java实现多线程,有两种方法:
1》实现多线程,继承Thread,资源不能共享
2》实现多线程 实现Runnable接口,可以实现资源共享
*wait()方法 在哪个线程中调用 则当前线程处于等待状态【在main方法中调用A.wait(),则是main线程等待,而不是A线程等待】
* join()方法 作用类似与wait()方法 理解:如上处调用join()方法
* 【注意:在A线程中调用B.join()--------表示A一直等待,直到B运行完成后才继续运行A】
* 在A线程中调用B.join(1000)----表示A仅等待B线程1000ms时间,不管B线程中是否有sleep()或者wait()等情况,只要超时,则A继续运行,B你随意
* notify()方法 无论B.wait()在A线程中运行还是在B线程中运行【在哪个线程中运行,则哪个线程等待】,但是想让那个等待的线程被唤醒,必须用B.notify()唤醒,不管在何处唤醒【即不管在A线程中调用B.notify()或者在main线程中调B.notify()】。

1 package com.sxd.thread; 2 3 /** 4 * 测试 多线程 的wait() 5 * @author Administrator 6 * 7 */ 8 public class TestThread implements Runnable{ 9 10 static Thread thread1 = null; 11 static Thread thread2 = null; 12 static int count = 20; //用来标识一下 各个线程运行的顺序 13 14 public TestThread() { 15 16 } 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 19 System.out.println("main线程运行---->"); 20 TestThread testThread = new TestThread(); 21 thread1 = new Thread(testThread,"AA"); 22 thread2 = new Thread(testThread,"BB"); 23 thread1.start(); 24 thread2.start(); 25 System.out.println("休眠--->main线程休眠5s"); 26 Thread.sleep(5000);//main线程 睡5s 27 System.out.println("唤醒--->AA线程"); 28 synchronized (thread1) { 29 thread1.notify();//唤醒AA线程 因为AA线程让thread1调用的wait,所以需要thread1唤醒 30 } 31 32 //BB线程先走 main线程等待2000ms 33 synchronized (thread2) { 34 thread2.join(2000);//理解:此处在主线程中: thread2调用join()方法,则main线程暂停运行,直到thread2【调用它的线程对象】运行结束才继续运行main线程 35 } 36 System.out.println("等不及BB线程,main线程输出"); 37 } 38 39 /** 40 * wait()方法 在哪个线程中调用 则当前线程处于等待状态【在main方法中调用A.wait(),则是main线程等待,而不是A线程等待】 41 * join()方法 作用类似与wait()方法 理解:如上处调用join()方法 42 * 注意:在A线程中调用B.join()--------表示A一直等待,直到B运行完成后才继续运行A 43 * 在A线程中调用B.join(1000)----表示A仅等待B线程1000ms时间,不管B线程中是否有sleep()或者wait()等情况,只要超时,则A继续运行,B你随意 44 * notify()方法 无论B.wait()在A线程中运行还是在B线程中运行【在哪个线程中运行,则哪个线程等待】,但是想让那个等待的线程被唤醒,必须用B.notify()唤醒,不管在何处唤醒【即不管在A线程中调用B.notify()或者在main线程中调用B.notify()】。 45 */ 46 @Override 47 public void run() { 48 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 49 synchronized (TestThread.class) { 50 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程运行"+count--); 51 } 52 53 if(i == 2){ 54 if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("AA")){//若是AA线程 则让AA进行wait() 55 synchronized (thread1) {//wait() join() notify() 这类方法 都需要synchronized 56 try { 57 System.out.println("等待--->AA开始等待"); 58 thread1.wait(); 59 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 60 e.printStackTrace(); 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 if(i == 3){ 66 if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("BB")){//若是BB线程 则让BB睡眠5000ms 67 try { 68 System.out.println("休眠--->BB线程进入休眠"); 69 Thread.sleep(5000); 70 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 71 e.printStackTrace(); 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 } 77 }
代码流程:
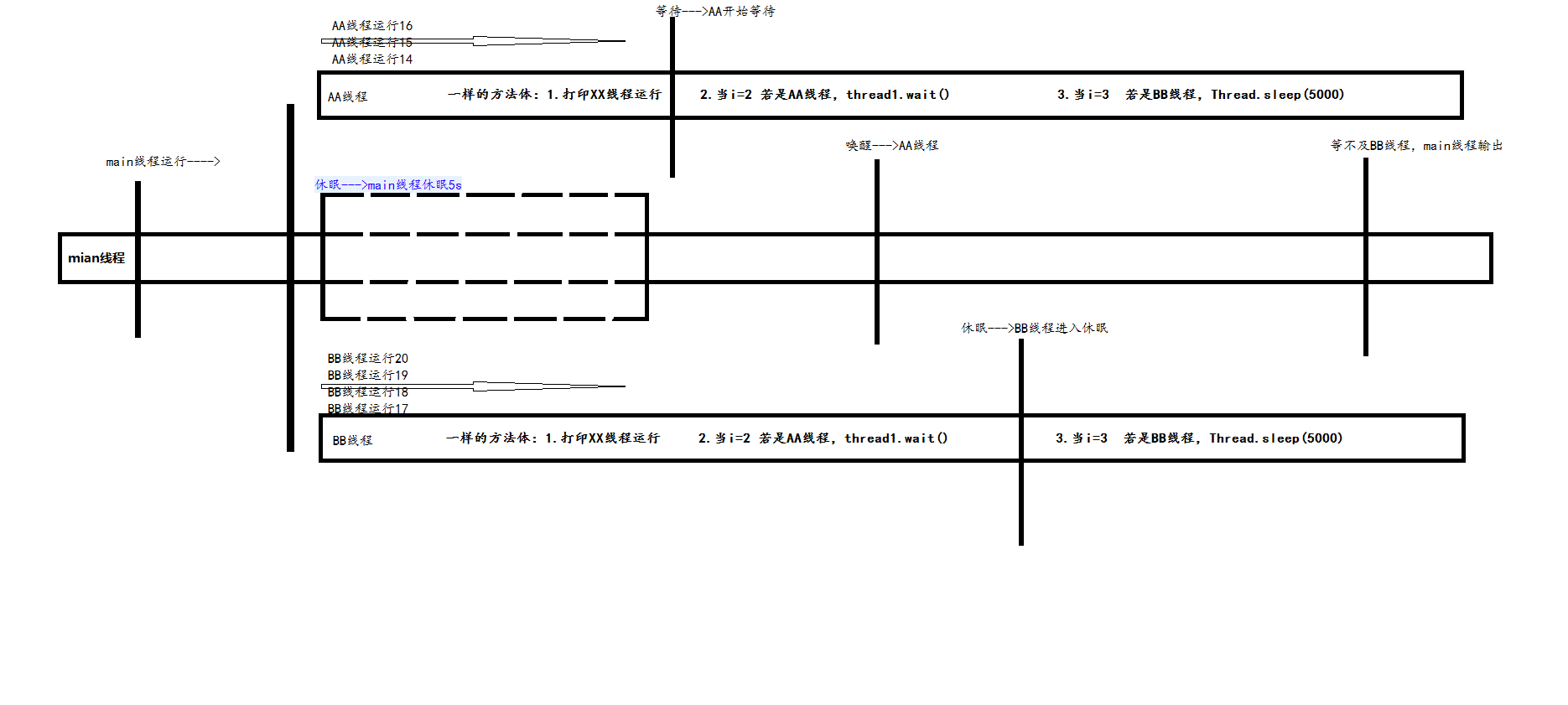
运行结果:

