一、实验目的
- 掌握类的设计、定义、实现和测试
- 深度理解面向对象编程思维与结构化编程思维的不同
二、实验准备
实验前,请围绕以下内容复习/学习指定内容
- C++程序以项目文件方式组织的多文件结构
学习教材「5.6.1 节 C++程序的一般组织结构」 - 编译预处理指令
学习教材「5.6.4 节 编译预处理指令」 - 类和对象的定义和使用
复习第 4 章相关内容
三、实验内容
-
练习将 C++ 程序以项目文件组织的多文件结构方式编写
将实验 3 中的 4-20 以多文件结构方式重写 -
基于已有信息,补足并扩充程序,体会面向对象编程与结构化编程思维的不同。 在 graph 文件夹里提供有三个文件
基于已有信息,补足并扩充程序,体会面向对象编程与结构化编程思维的不同。
在 graph 文件夹里提供有三个文件
| 文件 | 文件内容说明 |
|---|---|
| graph.h | 类 Graph 的声明 |
| graph.cpp | 类 Graph 的实现 |
| main.cpp | 类 Graph 的测试:定义 Graph 类的对象,调用 public 接口绘制图形 |
要求如下:
-
新建一个项目,添加以上三个文件到项目中。
-
补足 graph.cpp 中类的成员函数 draw()的实现,使得在 main()中对类的测试能够实现以下显示效果:
| 代码 | 效果 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
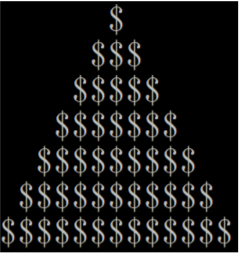 |
- 扩展类 Graph 的功能(选做)
- 支持重新设置显示的字符、尺寸,每次重新设置后,自动重绘图形;
- 支持图形的前景色、背景色设置和调整;
- 支持通过方向键控制图形水平移动或垂直移动,等等。
- 基于需求描述设计、定义并实现类 Fraction,并编写代码完成测试。
具体要求描述如下:
设计一个类 Fraction 描述分数(两个整数的比值)

类 Fraction 的数据成员包括两个 int 型变量 top 和 bottom,分别代表分子和分母。

经过分析后,通过设计和实现接口(即成员函数)实现如下要求:
-
类 Fraction 的基本功能列表
- 定义 Fraction 类对象时,支持如下形式:

提示:通过编写构造函数实现,并且,基于不同情形,编写重载构造函数。 - Faction 类对象能够进行如下操作:
- 加、减、乘、除运算
- 对两个分数值进行比较运算,返回其大小关系
- 分数的输入、输出
- 通过定义成员函数来实现。设计每一个成员函数时,从以下几个方面考虑:
- 成员函数的功能;
- 是否需要形参和返回值,如果需要,需要几个参数,参数的类型是什么,返回值的类型是什么
- 定义 Fraction 类对象时,支持如下形式:
-
类 Fraction 的扩展功能(选做)
- 对分数进行规范化处理,确保分数在形式上,只有分子为负数,并且,分数值是约简形式。
即:
2/-3 经过规范化处理后,转换为-2/3
15/21 经过规范化处理后,转换为 5/7
-2/-6 经过规范化处理后,转换为 1/3 - 实现分数到十进制之间的转换
例如:3/4 会转换为 0.75 输出
- 对分数进行规范化处理,确保分数在形式上,只有分子为负数,并且,分数值是约简形式。
-
设计并实现好 Fracton 类后,在 main()中测试时,要测试到各种情形,以确保你所设计和实现的类的各项功能都能正常运行。
-
以项目文件组织的多文件结构方式编写(fraction.h, fraction.cpp, main.cpp)
四、实验结论
0. 实验内容 1
- 如何在 Dev-Cpp 中创建多文件结构工程
- 文件-新建-项目
- 将 Project.h, Project.cpp, Main.cpp 添加到项目
- GIF演示

- C++ Code: 见上文
- Java Code:
Complex.java
package ex1;
public class Complex {
private double real;
private double imaginary;
public Complex(double r0,double i0){
real = r0;
imaginary = i0;
}
public Complex(double r0){
real = r0;
imaginary = 0;
}
public Complex(Complex c0){
real = c0.real;
imaginary = c0.imaginary;
}
public void add(Complex c0) {
real += c0.real;
imaginary += c0.imaginary;
}
public void show() {
if (imaginary > 0) System.out.println(real + "+" + imaginary + "i");
else if(imaginary < 0) System.out.println(real + "-" + imaginary + "i");
else System.out.println(real);
}
}
- console:
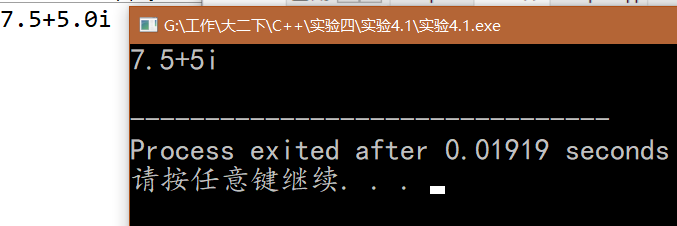
1. 实验内容 2
- 基于
Graph graph1('*',5);的图像分析 draw() 算法:
每一行输出的符号数为 2X行号-1 ,输出的空格数为 2X总行号-1 - 每行输出的符号数。 - 实验环境:Dev C++ 5.11
- C++ Code:
- Graph.cpp:
#define rap(a,b) for(int a=1;a<=b;++a)
#include<iostream>
#include"Graph.h"
using namespace std;
Graph::Graph(char s,int l){
sign=s;
line=l;
}
void Graph::draw(){
rap(i,line){
int tmp=line-i;
//cout<<tmp<<endl;
rap(j,tmp) cout<<" ";
rap(j,2*i-1)cout<<sign;
rap(j,tmp) cout<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
return ;
}
+ Graph.h:
class Graph{
protected:
char sign;
int line;
public:
Graph(char s,int l);
void draw();
};
+ main.cpp:
#include "Graph.h"
int main(){
Graph graph1('*',5);
graph1.draw();
Graph graph2('$',7);
graph2.draw();
return 0;
}
- Java Code:
- Graph.java:
public class Graph {
private static char sign;
private static int line;
public Graph(char s, int l) {
sign = s;
line = l;
}
public void draw() {
for(int i = 1; i <= line; ++ i) {
int tmp = line - i;
for(int j = 1; j <= tmp; ++j) System.out.print(" ");
for(int j = 1; j <= 2*i-1; ++j) System.out.print(sign);
for(int j = 1; j <= tmp; ++j) System.out.print(" ");
System.out.print("
");
}
}
public void renew(char s, int l) {
sign = s;
line = l;
draw();
}
}
+ Main.java:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Graph graph1=new Graph('*', 5);
graph1.draw();
Graph graph2=new Graph('$', 7);
graph2.draw();
graph2.renew('%', 8);
}
-
console:
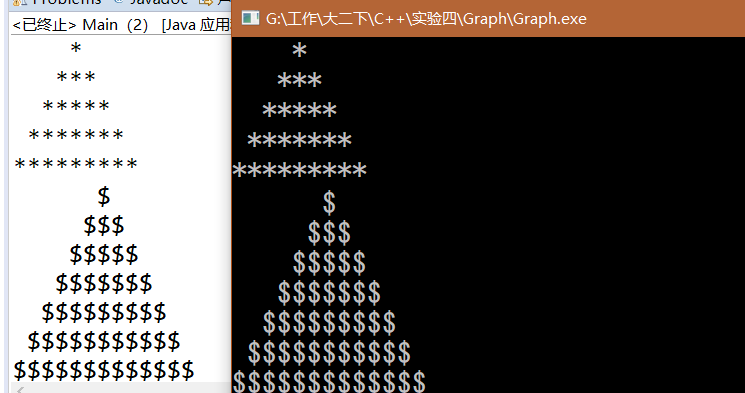
-
选做部分:
- 重新设置显示的字符、尺寸:
- Code(Graph.h):
void rewrite(char s,int l); - Code(Graph.cpp):
- Code(Graph.h):
- 重新设置显示的字符、尺寸:
void Graph::rewrite(char s,int l){
sign=s;
line=l;
draw();
}
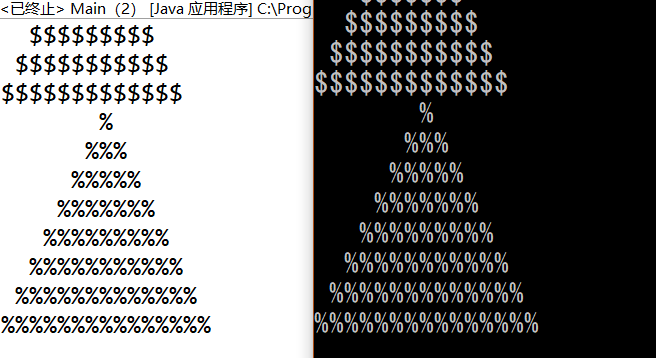
- Code(Main.cpp):`graph2.rewrite('%',8);`
- 演示:
+ 支持图形的前景色、背景色设置和调整;
- 设置console输出的颜色:
HANDLE consolehwnd=GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(consolehwnd,Color);
其中color为8位二进制数,高位存放前景色,低位存放背景色。
- 颜色编号
- Code(Graph.h):
protected unsigned int forecolor,backcolor;
int str2color(string a);
- Code(Graph.cpp):
int Graph::str2color(string a)
{
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "black") == 0)return 0;
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "blue") == 0)return 1;
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "green") == 0)return 2;
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "lackblue") == 0)return 3;
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "red") == 0)return 4;
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "purple") == 0)return 5;
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "yellow") == 0)return 6;
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "white") == 0)return 7;
if (strcasecmp(a.c_str(), "grey") == 0)return 8;
return 0;
}
void Graph::setcolor(string fore, string back){
forecolor=str2color(fore);
backcolor=str2color(back);
}
void Graph::draw(){
HANDLE consolehwnd=GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(consolehwnd,(forecolor<<4)+backcolor);
}
- Code(Main.cpp):
#include "Graph.h"
int main(){
Graph graph1('*',5);
graph1.setcolor("white","red");
graph1.draw();
Graph graph2('$',7);
graph2.setcolor("blue","yello");
graph2.draw();
graph2.setcolor("grey","green");
graph2.rewrite('%',8);
return 0;
}
- console:

+ 方向键控制图形移动:
- Code(Main.cpp):
while(1){
int ch=getch();
switch(ch){
case 72:if(offsety>0)offsety--;break;
case 75:if(offsetx>0)offsetx--;break;
case 77:offsetx++;break;
case 80:offsety++;break;
}
system("cls");
graph2.redraw(offsetx,offsety);
}
- Code(Graph.h):`void redraw(int x,int y);`
- Code(Graph.cpp):
void Graph::redraw(int x,int y){
rap(j,y)cout<<endl;
rap(i,line){
int tmp=line-i;
rap(j,x)cout<<" ";
rap(j,tmp) cout<<" ";
rap(j,2*i-1)cout<<sign;
rap(j,tmp) cout<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
- 演示GIF:
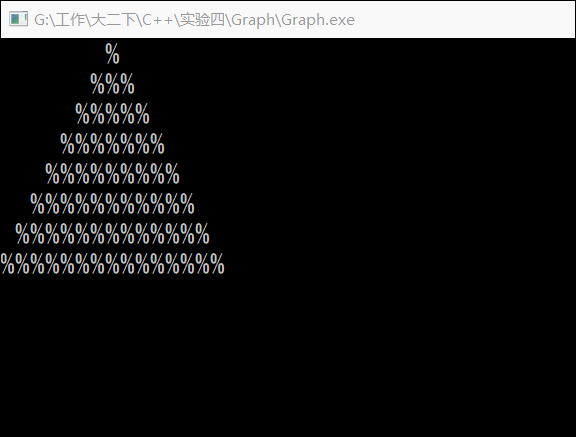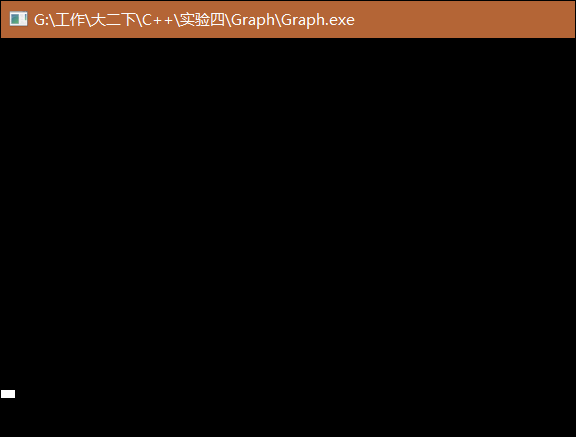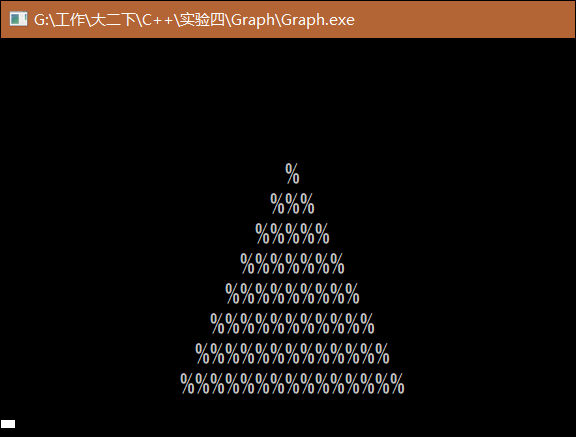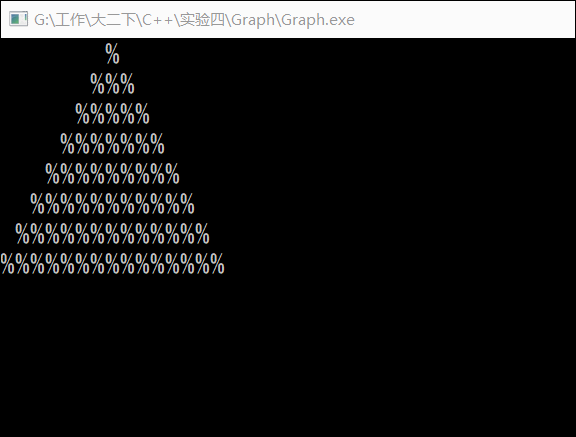
2. 实验内容 3
- UML类图:

- Code:
- Fraction.java
package ex3;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Fraction {
private int top;
private int bottom;
private int gcd(int a, int b) {
return a % b == 0 ? b : gcd(b, a%b);
}
private int abs(int a) {
return a > 0 ? a : -a;
}
public Fraction(int t, int b) {
