You are given two integers xx and yy. You can perform two types of operations:
- Pay aa dollars and increase or decrease any of these integers by 11. For example, if x=0x=0 and y=7y=7 there are four possible outcomes after this operation:
- x=0x=0, y=6y=6;
- x=0x=0, y=8y=8;
- x=−1x=−1, y=7y=7;
- x=1x=1, y=7y=7.
- Pay bb dollars and increase or decrease both integers by 11. For example, if x=0x=0 and y=7y=7 there are two possible outcomes after this operation:
- x=−1x=−1, y=6y=6;
- x=1x=1, y=8y=8.
Your goal is to make both given integers equal zero simultaneously, i.e. x=y=0x=y=0. There are no other requirements. In particular, it is possible to move from x=1x=1, y=0y=0 to x=y=0x=y=0.
Calculate the minimum amount of dollars you have to spend on it.
The first line contains one integer tt (1≤t≤1001≤t≤100) — the number of testcases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers xx and yy (0≤x,y≤1090≤x,y≤109).
The second line of each test case contains two integers aa and bb (1≤a,b≤1091≤a,b≤109).
For each test case print one integer — the minimum amount of dollars you have to spend.
判断一下就行,两种情况:一个是先把较大的数调成较小的数,然后在一块减去,或者各自减各自的,比较一下大小。

#include<iostream> typedef long long ll; using namespace std; int main() { int t; cin>>t; while(t--) { ll x,y; ll a,b; cin>>x>>y; cin>>a>>b; if(x==0&&y==0) { cout<<"0"<<endl; } else { ll sum1=0; ll sum2=0; if(x>=y){ ll s=x-y; sum1=s*a; sum1+=(y*b); sum2=x*a+y*a; cout<<min(sum2,sum1)<<endl; } if(x<y) { ll s=y-x; sum1=s*a; sum1+=(x*b); sum2=a*x+a*y; cout<<min(sum1,sum2)<<endl; } } } }
Let's say string ss has period kk if si=si+ksi=si+k for all ii from 11 to |s|−k|s|−k (|s||s| means length of string ss) and kk is the minimum positive integer with this property.
Some examples of a period: for ss="0101" the period is k=2k=2, for ss="0000" the period is k=1k=1, for ss="010" the period is k=2k=2, for ss="0011" the period is k=4k=4.
You are given string tt consisting only of 0's and 1's and you need to find such string ss that:
- String ss consists only of 0's and 1's;
- The length of ss doesn't exceed 2⋅|t|2⋅|t|;
- String tt is a subsequence of string ss;
- String ss has smallest possible period among all strings that meet conditions 1—3.
Let us recall that tt is a subsequence of ss if tt can be derived from ss by deleting zero or more elements (any) without changing the order of the remaining elements. For example, tt="011" is a subsequence of ss="10101".
The first line contains single integer TT (1≤T≤1001≤T≤100) — the number of test cases.
Next TT lines contain test cases — one per line. Each line contains string tt (1≤|t|≤1001≤|t|≤100) consisting only of 0's and 1's.
Print one string for each test case — string ss you needed to find. If there are multiple solutions print any one of them.
判断t中是否同时有0、1.
如果单一,最小周期为1:直接输出
如果同时有0,1,最小周期为2:输出01间隔串还要注意t是s的子串,不是s是t的子串(就因为这个在哪傻逼了半天。。。。)

#include<iostream> typedef long long ll; #include<map> using namespace std; int main() { int t; cin>>t; while(t--) { map<char,int>q; string s; cin>>s; int l=s.size(); int ans1=0; int ans2=0; for(int i=0;i<l;i++) { if(s[i]=='1') ans1++; else ans2++; } if(ans1==0||ans2==0) cout<<s; else { for(int i=0;i<l;i++) cout<<"01"; } cout<<endl; } }
You are given two integers aa and bb, and qq queries. The ii-th query consists of two numbers lili and riri, and the answer to it is the number of integers xx such that li≤x≤rili≤x≤ri, and ((xmoda)modb)≠((xmodb)moda)((xmoda)modb)≠((xmodb)moda). Calculate the answer for each query.
Recall that ymodzymodz is the remainder of the division of yy by zz. For example, 5mod3=25mod3=2, 7mod8=77mod8=7, 9mod4=19mod4=1, 9mod9=09mod9=0.
The first line contains one integer tt (1≤t≤1001≤t≤100) — the number of test cases. Then the test cases follow.
The first line of each test case contains three integers aa, bb and qq (1≤a,b≤2001≤a,b≤200; 1≤q≤5001≤q≤500).
Then qq lines follow, each containing two integers lili and riri (1≤li≤ri≤10181≤li≤ri≤1018) for the corresponding query.
For each test case, print qq integers — the answers to the queries of this test case in the order they appear.计算[0,ab)[0,ab)区间内满足数量
思路 :打表找规律,具有周期性a*b。
计算[1,ab]区间内满足数量,先处理好一个区间的,然后,后面的进项构造就行了。
前缀和处理好,然后( r/n - (l-1)/n )*num[n] + num[r%n] - num[(l-1)%n]。
解释一下:( r/n - (l-1)/n )*num[n] + num[r%n] - num[(l-1)%n].
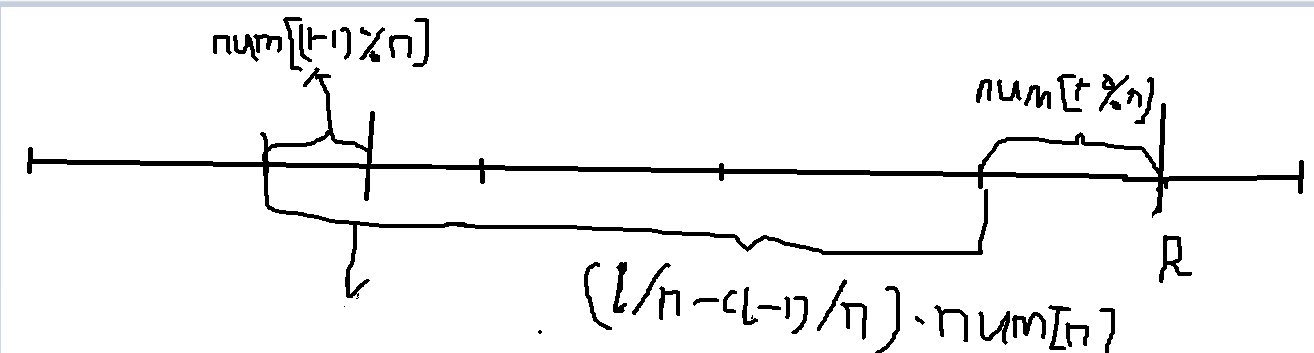
这样应该很明了了,注意处理边界(l-1);

#include<bits/stdc++.h> typedef long long ll; using namespace std; const long long Max=1e6+7; int main() { int t; cin>>t; while(t--) { ll a,b,q; ll num[Max]; cin>>a>>b>>q; ll n=a*b; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { num[i]=num[i-1]; if(i%a%b!=i%b%a) num[i]++; } ll l,r; while(q--) { cin>>l>>r; cout<<( r/n - (l-1)/n )*num[n] + num[r%n] - num[(l-1)%n]<<endl; } } }
