AOP简
spring中两大核心一个是IOC,另一个就是AOP,Aop被称为面向切面编程。
好处:功能增强,解耦
常用形式:声明式事务,日志监控,权限控制。。。
Aop中有几个重要概念:
- 切面 Aspect,使用注解@Aspect
- 切入点 pointCut, 使用注解@Pointcut
- 通知 advice
通知advice又有几种:
- 前置通知:before advice,使用@Before注解
- 后置通知:after advice,使用 @After注解
- 环绕通知: around advice,使用@Around注解
- 正常返回:after returning advice,使用@AfterReturning注解
- 异常通知:Throws advice,使用@AfterThrowing
Aop使用
我们目的是在方法的前后打印日志。
先创建一个Caluate类,里面有一个方法进行除法计算:
@Repository public class Caluate { public int divide(int x,int y){ return x/y; } }
创建一个日志切面类:用@Aspect来标记
@Repository @Aspect //标记这是一个切面类 public class logAspectJ { /** * 切入点表达式 */ @Pointcut("execution(public int com.springAop.Caluate.*(..))")//匹配该类的所有方法 public void pointCut(){ } @Before("pointCut()") public void logStart(){ System.out.println("在方法开始之前执行。。。。"); } @AfterReturning("pointCut()") public void logReturn(){ System.out.println("在方法正常返回执行。。。。"); } @After("pointCut()") public void logend(){ System.out.println("在方法结束之后执行。。。。"); } @AfterThrowing("pointCut()") public void logThrow(){ System.out.println("方法出现异常。。。。"); } }
创建配置类MainAopConfig:加上@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,开启切面自动代理
@Configuration @Import({Caluate.class,logAspectJ.class}) @EnableAspectJAutoProxy //一定要加上这个注解 public class MainAopConfig { }
测试:正常情况下输出
public class AopTest { @Test public void test(){ //创建容器 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainAopConfig.class); Caluate caluate = applicationContext.getBean(Caluate.class); caluate.divide(2,1); applicationContext.close(); } }
打印结果:
在方法开始之前执行。。。。
在方法结束之后执行。。。。
在方法正常后执行。。。。
测试:出现异常情况
public class AopTest { @Test public void test(){ //创建容器 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainAopConfig.class); Caluate caluate = applicationContext.getBean(Caluate.class); caluate.divide(2,0); applicationContext.close(); } }
打印结果:
在方法开始之前执行。。。。
在方法结束之后执行。。。。
方法出现异常。。。。
在通知的方法中可以使用JoinPoint来接收切点的方法信息:
@Before("pointCut()")
public void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Signature methodName = joinPoint.getSignature();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();
System.out.println("/////"+target);
System.out.println("在"+methodName+"方法开始之前执行。。。。参数有"+args[0]+","+args[1]);
}
JoinPoint有几个这样的方法:
Object getTarget();//获取到对象
Object[] getArgs();//获取到方法的参数
Signature getSignature();//获取到方法的信息
输出结果:
/////com.springAop.Caluate@1f59a598
在int com.springAop.Caluate.divide(int,int)方法开始之前执行。。。。参数有2,0
如果有返回值和异常也可以来接收参数
returning = "result" ,接收返回值
@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()",returning = "result") public void logReturn(Object result){ System.out.println("在方法正常后执行。。。。,返回值--》"+result); }
打印输出:
在方法正常后执行。。。。,返回值--》2
也可以加上JoinPoint参数来接收方法的信息,但JoinPoint必选放在前面
@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()",returning = "result") public void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint ,Object result){ System.out.println("在"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"方法正常后执行。。。。,返回值--》"+result); }
打印输出:
在divide方法正常后执行。。。。,返回值--》2
throwing = "exp",抛出异常
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()",throwing = "exp") public void logThrow(Exception exp){ System.out.println("方法出现异常。。。。,抛出的异常—-》"+exp); }
打印输出:
方法出现异常。。。。,抛出的异常—-》java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
环绕通知:使用ProceedingJoinPoin
@Around("pointCut()")
public Object logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知前。。。。。");
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知返回的结果。。。"+proceed);
System.out.println("环绕通知后。。。。。");
return proceed;
}
打印输出:在方法执行的前后进行操作
环绕通知前。。。。。
在int com.springAop.Caluate.divide(int,int)方法开始之前执行。。。。参数有2,1
环绕通知返回的结果。。。2
环绕通知后。。。。。
Aop 源码解析
在aop中关键的注解是@EnableAspectJAutoProxy,然后看它的源码,它导入了AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar这个类
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import({AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class}) public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy { boolean proxyTargetClass() default false; boolean exposeProxy() default false; }
AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar实现了接口ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,这个接口的作用就是将自定义bean加入到容器中
public interface ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata var1, BeanDefinitionRegistry var2); }
在@Import中,也可以通过实现该接口来导入自定义bean。
下面我们来写个例子看看ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口的作用:
》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》0
例如在配置类MainAopConfig中导入MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar自定义类,实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口
我们还是将Caluate.class和logAspectJ.class,注册到容器中,这次我们导入的MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar类
@Configuration @Import({MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class}) @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class MainAopConfig { }
自定义MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar类:
public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) { RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(Caluate.class); RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition2 = new RootBeanDefinition(logAspectJ.class); //前一个参数指定bean的名称,后一个参数传入BeanDefinition,这里传入BeanDefinition的实现类RootBeanDefinition beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("caluate",rootBeanDefinition); beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("logAspectJ",rootBeanDefinition2); } }
可以这样实现将这两个组件加入到容器中。所以这里就是通过AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar自定义给容器中注册bean。
》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》1
那么我们看看AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar向容器中注册了什么东西?:
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。0
AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar 的部分源码:AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);//调用这个方法
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar() { } public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);//调用这个方法 AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class); if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry); } if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry); } } }
然后去调用registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired这个方法,传入AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类作为参数
public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { return registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry, (Object)null); } public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) { return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source); }
再来看看registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired的详细方法,它接受了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator参数,并返回BeanDefinition,
if先判断BeanDefinitionRegistry这里面有没有internalAutoProxyCreator,没有就进行注册,并设置名称为org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) { Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null"); if (registry.containsBeanDefinition("org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator")) { BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition("org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator"); if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) { int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName()); int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls); if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) { apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName()); } } return null; } else { RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls); beanDefinition.setSource(source); beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", -2147483648); beanDefinition.setRole(2); registry.registerBeanDefinition("org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator", beanDefinition); return beanDefinition; } }
所以AspectJAutoProxyRegistr的作用就是在容器中注册一个AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。1
那么我们就需要知道AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的作用,才知道为什么要容器里注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator:
————————————————————————————————————》0
下面是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的继承关系
Class AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
java.lang.Object
org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyConfig
org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyProcessorSupport
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
All Implemented Interfaces:
Serializable, AopInfrastructureBean, Aware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, BeanPostProcessor,
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, Ordered
看代码可知,其中AbstractAutoProxyCreator这个抽象类实现了implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware,
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口继承了BeanPostProcessor(后置处理器)接口,这是个很重要的接口,这个接口的作用就是在bean的初始化前进行操作。
BeanPostProcessor有两个方法:postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean初始化之前操作)和postProcessAfterInitialization(bean初始化之后操作)
public interface BeanPostProcessor { Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object var1, String var2) throws BeansException; Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object var1, String var2) throws BeansException; }
我们举个例子看看BeanPostProcessor的作用。
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________0
自定义一个MyBeanPostProcesser implements BeanPostProcessor,在Caluated的初始化前后操作:让Caluated实现InitializingBean接口
@Repository public class Caluate implements InitializingBean { public int divide(int x,int y){ return x/y; } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("caluate进行初始化。。。。"); } }
自定义的MyBeanPostProcesser :/** *后置处理器,处理前后初始化的工作 */ @Component public class MyBeanPostProcesser implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { System.out.println(" postProcessBeforeInitialization ...beanname="+s+"---》》,bean="+o); return o; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization.... beanname="+s+"----》》,bean="+o); return o; } }
配置文件中,将MyBeanPostProcesser导入到配置文件中:
@Configuration @Import({MyBeanPostProcesser.class,MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class}) @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class MainAopConfig { }
测试:打印输出:
postProcessBeforeInitialization ...beanname=caluate---》》,bean=com.springAop.Caluate@459e9125
caluate进行初始化。。。。
postProcessAfterInitialization.... beanname=caluate----》》,bean=com.springAop.Caluate@459e9125
所以我们可以知道AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator有后置处理器这样的一个功能。
________________________________________________________________________________________________1
——————————————————————————————————————————————————》1
那么AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreatory后置处理器这样的功能,它如何创建?具体的作用?我们再来看看AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的继承关系中的一个个父类。
首先分析这个AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware的抽象类,我们只看和BeanPostProcessor(后置处理器)有关的方法。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreatory创建
》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》0
setBeanFactory(),postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
AbstractAutoProxyCreator的子类AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator中的方法
setBeanFactory(),initBeanFactory()
可以看到AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的setBeanFactory()重写了AbstractAutoProxyCreator的setBeanFactory()
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的子类AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator中的方法:没有相关的方法。
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的子类AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator中的方法:
initBeanFactory()
可以看到AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的initBeanFactory()重写了AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的initBeanFactory()
在相应的方法上打上断点,来一步一步debug,从test()开始:
public class AopTest { @Test public void test(){ //创建容器 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainAopConfig.class); Caluate caluate = applicationContext.getBean(Caluate.class); caluate.divide(2, 1); applicationContext.close(); } }
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的构造方法:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class... annotatedClasses) { this(); this.register(annotatedClasses); this.refresh(); }
