【实验目的】
通过完成预测分析法的语法分析程序,了解预测分析法和递归子程序法的区别和联系。使了解语法分析的功能,掌握语法分析程序设计的原理和构造方法,训练掌握开发应用程序的基本方法。
【实验内容】
u 根据某一文法编制调试 LL ( 1 )分析程序,以便对任意输入的符号串进行分析。
u 构造预测分析表,并利用分析表和一个栈来实现对上述程序设计语言的分析程序。
u 分析法的功能是利用LL(1)控制程序根据显示栈顶内容、向前看符号以及LL(1)分析表,对输入符号串自上而下的分析过程。
【设计思想】
(1)定义部分:定义常量、变量、数据结构。
(2)初始化:设立LL(1)分析表、初始化变量空间(包括堆栈、结构体、数组、临时变量等);
(3)控制部分:从键盘输入一个表达式符号串;
(4)利用LL(1)分析算法进行表达式处理:根据LL(1)分析表对表达式符号串进行堆栈(或其他)操作,输出分析结果,如果遇到错误则显示错误信息。
【实验要求】
(1)编程时注意编程风格:空行的使用、注释的使用、缩进的使用等。
(2)如果遇到错误的表达式,应输出错误提示信息。
代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
|
#include<iostream>#include<string>#include<map>#include<vector>#include<stack>#include<set>#include<cstring>using namespace std;map<char, int>getnum;char text[100]; //获得对应字符vector<string>proce;int table[100][100]; //预测分析表int num = 0; int numvt = 0; //numvt是终结符集合,0是'#',numvt表空字string first[100];string follow[200];void readin(){ memset(table, -1, sizeof(table)); getnum['#'] = 0; text[0] = '#'; cout << "请输入所有的终结符:" << endl; char x; do { cin >> x; getnum[x] = ++num; text[num] = x; } while (cin.peek() != '
'); numvt = ++num; getnum['@'] = numvt; //kong zi text[num] = ('@'); cout << "请输入所有非终结符:" << endl; do { cin >> x; getnum[x] = ++num; text[num] = x; } while (cin.peek() != '
'); cout << "输入产生式集合(空用'@'表示),以'end'结束:" << endl; string pro; while (cin >> pro&&pro != "end") { string ss; ss += pro[0]; for (int i = 3; i<pro.size(); i++) { if (pro[i] == '|') { proce.push_back(ss); ss.clear(); ss += pro[0]; } else { ss += pro[i]; } } proce.push_back(ss); }}void jiaoji(string &a, string b) //a=a or b 取a,b交集赋值给a{ set<char>se; for (int i = 0; i<a.size(); i++) se.insert(a[i]); for (int i = 0; i<b.size(); i++) se.insert(b[i]); string ans; set<char>::iterator it; for (it = se.begin(); it != se.end(); it++) ans += *it; a = ans;}string get_f(int vn, int & has_0) //dfs:vn能推出的不含空字的vt集合,并且判断vn能否推出空字{ if (vn == numvt)has_0 = 1; if (vn<numvt)return first[vn]; string ans; for (int i = 0; i<proce.size(); i++) { if (getnum[proce[i][0]] == vn) ans += get_f(getnum[proce[i][1]], has_0); } return ans;}void getfirst(){ for (int i = 1; i <= numvt; i++) //终结符,first集是其本身。 { first[i] += ('0' + i); } for (int j = 0; j<proce.size(); j++) //扫描所有产生式 { int k = 0; int has_0 = 0; //k扫瞄该产生式 do{ has_0 = 0; k++; if (k == proce[j].size()) //推到最后一个了,则附加空字 { first[getnum[proce[j][0]]] += ('0' + numvt); break; } //合并之 jiaoji(first[getnum[proce[j][0]]], get_f(getnum[proce[j][k]], has_0)); } while (has_0); //到无法推出空字为止 }}void print_first(){ cout << "first集:" << endl; for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) { cout << "first [" << text[i] << "]: "; for (int j = 0; j<first[i].size(); j++) cout << text[first[i][j] - '0'] << " "; cout << endl; } cout << endl;}void getfollow(){ jiaoji(follow[getnum[proce[0][0]]], "0"); //先添加'#'; for (int j = 0; j<proce.size(); j++) //扫所有产生式 { for (int jj = 1; jj<proce[j].size(); jj++) //每个非终结符的follow集 { if (getnum[proce[j][jj]] <= numvt)continue; //vt无follow集 int k = jj; int has_0; do { has_0 = 0; k++; if (k == proce[j].size()) //都能推出空字,follow集=产生式左边的vn, { jiaoji(follow[getnum[proce[j][jj]]], follow[getnum[proce[j][0]]]); break; } jiaoji(follow[getnum[proce[j][jj]]], get_f(getnum[proce[j][k]], has_0)); } while (has_0); } }}void gettable() //得预测分析表{ for (int i = 0; i<proce.size(); i++) //扫所有产生式 { if (proce[i][1] == '@') //直接推出空字的,特判下(follow集=产生式左边的vn中元素填) { string flw = follow[getnum[proce[i][0]]]; for (int k = 0; k<flw.size(); k++) { table[getnum[proce[i][0]]][flw[k] - '0'] = i; } } string temps = first[getnum[proce[i][1]]]; for (int j = 0; j<temps.size(); j++) //考察first集 { if (temps[j] != ('0' + numvt)) { table[getnum[proce[i][0]]][temps[j] - '0'] = i; } else //有空字的,考察follw集 { string flw = follow[getnum[proce[i][1]]]; for (int k = 0; k<flw.size(); k++) { table[getnum[proce[i][0]]][flw[k] - '0'] = i; } } } }}string get_proce(int i) //由对应下标获得对应产生式。{ if (i<0)return " "; //无该产生式 string ans; ans += proce[i][0]; ans += "->"; for (int j = 1; j<proce[i].size(); j++) ans += proce[i][j]; return ans;}void print_table(){ cout << "预测分析表:" << endl; for (int i = 0; i<numvt; i++) cout << ' ' << text[i]; cout << endl; for (int i = numvt + 1; i <= num; i++) { cout << text[i]; for (int j = 0; j<numvt; j++) { cout << ' ' << get_proce(table[i][j]); } cout << endl; } cout << endl;}void print_follow(){ cout << "follow集:" << endl; for (int i = numvt + 1; i <= num; i++) { cout << "follow [" << text[i] << "]: "; for (int j = 0; j<follow[i].size(); j++) cout << text[follow[i][j] - '0'] << " "; cout << endl; } cout << endl;}string word;bool analyze() //总控,分析字word的合法性,若合法,输出所有产生式。{ stack<char>sta; sta.push('#'); sta.push(proce[0][0]); int i = 0; while (!sta.empty()) { int cur = sta.top(); sta.pop(); if (cur == word[i]) //是终结符,推进 { i++; } else if (cur == '#') //成功,结束 { return 1; } else if (table[getnum[cur]][getnum[word[i]]] != -1) //查表 { int k = table[getnum[cur]][getnum[word[i]]]; cout << proce[k][0] << "->"; for (int j = 1; j<proce[k].size(); j++) cout << proce[k][j]; cout << endl; for (int j = proce[k].size() - 1; j>0; j--) //逆序入栈 { if (proce[k][j] != '@') sta.push(proce[k][j]); } } else //失败! { return 0; } } return 1;}int main(){ readin(); getfirst(); getfollow(); getfollow(); gettable(); print_first(); print_follow(); print_table(); cout << "请输入字:" << endl; cin >> word; if (analyze()) cout << "succeed!该字有效,所用产生式如上。" << endl; else cout << "error!" << endl; return 0;} |
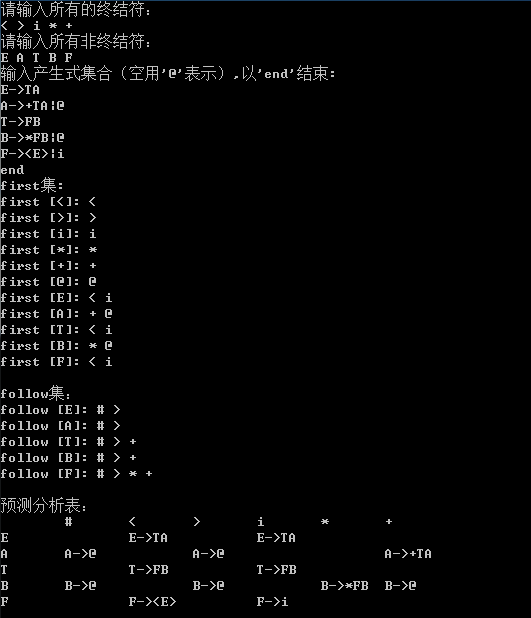
运行截图: