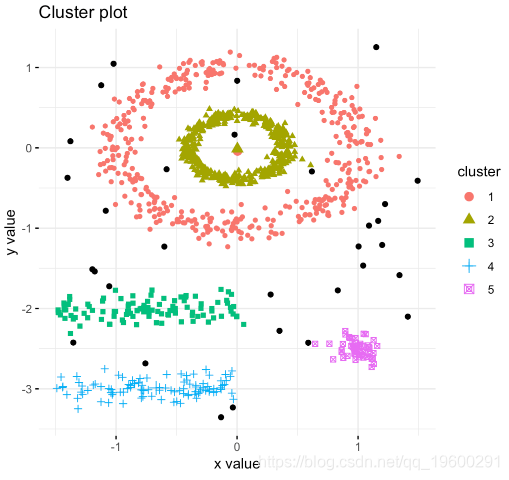
划分聚类
、算法是将数据集细分为一组k个组的聚类技术,其中k是分析人员预先指定的组的数量。
k-means聚类的替代方案是K-medoids聚类或PAM(Partitioning Around Medoids,Kaufman和Rousseeuw,1990),与k-means相比,它对异常值不太敏感。
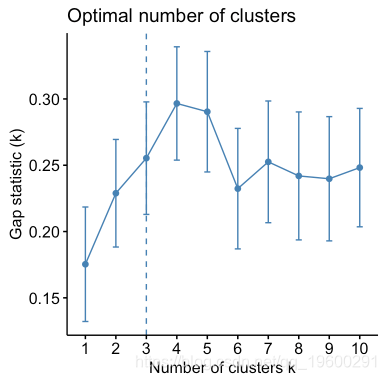
以下R代码显示如何确定最佳簇数以及如何在R中计算k-means和PAM聚类。
fviz_nbclust(my_data, kmeans, method = "gap_stat")
set.seed(123)
# Visualize
fviz_cluster(km.res, data = my_data,
ellipse.type = "convex",
palette = "jco",
ggtheme = theme_minimal())# Compute PAM
pam.res <- pam(my_data, 3)
# Visualize
fviz_cluster(pam.res)分层聚类
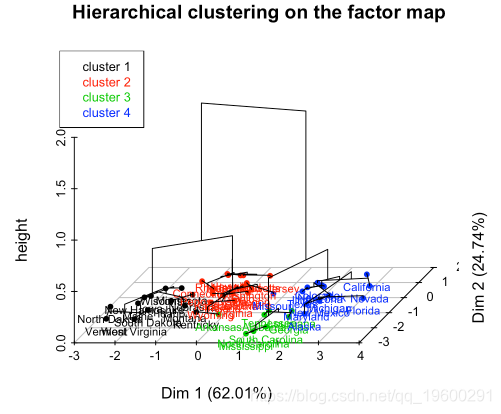
分层聚类是一种分区聚类的替代方法,用于识别数据集中的组。它不需要预先指定要生成的簇的数量。
# Compute hierarchical clustering
res.hc <- USArrests %>%
scale() %>% # Scale the data
hclust(method = "ward.D2") # Compute hierachical clustering
# Visualize using factoextra
# Cut in 4 groups and color by groups
fviz_dend(res.hc, k = 4, # Cut in four groups
color_labels_by_k = TRUE, # color labels by groups
rect = TRUE # Add rectangle around groups
)评估聚类倾向
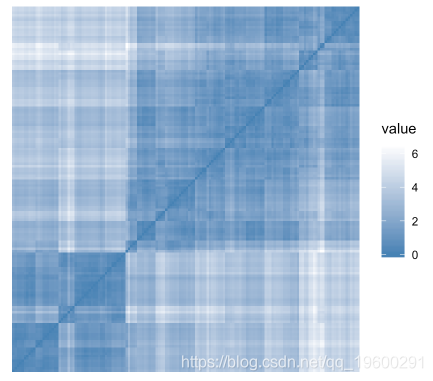
为了评估聚类倾向,可以使用Hopkins的统计量和视觉方法。
- Hopkins统计:如果Hopkins统计量的值接近1(远高于0.5),那么我们可以得出结论,数据集是显着可聚类的。
- 视觉方法:视觉方法通过计算有序相异度图像中沿对角线的方形黑暗(或彩色)块的数量来检测聚类趋势。
R代码:
iris[, -5] %>% # Remove column 5 (Species)
