前言
出去面试的时候,对java的集合框架考察的知识点还是蛮多的。除了基础的集合常见API使用,对集合底层的实现原理以及数据结构等也有很多考察方面。而自己对这方面知之甚少,特地抽空进行研究和学习一下。
为什么要有集合
提到集合就不得不提一下数组,好多集合底层都是依赖于数组的实现。数组一旦初始化后,长度就确定了,存储数据对象不能达到动态扩展,其次数组存储元素不便于对数组进行添加、修改、删除操作,而且数组可以存储重复元素。这个时候集合对作用显现出来了。集合分为Collection和Map两种体系。下面先介绍Collection的集合类的继承树如下图所示:
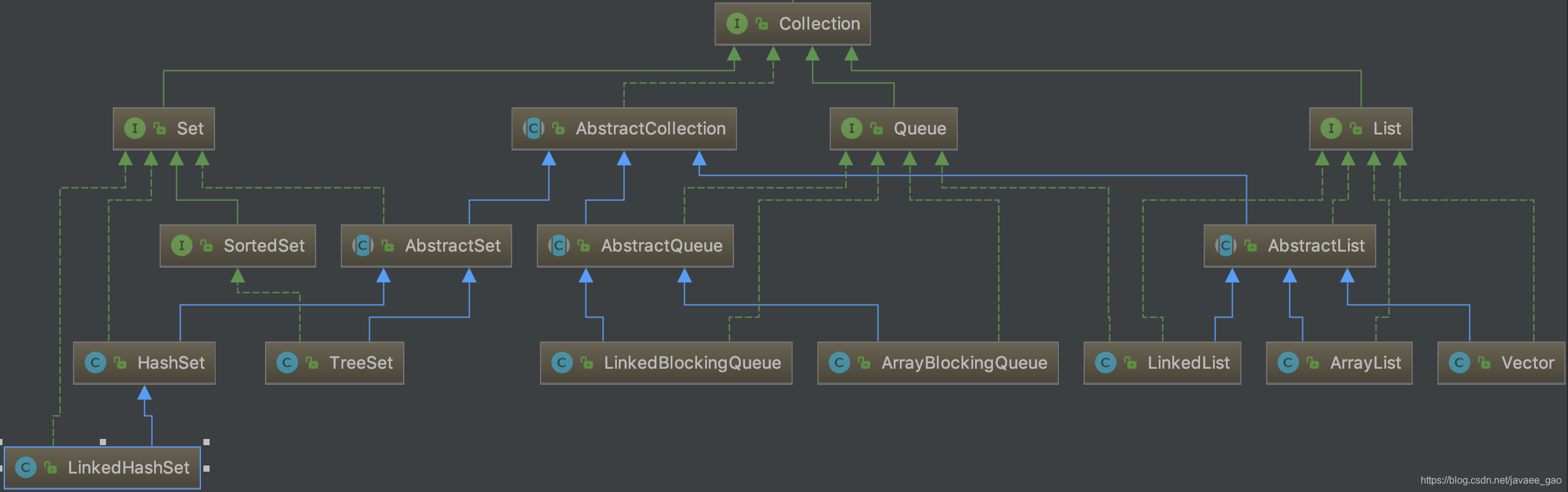
Collection接口是 (java.util.Collection)是Java集合类的顶级接口之一,整个集合框架就围绕一组标准接口而设计,本文研究的集合基于JDK8的实现,下面将会进行多个集合类方法使用和主要方法源码分析,以作为后续出去面试的参考资料。
Collection方法接口介绍
Collection 接口有 3 种子类型集合: List、Set 和 Queue,再下面是一些抽象类,最后是具体实现类,常用的有 ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet、LinkedHashSet、ArrayBlockingQueue等,下面是Collection的所有方法
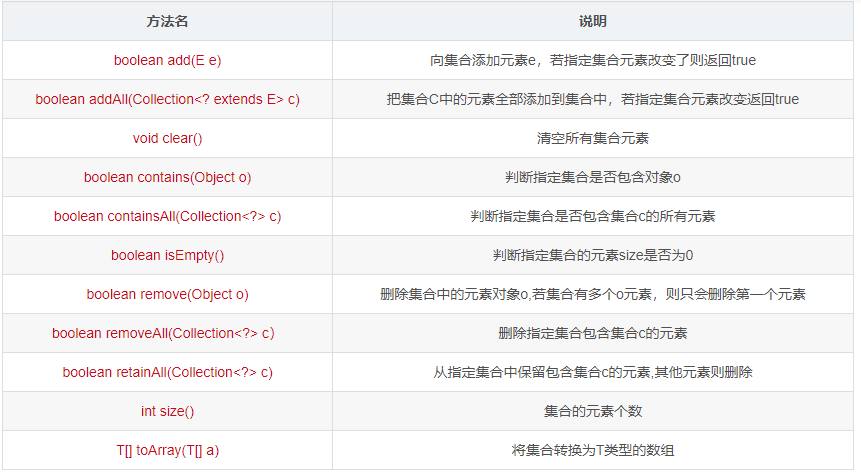
- 下面是主要方法的演示:
@Test
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public void testCollection() {
// 创建Collection接口的实现
Collection collection = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加元素
collection.add("嘻嘻");
String src = "????";
collection.add(src);
System.out.println(collection);
// 创建Collection的实现
Collection<String> coll = new HashSet<>();
coll.add("?");
coll.add("?");
coll.add("?");
System.out.println(coll);
// 添加一个集合数据
collection.addAll(coll);
// 输出集合的长度
System.out.println(collection);
// 判断是否包含
System.out.println(collection.contains("?"));
// 移除元素
collection.remove("?");
// 添加对象
collection.add(new Person("张三", 23, 5000d));
// 当认为两个对象属性一致,相等时候,需重写hashCode 和 equals方法
System.out.println(collection.contains(new Person("张三", 23, 5000d)));
System.out.println("-------");
collection.add(null);
Collection<String> collection1 = new ArrayList<>();
collection1.add("嘻嘻");
collection1.add("?");
// 求两个集合的交集(只保留collection1存在的元素)
collection.retainAll(collection1);
System.out.println(collection);
// 清空元素
collection.clear();
System.out.println(collection);
}
java8新特性操作集合
- 使用lambda表达式遍历集合
java8为Collection的父接口(Iterable)提供了一个默认的Foreach方法,我们可以使用它进行集合遍历,若对lambda不太了解,不妨访问一下这篇文章☞
https://blog.csdn.net/javaee_gao/article/details/90176372