top = t;
bottom = b;
}
public Fraction(int t) {
top = t;
bottom = 1;
}
public Fraction() {
top = 0;
bottom = 1;
}
public void simplify() {
if(bottom < 0) {
top = - top;
bottom = - bottom;
}
int g = gcd(abs(top),abs(bottom));
top /= g;
bottom /= g;
}
public void add(Fraction c0) {
bottom = bottom * c0.bottom;
top = top * c0.bottom + c0.top * bottom;
simplify();
}
public void subtract(Fraction c0) {
bottom = bottom * c0.bottom;
top = top * c0.bottom - c0.top * bottom;
if(bottom < 0) {
top = - top;
bottom = - bottom;
}
simplify();
}
public void multiple(Fraction c0) {
top *= c0.top;
bottom *= c0.bottom;
simplify();
}
public void divde(Fraction c0) {
if(c0.top == 0) {
System.out.println("Error: Zero can't be divided.");
return ;
}
top *= c0.bottom;
bottom *= c0.top;
simplify();
}
public boolean compare(Fraction c0) {
return top * gcd(bottom, c0.bottom) - c0.top
* gcd(bottom, c0.bottom) > 0 ? true : false;
}
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public void readln() {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Plz input the Numerator and Denominator");
top = sc.nextInt();
int tmp = sc.nextInt();
while (tmp == 0) {
System.out.println("Zero can't be the Denominator, plz try again!");
tmp = sc.nextInt();
}
bottom = tmp;
}
public void writeln() {
if(bottom != 1) System.out.println(top + "/" + bottom);
else System.out.println(top);
}
public double todecimal() {
return (double)top/bottom;
}
}
+ Main.java
package ex3;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Fraction c1 = new Fraction (11,22);
Fraction c2 = new Fraction (4);
Fraction c3 = new Fraction ();
c1.add(c2);
c1.writeln();
c1.subtract(c2);
c1.writeln();
c1.multiple(c2);
System.out.println(c1.todecimal());
c1.writeln();
c1.divde(c2);
c1.writeln();
}
}
+ Fraction.h
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
class Fraction
{
protected:
int top, bottom;
int gcd(int a, int b);
public:
Fraction(int t, int b);
Fraction(int t);
Fraction();
void simplify();
void add(Fraction c0);
void subtract(Fraction c0);
void multiple(Fraction c0);
void divde(Fraction c0);
bool compare(Fraction c0);
void readln();
void writeln();
double todecimal();