如果开启了source和documentation功能,源码中有注释会没有this
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) { this(); register(annotatedClasses); refresh(); }
整体流程:
- 首先传入配置类,创建ioc容器
- 注册配置类,刷新ioc容器
this.refresh()

@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
refresh
里面有一个registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法,作用用来注册bean的处理器,拦截bean的创建。
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
然后调用registerBeanPostProcessors方法,注册后置处理器
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this); }
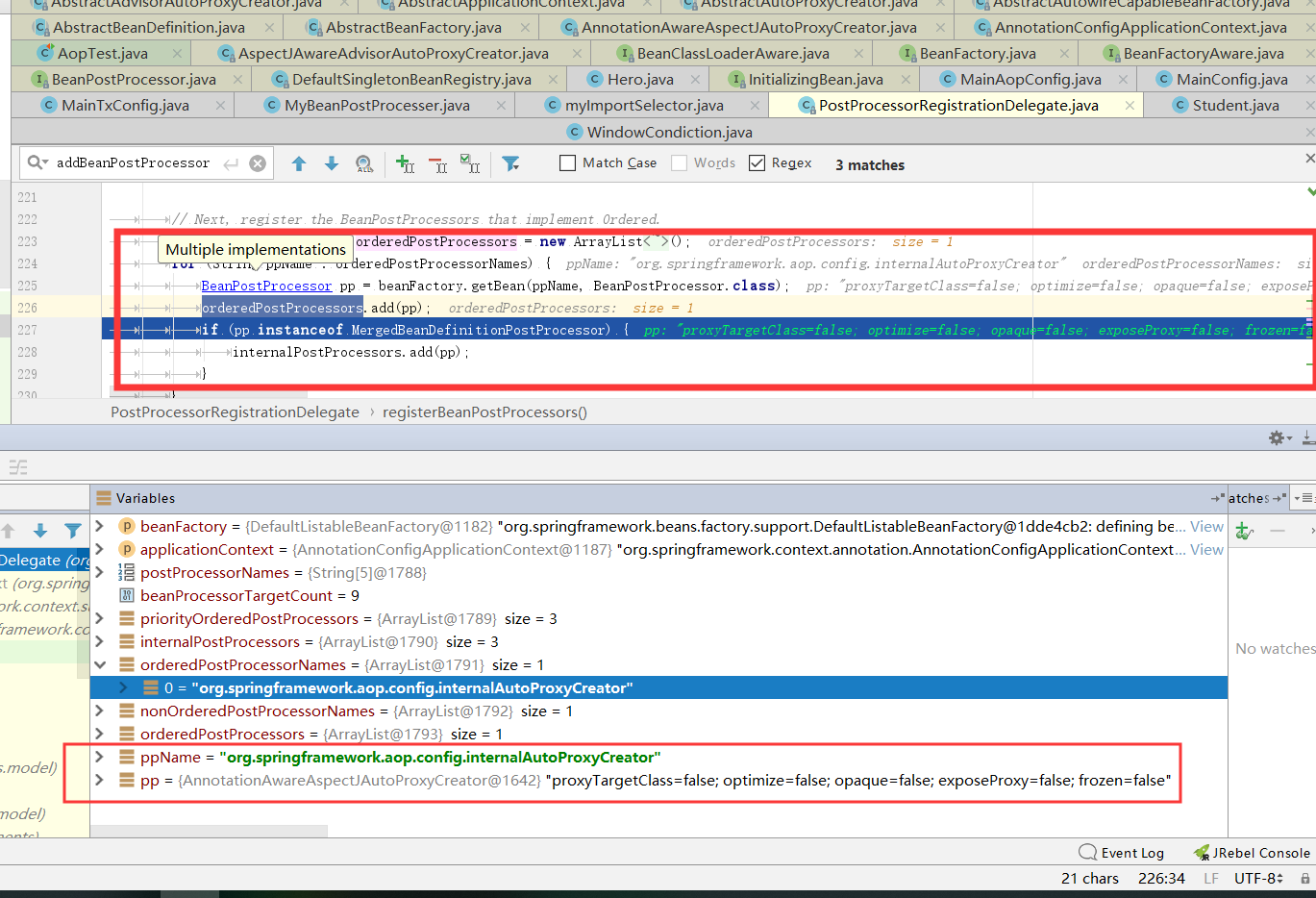
registerBeanPostProcessors方法源码:

public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors. List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors. sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners, // moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc). beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); }
registerBeanPostProcessors
它做了几件事,根据源码的注释我们可以知道:
- 获取在ioc容器中已经定义了的需要创建的所有BeanPostProcessor
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
- 添加别的BeanPostProcessor
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
- 优先注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
- 再来注册实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
- 最后注册没有实现接口的BeanPostProcessor
- 注册BeanPostProcessor,实际上就是创建BeanPostProcessor对象,保存在容器中。
//获取bean
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
它会调用AbstractBeanFactory的doGetBean方法,做了几件事:
 doGetBean
doGetBean创建bean实例
populate给bean赋值
initiallizeBean初始化bean
// Create bean instance. if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); }
这里面有一个createBean方法,调用的是AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory中的方法createBean,然后调用doCreateBean方法

protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null); Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null); mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition. synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { try { applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex); } mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean); } }); } // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); if (exposedObject != null) { exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } if (earlySingletonExposure) { Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); if (earlySingletonReference != null) { if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); } } } } // Register bean as disposable. try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; }
创建bean:
// Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); }
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);给bean赋值
// Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); if (exposedObject != null) { exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } }
初始化:initializeBean方法:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
在initializeBean方法中invokeAwareMethods方法用来处理Aware接口的方法回调
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization:里面调用了postProcessBeforeInitialization,就是后置处理器在bean初始化前的调用
@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (result == null) { return result; } } return result; }
invokeInitMethods方法来执行初始化方法
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization:里面调用了postProcessAfterInitialization就是后置处理器在bean初始化后的调用
最终创建完AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
创建完成后,根据优先等级,把它注册到beanFactory中
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
/**
* Register the given BeanPostProcessor beans.
*/
private static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) {
for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);
}
}
这是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的创建
》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》》1
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator具体作用:
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////0
创建完AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator后,registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);结束执行
执行refresh()中的finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
它的作用就是实例化剩下的单例,完成BeanFactory的初始化:
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
进入方法里:调用beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
preInstantiateSingletons源码:

@Override public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this); } // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions. // While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine. List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames); // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans... for (String beanName : beanNames) { RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); boolean isEagerInit; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) { isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() { @Override public Boolean run() { return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit(); } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit()); } if (isEagerInit) { getBean(beanName); } } else { getBean(beanName); } } } // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans... for (String beanName : beanNames) { Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) { final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); } } } }
方法里面有个for循环,触发所有非懒加载单实例bean的初始化,对所有的bean进行创建,调用getBean(beanname)
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
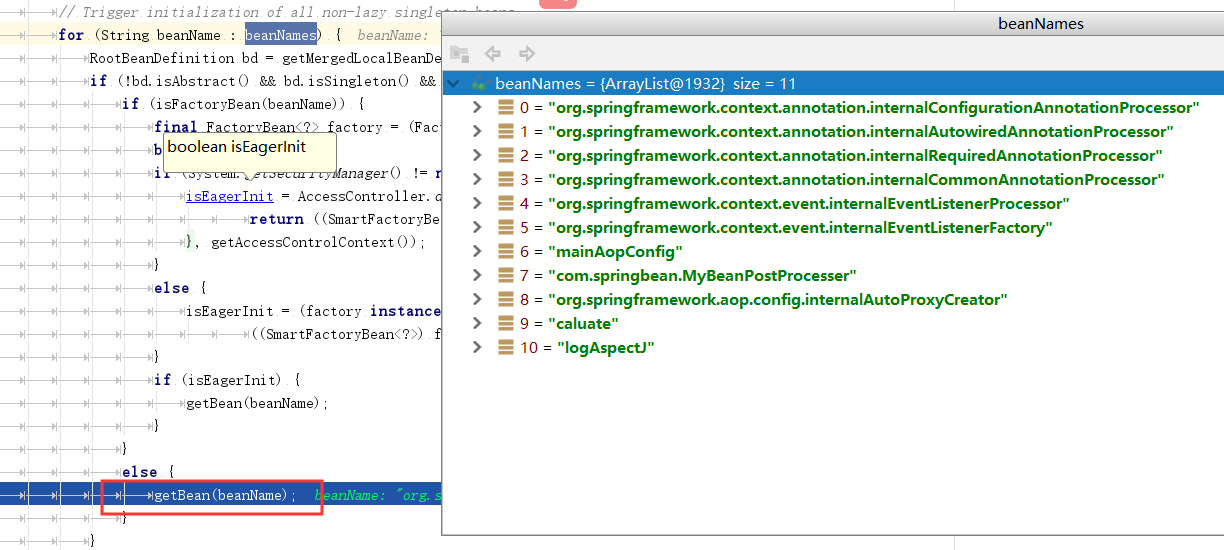
getBean()调用doGetBean(),调用getSingleton(),它会首先是从缓存中中获取单例bean:
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons. Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) { Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
singletonObjects是一个缓存map,线程安全的ConcurrentHashMap
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance */ private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(256);
如果找不到,才会创建bean,已经创建的bean就会丢进map中。
// Create bean instance. if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
createBean()创建bean,调用resolveBeforeInstantiation()// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance. Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
希望后置 处理器能返回一个代理对象,如果能返回就直接返回bean,如果不能就创建
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
doCreateBean(),这个方法上面已经用过,就是用来创建初始化bean的方法

protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null); Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null); mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition. synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { try { applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex); } mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean); } }); } // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); if (exposedObject != null) { exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } if (earlySingletonExposure) { Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); if (earlySingletonReference != null) { if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); } } } } // Register bean as disposable. try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; }
doCreateBean
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);给bean赋值初始化:
initializeBean方法:初始化
我们继续来看 Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse),它希望后置处理器能返回一个代理对象。
resolveBeforeInstantiation()方法里面的操作。
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { Object bean = null; if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) { // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point. if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd); if (targetType != null) { bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName); if (bean != null) { bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName); } } } mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null); } return bean; }
它里面执行了applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation和applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
先来判断是否是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的实例,InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor继承自BeanPostProcessor接口
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName); if (result != null) { return result; } } } return null; }