@Test
public void testForeach() {
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add("i");
collection.add("love");
collection.add("china");
// foreach遍历
collection.forEach(e-> System.out.println(e));
// 可以使用方法引用简写
collection.forEach(System.out::println);
// 或者迭代器的forEachRemaining方法
collection.iterator().forEachRemaining(System.out::println);
}
- 使用java8的predicate操作集合
@Test
public void testPredicate() {
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加0-49
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
collection.add(i);
}
// 移除10-49的数字
collection.removeIf(e -> (e > 9 && e < 50));
System.out.println(collection);// 输出[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
}
- 基于流操作集合
java8之后引入了Stream相关流操作java集合,通过流大大简化了对集合操作,关于这些流式操作,可以查看这篇文章☞ Stream入门学习,下面是基于流的一些简单演示:
@Test
public void testIntStream() {
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<>();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
collection.add(random.nextInt(100));
}
System.out.println(collection);
// collection存储的数值是包装类型,可以将其转换为IntStream
IntStream intStream = collection.stream().mapToInt(e -> e);
// intStream.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println(collection.stream().mapToInt(e -> e).sum());
// 输出最大值
collection.stream().mapToInt(e -> e).max().ifPresent(System.out::println);
// 输出最小值
collection.stream().mapToInt(e -> e).min().ifPresent(System.out::println);
// 统计大于50的数
System.out.println(collection.stream().filter(e -> e > 50).count());
// 原集合每一个值加1
collection.stream().mapToInt(e-> e+1).forEach(System.out::println);
// 排序
collection.stream().mapToInt(e-> e).sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
// 原数值每一个元素扩大2倍
int[] ints = collection.stream().mapToInt(e -> e << 1).toArray();
// 输出原数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
// 将数组转流
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(ints);
// 输出流平均数
System.out.println(stream.average().getAsDouble());
}