};
+ Fraction.cpp
int Fraction::gcd(int a, int b) {
return a % b == 0 ? b : gcd(b, a%b);
}
Fraction::Fraction(int t, int b) {
top = t;
bottom = b;
}
Fraction::Fraction(int t) {
top = t;
bottom = 1;
}
Fraction::Fraction() {
top = 0;
bottom = 1;
}
void Fraction::simplify() {
if(bottom < 0) {
top = - top;
bottom = - bottom;
}
int g = gcd(abs(top),abs(bottom));
top /= g;
bottom /= g;
}
void Fraction::add(Fraction c0) {
bottom = bottom * c0.bottom;
top = top * c0.bottom + c0.top * bottom;
simplify();
}
void Fraction::subtract(Fraction c0) {
bottom = bottom * c0.bottom;
top = top * c0.bottom - c0.top * bottom;
if(bottom < 0) {
top = - top;
bottom = - bottom;
}
simplify();
}
void Fraction::multiple(Fraction c0) {
top *= c0.top;
bottom *= c0.bottom;
simplify();
}
void Fraction::divde(Fraction c0) {
if(c0.top == 0) {
cout << "Error: Zero can't be divided.
";
return ;
}
top *= c0.bottom;
bottom *= c0.top;
simplify();
}
bool Fraction::compare(Fraction c0) {
return top * gcd(bottom, c0.bottom) - c0.top* gcd(bottom, c0.bottom) > 0 ? true : false;
}
void Fraction::readln() {
cout << "Plz input the Numerator and Denominator" << endl;
cin >> top;
int tmp;
cin >> tmp;
while (tmp == 0) {
cout << "Zero can't be the Denominator, plz try again!" << endl;
cin >> tmp;
}
bottom = tmp;
}
void Fraction::writeln() {
if(bottom != 1) cout << top << "/" << bottom << endl;
else cout << top <<endl;
}
double Fraction::todecimal() {
return (double)top / bottom;
}
+ Main.cpp
#include "Fraction.h"
#include <iomanip>
int main() {
Fraction c1 (11,-22);
Fraction c2 (4);
Fraction c3 ;
c1.writeln();
c1.add(c2);
c1.writeln();
cout << fixed<< setprecision(2) << c1.todecimal() << endl;
c1.subtract(c2);
c1.writeln();
c1.multiple(c2);
c1.writeln();
c1.divde(c2);
c1.writeln();
return 0;
}
- console:

- 选做部分:
- 规范化处理:
void Fraction:: simplify() {
if(bottom < 0) {
top = - top;
bottom = - bottom;
}
int g = gcd(abs(top),abs(bottom));
top /= g;
bottom /= g;
}
+ 转换为十进制:
double Fraction:: todecimal() {
return (double)top / bottom;
}
五、实验总结与体会
- 多文件结构式的项目在日后实际开发中更容易进行多人合作。
- 作为从C++衍生出来的Java,所有东西都必须置入一个类,没有类声明,只有类定义。
- My pleasure to participate in the design of this experiment~
