串
串及其匹配
串或字符串属于线性结构,结构简单,规模庞大,元素重复率高
- 相关术语:

- 接口:
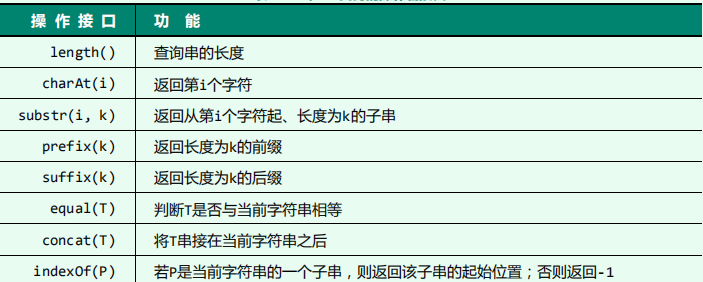
- 测评标准
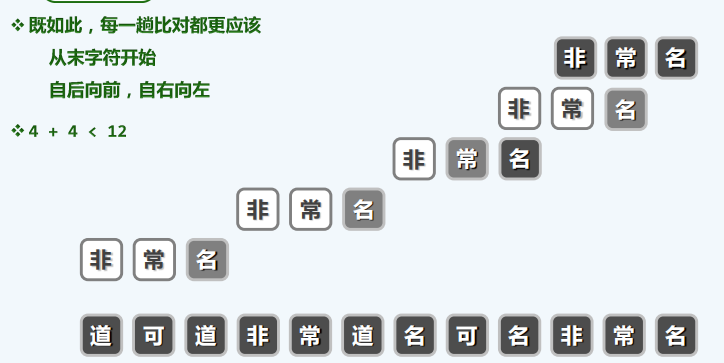
有效涵盖成功匹配情况的一种简便策略是,随机选取文本串T,并从T中随机取出长度为m的子串作为模式串P。
蛮力算法
原理


实现
package com.atguigu.string;
/**
* @anthor shkstart
* @create 2020-08-16 8:57
*/
public class brute extends Str{
public static int match1(char[] P, char[] T){
int n = P.length;
int m = T.length;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (j < m && i < n){
if (T[i] == P[j]){
i++;
j++;
} else {
i -= j - 1;
j = 0;
}
}
return i - j;
}
public static int match2(char[] P, char[] T){
int n = P.length;
int m = T.length;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (;i < n - m;i++){
for (;j < m;j++){
if (T[i+j] != P[j]) break;
}
if ( j >= m) break;
}
return i;
}
}
效率

KMP算法
分析上面的方法:
-
发现问题在于这里存在大量的局部匹配:每一轮的m次比对中,仅最后一次可能失配。而一旦发现失配,文本串、模式串的字符指针都要回退,并从头开始下一轮尝试。没有很好的利用已经掌握的信息。
-
利用以往的成功比对所提供的信息(记忆),不仅可避免文本串字符指针的回退,而且可使模式串尽可能大跨度地右移