前面所创建向容器中注册的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的实现类
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor继承自BeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor的区别:
前者是在bean对象创建完成后初始化前后调用的
后者是在创建bean实例之前先尝试用后置处理器返回对象时调用的
所以AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator会在任何bean创建之前先尝试返回bean的实例
会在所有bean创建之前拦截bean,会调用postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法。

@Override public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName); if (beanName == null || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) { return null; } if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return null; } } // Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource. // Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean: // The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion. if (beanName != null) { TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName); if (targetSource != null) { this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName); Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource); Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } } return null; }
postProcessBeforeInitialization
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的作用:- 每一个bean创建之前,都会调用postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法;
- 先来判断是否是增强的bean,保存在advisedBeans中
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) { return null; }
advisedBeans是map集合
private final Map<Object, Boolean> advisedBeans = new ConcurrentHashMap<Object, Boolean>(256);
- 再来判断是否是实现了这些接口的Advice,Pointcut,Advisor,AopInfrastructureBean或者是否是切面
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return null; }
protected boolean isInfrastructureClass(Class<?> beanClass) { boolean retVal = Advice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Pointcut.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Advisor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass); if (retVal && logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Did not attempt to auto-proxy infrastructure class [" + beanClass.getName() + "]"); } return retVal; }
- 判断是否需要跳过,先找到所有的候选增强器,再判断是否是属于AspectJPointcutAdvisor的,是的话返回true,否则返回false;
@Override protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { // TODO: Consider optimization by caching the list of the aspect names List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) { if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor) { if (((AbstractAspectJAdvice) advisor.getAdvice()).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) { return true; } } } return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName); }
然后调用postProcessAfterInitialization()方法,wrapIfNecessary()判断是否需要包装
@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean != null) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
前面是判断,满足条件直接返回,否则创建代理,首先会获取到当前bean的所有增强器,也就是通知方法。
- 先获取所有的候选的增强器
- 再进行一些判断后,得到可在当前bean应用的增强器。
- 并给增强器排序。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } // Create proxy if we have advice. Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
例如我们获取到作用在caluate类中的候选增强器:
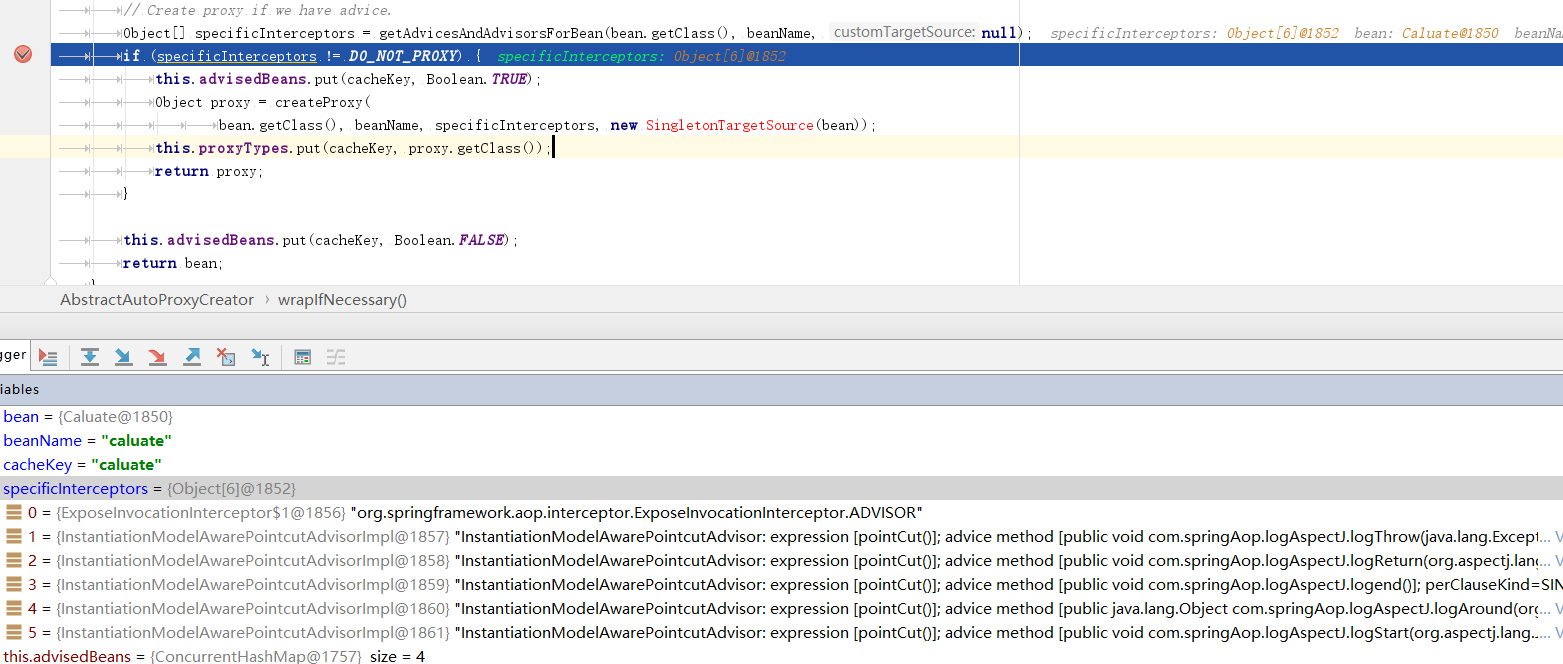
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean()方法会去调用findEligibleAdvisors()方法,最后返回可用的增强器
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
得到可用的增强器之后,this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE),放在map中缓存,如果当前bean需要增强,就创建当前bean的代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
- 获取到所有的增强器
- 保存到proxyFactory中
- 创建代理对象,spring自动决定
创建JdkDynamicAopProxy;jdk动态代理
创建ObjenesisCglibAopProxy;cglib代理
- 给容器返回当前组件使用cglib增强了的代理对象
- 容器中获取的就是这个组件的代理对象,执行目标方法的时候,代理对象就会执行通知方法的流程。
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
有代理工厂帮我们创建对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) { return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader); }
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() { if (!this.active) { activate(); } return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this); }
创建代理对象
@Override public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } }
这是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreatory具体的作用
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////1
接着来看通知方法如何执行的,拦截器的作用
***********************************************************************0
在测试中运行
容器中保存了组件的代理对象(cligb增强后的对象),这个对象里面保存了详细信息(增强器,代理象。。。)进入到CglibAopProxy的intercept()拦截器中,在目标方法执行之前该方法。

@Override public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; Class<?> targetClass = null; Object target = null; try { if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // Make invocation available if necessary. oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } // May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we // "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool... target = getTarget(); if (target != null) { targetClass = target.getClass(); } List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); Object retVal; // Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is, // no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target. if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly. // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know // it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot // swapping or fancy proxying. Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse); } else { // We need to create a method invocation... retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed(); } retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal); return retVal; } finally { if (target != null) { releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } }
intercept
根据proxyFactory获取到将要执行的目标方法的拦截器链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
如果没有当前方法的拦截器链,就去直接执行目标的方法。
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is, // no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target. if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly. // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know // it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot // swapping or fancy proxying. Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse); }
如果有当前方法的拦截器链,把需要执行的目标方法,目标对象,拦截器链对象等信息传入到CglibMethodInvocation对象中,并调用proceed()方法。
// We need to create a method invocation... retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
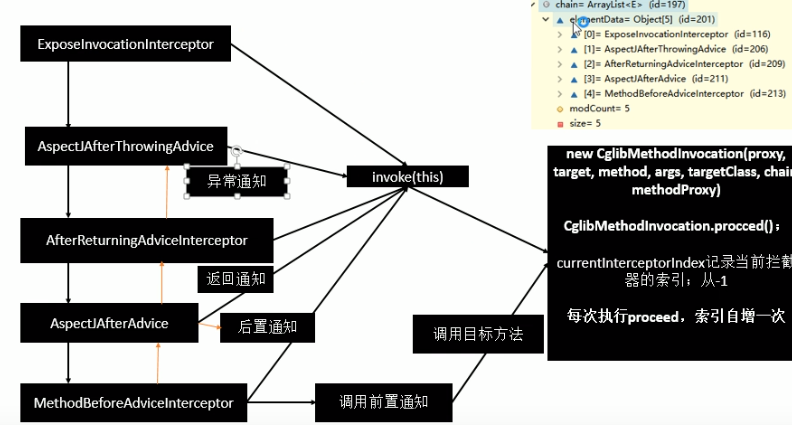
拦截器链的触发proceed():

@Override public Object proceed() throws Throwable { // We start with an index of -1 and increment early. if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { return invokeJoinpoint(); } Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) { // Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have // been evaluated and found to match. InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice; if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) { return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); } else { // Dynamic matching failed. // Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain. return proceed(); } } else { // It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have // been evaluated statically before this object was constructed. return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); } }
currentInterceptorIndex:当前拦截器的索引
1》如果没有拦截器执行目标方法,或者拦截器的索引和拦截器的数据-1大小一样执行目标方法
2》链式获取每一个拦截器,拦截器执行invoke方法,每一个拦截器等待下一个拦截器执行完成返回以后再执行,
拦截链的机制,保证通知方法与目标方法的执行顺序。
********************************************************************************1
AOP简结
1》@EnableAspectJAutoProxy开启Aop功能
2》@EnableAspectJAutoProxy会给容器中注册一个组件AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
3》AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是一个后置处理器
4》容器的创建流程:
1》registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);注册后置处理器,创建AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
2》finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);初始化剩下的单实例bean
3》组件创建完成之后,判断组件是否需要增强,
是:将切面的通知方法,包装成增强器(Advisor);给业务组件创建一个代理对象
5》执行目标方法:
1》代理对象执行目标方法
2》CglibAopProxy中执行intercept()方法,
1》得到目标方法的拦截器链(增强器包装成拦截器MethodInterceptor)
2》利用拦截器链的链式机制,依次进入每一个拦截器进行执行;
3》效果:
正常执行:前置通知———》目标方法———》后置通知———》返回结果
异常执行:前置通知———》目标方法———》后置通知———》抛出异常
