1、SQL语句结构
select distinct < select_list >
from < left_table > < join_type >
join < right_table >
on < join_condition >
where < where_condition >
group by < group_by_list >
having < having_condition >
order by < order_by_condition >
limit < limit_number >
2、7种Join方式及实例
实验脚本:
drop table IF EXISTS shuzi ;
create table shuzi (id tinyint,note varchar(20));
insert into shuzi values (1,'一'),(2,'二'),(3,'三'),(4,'四'),(5,'五'),(6,'六'),(7,'七'),(8,'八'),(9,'九'),(10,'十');
select * from shuzi;
drop table IF EXISTS qianshu ;
create table qianshu (id int,des varchar(20));
insert into qianshu values (1,'壹'),(2,'贰'),(4,'肆'),(5,'伍'),(6,'陆'),(10,'拾'),(100,'佰'),(1000,'仟'),(10000,'万');
select * from qianshu;

- 左连接,左表的全部,右表不满足的列补空
select a.id,a.note,b.id,b.des from shuzi a left join qianshu b on a.id=b.id order by a.id;

- 右连接,右表的全部,左表不满足的列补空
select a.id,a.note,b.id,b.des from shuzi a right join qianshu b on a.id=b.id order by b.id;
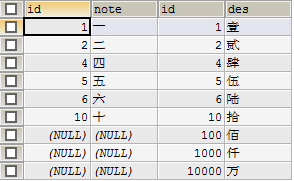
- 内连接,只输出左右表均存在的记录(默认from a,b方式)
SELECT a.id,a.note,b.id,b.des FROM shuzi a INNER JOIN qianshu b ON a.id=b.id ORDER BY b.id;

- 左连接,只保留左表特有数据(差集)
select a.id,a.note,b.id,b.des from shuzi a left join qianshu b on a.id=b.id where b.id is null order by a.id

- 右连接,只保留右表特有数据(差集)
SELECT a.id,a.note,b.id,b.des FROM shuzi a RIGHT JOIN qianshu b ON a.id=b.id WHERE a.id IS NULL ORDER BY b.id;

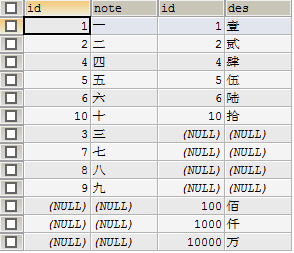
- 全外连接,获取左右表的所有记录,各自没有时补空
mysql不支持full outer join,要实现全外连接可以通过合并左,右外连接结果集实现
select a.id,a.note,b.id,b.des from shuzi a left join qianshu b on a.id=b.id
union
select a.id,a.note,b.id,b.des from shuzi a right join qianshu b on a.id=b.id
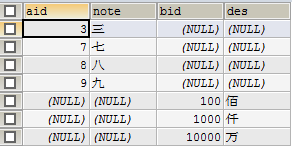
- 获取两表连接交集的补集(最后一个)
SELECT * FROM (
SELECT a.id aid,a.note,b.id bid,b.des FROM shuzi a LEFT JOIN qianshu b ON a.id=b.id
UNION
SELECT a.id aid,a.note,b.id bid,b.des FROM shuzi a RIGHT JOIN qianshu b ON a.id=b.id) v_a
WHERE aid IS NULL OR bid IS NULL;
SQL JOIN
SQL join 用于根据两个或多个表中的列之间的关系,从这些表中查询数据。
Join 和 Key
有时为了得到完整的结果,我们需要从两个或更多的表中获取结果。我们就需要执行 join。
数据库中的表可通过键将彼此联系起来。主键(Primary Key)是一个列,在这个列中的每一行的值都是唯一的。在表中,每个主键的值都是唯一的。这样做的目的是在不重复每个表中的所有数据的情况下,把表间的数据交叉捆绑在一起。
请看 "Persons" 表:
| Id_P | LastName | FirstName | Address | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adams | John | Oxford Street | London |
| 2 | Bush | George | Fifth Avenue | New York |
| 3 | Carter | Thomas | Changan Street | Beijing |
请注意,"Id_P" 列是 Persons 表中的的主键。这意味着没有两行能够拥有相同的 Id_P。即使两个人的姓名完全相同,Id_P 也可以区分他们。
接下来请看 "Orders" 表:
| Id_O | OrderNo | Id_P |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 77895 | 3 |
| 2 | 44678 | 3 |
| 3 | 22456 | 1 |
| 4 | 24562 | 1 |
| 5 | 34764 | 65 |
请注意,"Id_O" 列是 Orders 表中的的主键,同时,"Orders" 表中的 "Id_P" 列用于引用 "Persons" 表中的人,而无需使用他们的确切姓名。
请留意,"Id_P" 列把上面的两个表联系了起来。
引用两个表
我们可以通过引用两个表的方式,从两个表中获取数据:
谁订购了产品,并且他们订购了什么产品?
SELECT Persons.LastName, Persons.FirstName, Orders.OrderNo FROM Persons, Orders WHERE Persons.Id_P = Orders.Id_P
结果集:
| LastName | FirstName | OrderNo |
|---|---|---|
| Adams | John | 22456 |
| Adams | John | 24562 |
| Carter | Thomas | 77895 |
| Carter | Thomas | 44678 |
SQL JOIN - 使用 Join
除了上面的方法,我们也可以使用关键词 JOIN 来从两个表中获取数据。
如果我们希望列出所有人的定购,可以使用下面的 SELECT 语句:
SELECT Persons.LastName, Persons.FirstName, Orders.OrderNo
FROM Persons
INNER JOIN Orders
ON Persons.Id_P = Orders.Id_P
ORDER BY Persons.LastName
结果集:
| LastName | FirstName | OrderNo |
|---|---|---|
| Adams | John | 22456 |
| Adams | John | 24562 |
| Carter | Thomas | 77895 |
| Carter | Thomas | 44678 |
不同的 SQL JOIN
除了我们在上面的例子中使用的 INNER JOIN(内连接),我们还可以使用其他几种连接。
下面列出了您可以使用的 JOIN 类型,以及它们之间的差异。
- JOIN: 如果表中有至少一个匹配,则返回行
- LEFT JOIN: 即使右表中没有匹配,也从左表返回所有的行
- RIGHT JOIN: 即使左表中没有匹配,也从右表返回所有的行
- FULL JOIN: 只要其中一个表中存在匹配,就返回行