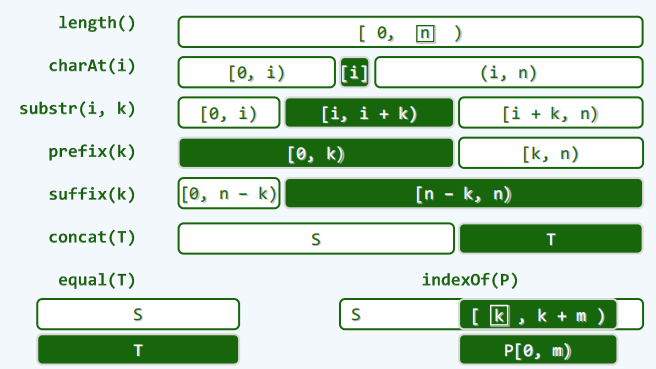
next表


- 满足条件:P[0, t) = T[i - t, i) = P[j - t, j)
- 原理

- 实现
public int[] buildNext1(char[] P){
int m = P.length;
int j = 0;
int[] N = new int[m];
int t = N[0] = -1;
while (j < m-1){
if (0 > t || P[j] == P[t]){
j++;
t++;
N[j] = t;
} else {
t = N[t];
}
}
return N;
}
public int[] buildNext2(char[] P){
int m = P.length;
int j = 0;
int[] N = new int[m];
int t = N[0] = -1;
while (j < m-1){
if (0 > t || P[j] == P[t]){
j++;
t++;
N[j] = (P[j] != P[t] ? t:N[t]);
} else {
t = N[t];
}
}
return N;
}
实现
package com.atguigu.string;
/**
* @anthor shkstart
* @create 2020-08-16 8:57
*/
public class Kmp extends Str{
public int match(char[] P, char[] T){
int[] next = buildNext1(P);
int n = P.length;
int m = T.length;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (j < m && i < n){
if (T[i] == P[j]){
i++;
j++;
} else {
j = next[j];
}
}
return i - j;
}
public int[] buildNext1(char[] P){
int m = P.length;
int j = 0;
int[] N = new int[m];
int t = N[0] = -1;
while (j < m-1){
if (0 > t || P[j] == P[t]){
j++;
t++;
N[j] = t;
} else {
t = N[t];
}
}
return N;
}
public int[] buildNext2(char[] P){
int m = P.length;
int j = 0;
int[] N = new int[m];
int t = N[0] = -1;
while (j < m-1){
if (0 > t || P[j] == P[t]){
j++;
t++;
N[j] = (P[j] != P[t] ? t:N[t]);
} else {
t = N[t];
}
}
return N;
}
}
实例

BM算法
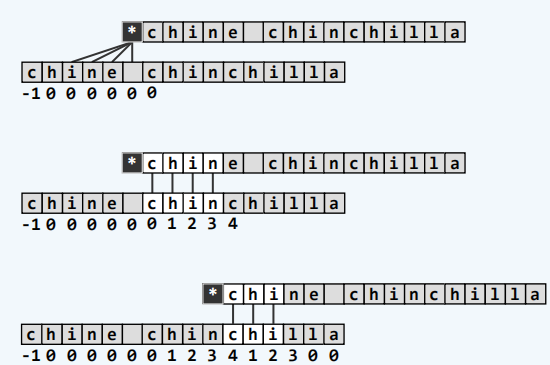
原理
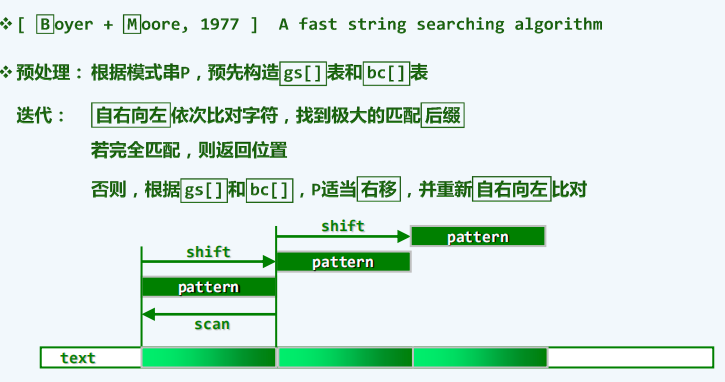
KMP算法的思路可概括为:当前比对一旦失配,即利用此前的比对(无论成功或失败)所提 供的信息,尽可能长距离地移动模式串。事先根据模式串预测出所可能出现的失配情况,并将这些信息 “浓缩”为一张next表。而BM算法一旦局部失配,这里不再是机械地令i += 1并在下一字符处重新对齐,而是采用了两种启发式策略确定最大的安全移动距离