scale() %>% # Scale variables
get_clust_tendency(n = 50, gradient = gradient.color)
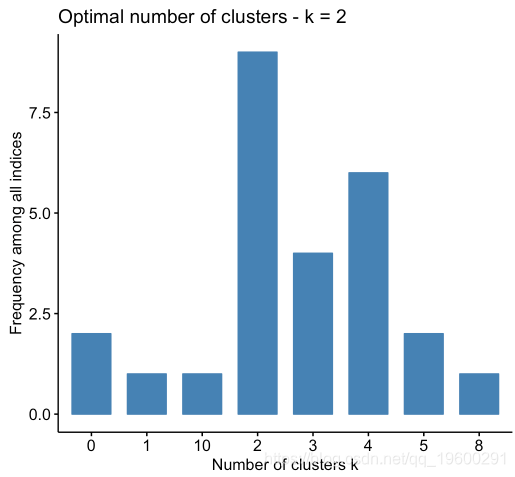
确定最佳簇数
set.seed(123)
# Compute
res.nbclust <- USArrests %>%
scale() %>%
(distance = "euclidean",
min.nc = 2, max.nc = 10,
method = "complete", index ="all") # Visualize
fviz_nbclust(res.nbclust, ggtheme = theme_minimal())
群集验证统计信息
在下面的R代码中,我们将计算和评估层次聚类方法的结果。
- 计算和可视化层次聚类:
# Enhanced hierarchical clustering, cut in 3 groups
res.hc <- iris[, -5] %>%
scale() %>%
("hclust", k = 3, graph = FALSE)
# Visualize with factoextra
(res.hc, palette = "jco",
rect = TRUE, show_labels = FALSE)
(res.hc)
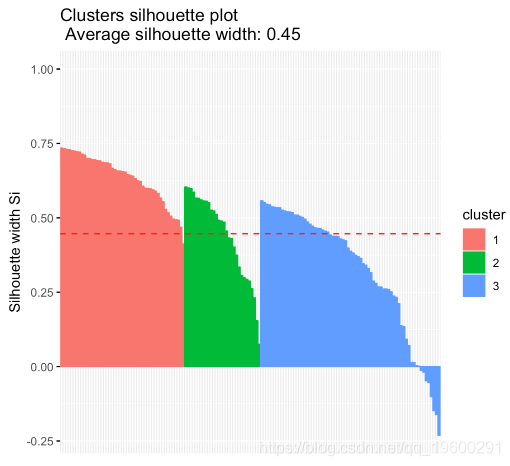
- 哪些样品有负面轮廓?他们更接近什么集群?
# Silhouette width of observations
sil <- res.hc$silinfo$widths[, 1:3]
# Objects with negative silhouette
neg_sil_index <- which(sil[, 'sil_width'] < 0)
sil[neg_sil_index, , drop = FALSE]高级聚类方法
混合聚类方法
- 分层K均值聚类:一种改进k均值结果的混合方法
- HCPC:主成分上的分层聚类
模糊聚类
模糊聚类也称为软聚类方法。标准聚类方法(K-means,PAM),其中每个观察仅属于一个聚类。这称为硬聚类。
基于模型的聚类
在基于模型的聚类中,数据被视为来自两个或多个聚类的混合的分布。它找到了最适合模型的数据并估计了簇的数量。
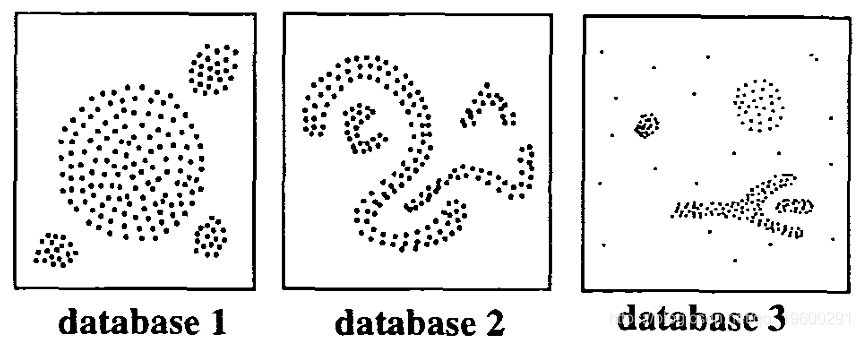
DBSCAN:基于密度的聚类
DBSCAN是Ester等人引入的聚类方法。(1996)。它可以从包含噪声和异常值的数据中找出不同形状和大小的簇(Ester等,1996)。基于密度的聚类方法背后的基本思想源于人类直观的聚类方法。
R链中的DBSCAN的描述和实现