一、前言
上一节已经将raincat demo工程运行起来了,这一节来分析下raincat的源码
二、协调者启动过程
主要就是在启动类中通过如下代码来启动 netty
nettyService.start()
三、参与者启动过程
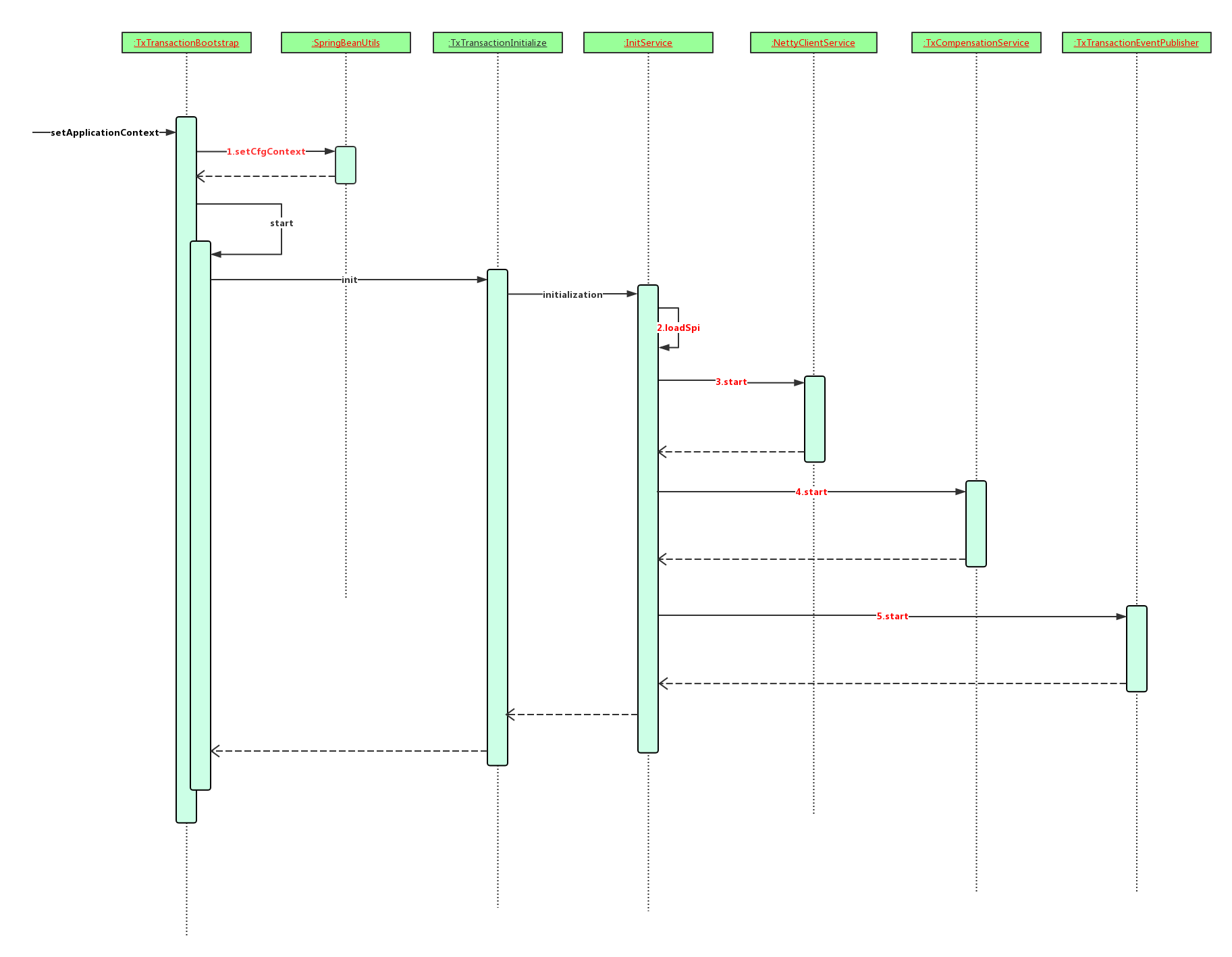
1.参与者启动时序图
参与者在启动过程中,主要做了如下4件事:
(1)保存SpringContext上下文
(2)通过加载spi,来使用用户自定义配置
(3)启动Netty客户端,与txManager进行连接,并且维持心跳。
(4)启动事务补偿任务,建表,定时补偿。
(5)启动事务事件发布器。
如下图:
2.保存Spring上下文
源码见 SpringBeanUtils 类,设置Spring 上下文,并提供spring bean 的注册与获取方法。

/* * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more * contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with * this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. * The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 * (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with * the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package com.raincat.core.helper; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; /** * SpringBeanUtils. * @author xiaoyu */ public final class SpringBeanUtils { private static final SpringBeanUtils INSTANCE = new SpringBeanUtils(); private ConfigurableApplicationContext cfgContext; private SpringBeanUtils() { if (INSTANCE != null) { throw new Error("error"); } } /** * get SpringBeanUtils. * @return SpringBeanUtils */ public static SpringBeanUtils getInstance() { return INSTANCE; } /** * acquire spring bean. * * @param type type * @param <T> class * @return bean */ public <T> T getBean(final Class<T> type) { return cfgContext.getBean(type); } /** * register bean in spring ioc. * @param beanName bean name * @param obj bean */ public void registerBean(final String beanName, final Object obj) { cfgContext.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(beanName, obj); } /** * set application context. * @param cfgContext application context */ public void setCfgContext(final ConfigurableApplicationContext cfgContext) { this.cfgContext = cfgContext; } }
3.加载spi

/** * load spi. * * @param txConfig {@linkplain TxConfig} */ private void loadSpi(final TxConfig txConfig) { //spi serialize final SerializeProtocolEnum serializeProtocolEnum = SerializeProtocolEnum.acquireSerializeProtocol(txConfig.getSerializer()); final ServiceLoader<ObjectSerializer> objectSerializers = ServiceBootstrap.loadAll(ObjectSerializer.class); final ObjectSerializer serializer = StreamSupport.stream(objectSerializers.spliterator(), false) .filter(s -> Objects.equals(s.getScheme(), serializeProtocolEnum.getSerializeProtocol())) .findFirst().orElse(new KryoSerializer()); //spi RecoverRepository support final CompensationCacheTypeEnum compensationCacheTypeEnum = CompensationCacheTypeEnum.acquireCompensationCacheType(txConfig.getCompensationCacheType()); final ServiceLoader<TransactionRecoverRepository> recoverRepositories = ServiceBootstrap.loadAll(TransactionRecoverRepository.class); final TransactionRecoverRepository repository = StreamSupport.stream(recoverRepositories.spliterator(), false) .filter(r -> Objects.equals(r.getScheme(), compensationCacheTypeEnum.getCompensationCacheType())) .findFirst().orElse(new JdbcTransactionRecoverRepository()); //将compensationCache实现注入到spring容器 repository.setSerializer(serializer); SpringBeanUtils.getInstance().registerBean(TransactionRecoverRepository.class.getName(), repository); }
(1)作用
SPI的全名为Service Provider Interface,该机制其实就是为接口寻找服务实现类
(2)如何使用
当服务的提供者,提供了服务接口的一种实现之后,在jar包的META-INF/services/目录里同时创建一个以服务接口命名的文件。
该文件里就是实现该服务接口的具体实现类。
而当外部程序装配这个模块的时候,就能通过该jar包META-INF/services/里的配置文件找到具体的实现类名,并装载实例化,完成模块的注入。