坏字符策略
- 快速排序不能对齐的位置

移动情况:从右至左,一旦不匹配.从右开始找与x匹配的数,然后移动;或者太靠右,只移动一位 - 构建bc表
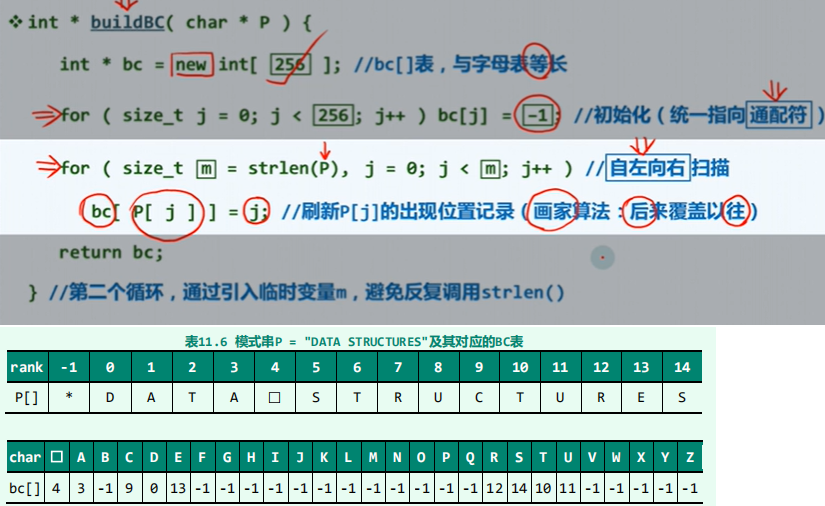
public int[] buildBc(char[] P){
int[] bc = new int[256];
for (int j = 0;j < 256;j++) bc[j] = -1;
for (int m = P.length,j = 0;j < m;j++){
bc[P[j]] = j;
}
return bc;
}
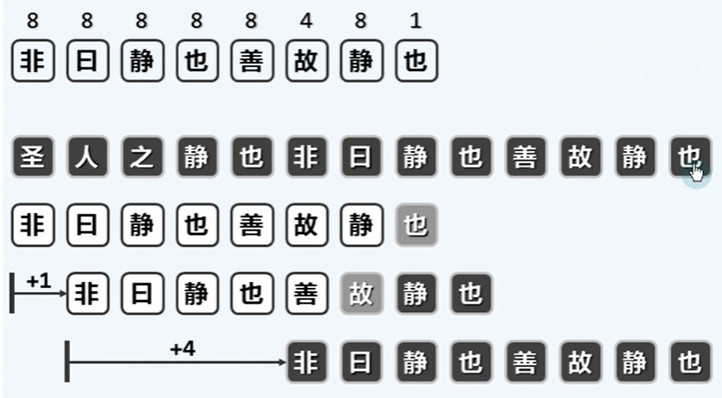
好后缀策略
- 成功的对比
坏字符策略仅利用了此前(最后一次)失败比对所提供的“教训”。而实际上在此之前,还做过一系列成功的比对,而这些“经验”却被忽略了

- 分析

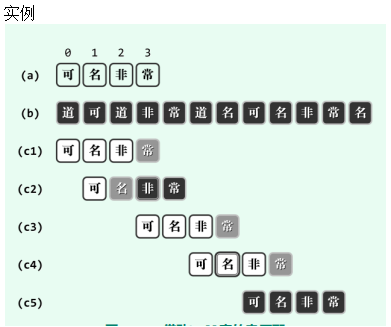
对齐的情况:
已经发现w与U一直都对齐,直到x与y不同
需要从在p中从右向左找到一个子串能够满足v(k)=u且k处与J处不相等
如果不存在,则从p的所有前缀中找与某一后缀最匹配长度的
- gs、ss表的构建
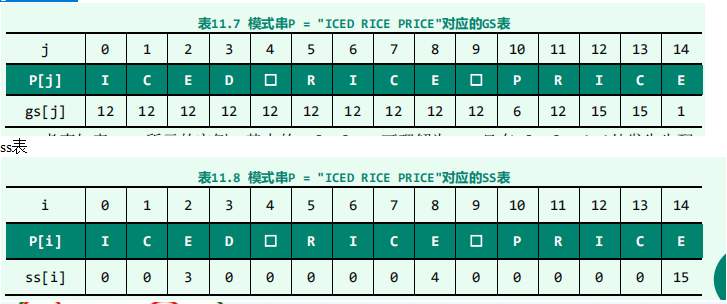
gs表每个位置对应,应该移动多少位;其中的gs[10] = 6可理解为:一旦在P[10] = 'P'处发生失配,则应将模式串P右移6个字符,即用P[10 - 6] = P[4] = '□'对准文本串T的失配字符,然后启动下一轮比对
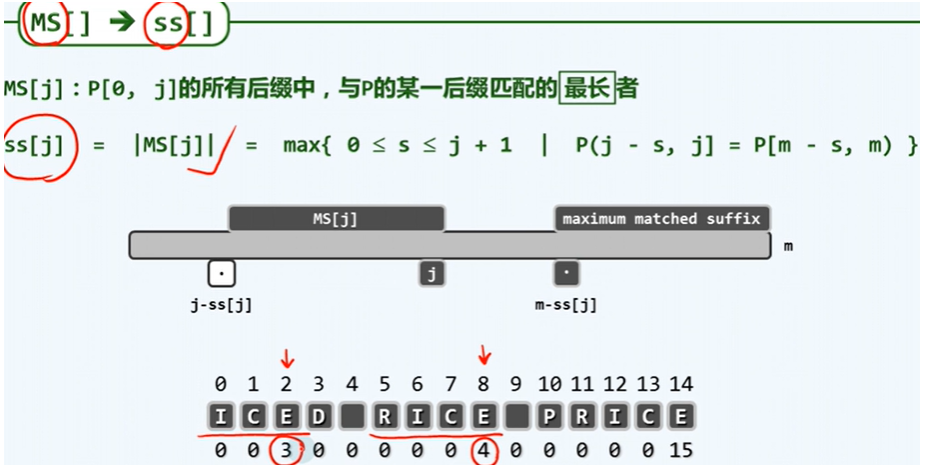
ss表对于任一整数j Î [0, m),在P[0, j]的所后缀中,考查那些与P的某一后缀匹配者。若将其中的最长者记作MS[j],则ss[j]就是该串的长度|MS[j]|。


public int[] buildGS(char[] P){
int[] ss = buildSS(P);
int m = P.length;
int[] gs = new int[m];
for (int j = 0; j < m;j++) gs[j] = m;
for (int i = 0,j = m-1;j > 0;j--){
if (j + 1 == ss[j]){
while (i < m - j - 1){
gs[i++] = m - j -1;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0;j < m-1;j++){
gs[m - ss[j] - 1] = m-j - 1;
}
return gs;
}
public int[] buildSS(char[] P){
int m = P.length;
int[] ss = new int[m];
ss[m-1] = m;
for (int lo = m-1,hi = m - 1,j = lo - 1;j >= 0;j--){
if ((lo < j) && (ss[m - hi + j -1] <= j - lo)){
ss[j] = ss[m - hi +j -1];
} else {
hi = j;
lo = Math.min(lo,hi);
while ((0 <= lo) && (P[lo] == P[m - hi + lo -1])){
lo--;
}
ss[j] = hi -lo;
}
}
return ss;
}
java实现
package com.atguigu.string;
/**
* @anthor shkstart
* @create 2020-08-16 8:57
*/
public class Bm extends Str{
public int match(char[] P, char[] T){
int[] bc = buildBc(P);
int[] gs = buildGS(P);
int i = 0;
while (T.length >= i + P.length){
int j = P.length - 1;
while (P[j] == T[i+j]){
if (0 > --j) break;
}
if (0 > j){
break;
} else {
i += Math.max(gs[j],j - bc[T[i+j]]);
}
}
return i;
}
public int[] buildBc(char[] P){
int[] bc = new int[256];
for (int j = 0;j < 256;j++) bc[j] = -1;
for (int m = P.length,j = 0;j < m;j++){
bc[P[j]] = j;
}
return bc;
}
public int[] buildGS(char[] P){
int[] ss = buildSS(P);
int m = P.length;
int[] gs = new int[m];
for (int j = 0; j < m;j++) gs[j] = m;
for (int i = 0,j = m-1;j > 0;j--){
if (j + 1 == ss[j]){
while (i < m - j - 1){
gs[i++] = m - j -1;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0;j < m-1;j++){
gs[m - ss[j] - 1] = m-j - 1;
}
return gs;
}
public int[] buildSS(char[] P){
int m = P.length;
int[] ss = new int[m];
ss[m-1] = m;
for (int lo = m-1,hi = m - 1,j = lo - 1;j >= 0;j--){
if ((lo < j) && (ss[m - hi + j -1] <= j - lo)){
ss[j] = ss[m - hi +j -1];
} else {
hi = j;
lo = Math.min(lo,hi);
while ((0 <= lo) && (P[lo] == P[m - hi + lo -1])){
lo--;
}
ss[j] = hi -lo;
}
}
return ss;
}
}
效率
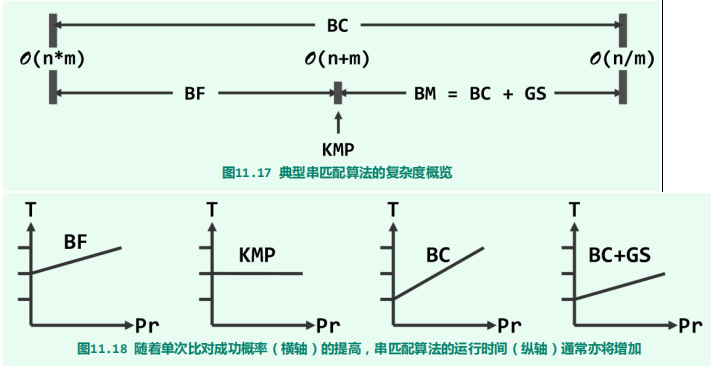
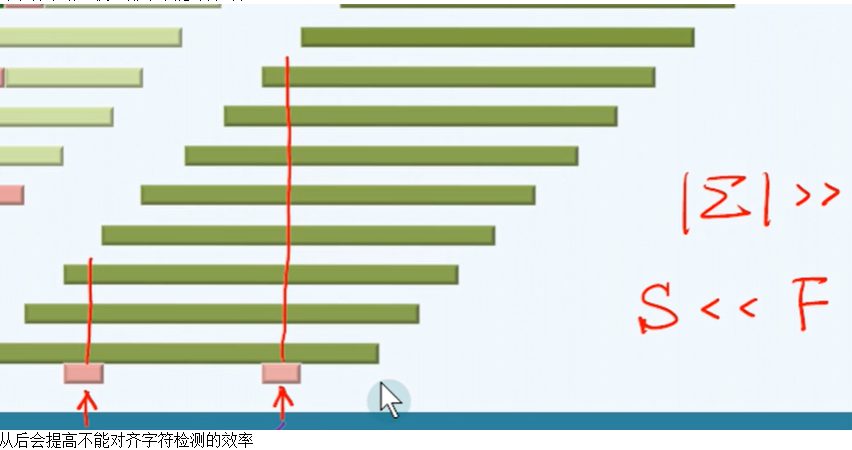
单次比对成功的概率,是决定串匹配算法时间效率的一项关键因素。对于同一算法,计算时间与Pr具有单调正相关关系
Karp-Rabin算法
凡事皆树:将任一有限长度的整数向量视作自然数,进而在字符串与自然数之间建立联系

原理
判断模式串P是否与文本串T匹配”的问题,可以转化为“判断T中是否 某个子串与模式串P拥相同的指纹

- 散列压缩

- 散列冲突
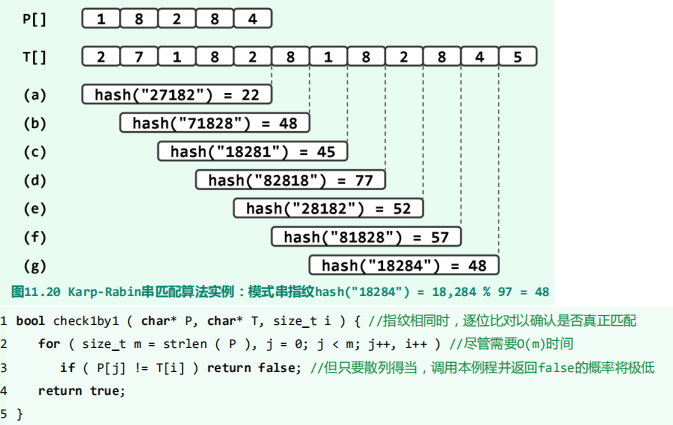
- 指纹快速更新

实现
package com.atguigu.string;
/**
* @anthor shkstart
* @create 2020-08-16 8:57
*/
public class Fingerprint extends Str{
public int match(char[] P, char[] T){
int m = P.length;
int n = T.length;
int Dm = peapreDm(m),hashP = 0,hashT = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < m;i++){
hashP = (hashP * R + DIGIT(P,i)) % M;
hashT = (hashT * R + DIGIT(T,i)) % M;
}
for (int k = 0; ;){
if (hashT == hashP){
if (check1by1(P,T,k)) return k;
}
if (++k > n -m) return k; else updateHash(hashT,T,m,k,Dm);
}
}
public static int M = 97;
public static int R = 10;
public int DIGIT(char[] S,int i){
return S[i] - '0';
}
public Boolean check1by1(char[] P,char[] T,int i){
for (int m = P.length,j = 0;j < m;j++,i++){
if (P[j] != T[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
public int peapreDm(int m){
int Dm = 1;
for (int i = 1;i < m;i++){
Dm = (R * Dm) % M;
}
return Dm;
}
public void updateHash(int hashT,char[] T,int m,int k,int Dm){
hashT = (hashT - DIGIT(T,k - 1) * Dm) % M;
hashT = (hashT * R + DIGIT(T,k + m - 1)) % M;
if (0 > hashT) hashT += M;
}
}