Tensor create
#创建特定shape value为random值的tensor
input = torch.rand((64,64,3))
Tensor slice
- 以[2,3]矩阵为例,slice后可以得到任意shape的矩阵,并不是说一定会小于2行3列.
import torch
truths=torch.Tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
#代表新生成一个[3,]的矩阵,行位置分别取原先矩阵的第1,第0,第1行.
print(truths[[1,0,1],:])
print(truths[[1,0,1]]) #等同于truths[[1,0,1],:]
#代表新生成一个[,4]的矩阵,列位置分别取原先矩阵的第2,第2,第2,第2列
print(truths[:,[2,2,2,2]])
输出

- 用bool型的tensor去切片
import torch
x = torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
index = x>2
print(index.type())
x[index]

tensor扩展
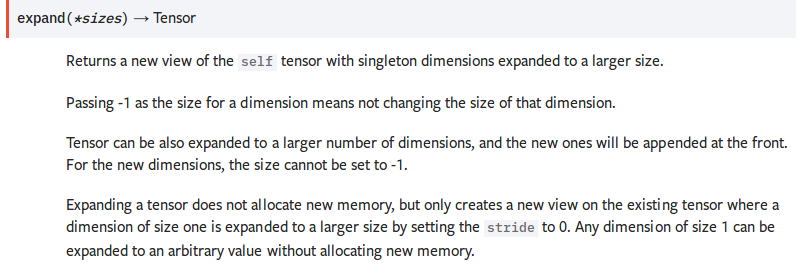
Expanding a tensor does not allocate new memory, but only creates a new view on the existing tensor where a dimension of size one is expanded to a larger size by setting the stride to 0. Any dimension of size 1 can be expanded to an arbitrary value without allocating new memory.
并不分配新内存. 只是改变了已有tensor的view. size为1的维度被扩展为更大的size.
>>> x = torch.tensor([[1], [2], [3]])
>>> x.size()
torch.Size([3, 1])
>>> x.expand(3, 4)
tensor([[ 1, 1, 1, 1],
[ 2, 2, 2, 2],
[ 3, 3, 3, 3]])
>>> x.expand(-1, 4) # -1 means not changing the size of that dimension
tensor([[ 1, 1, 1, 1],
[ 2, 2, 2, 2],
[ 3, 3, 3, 3]])
gather
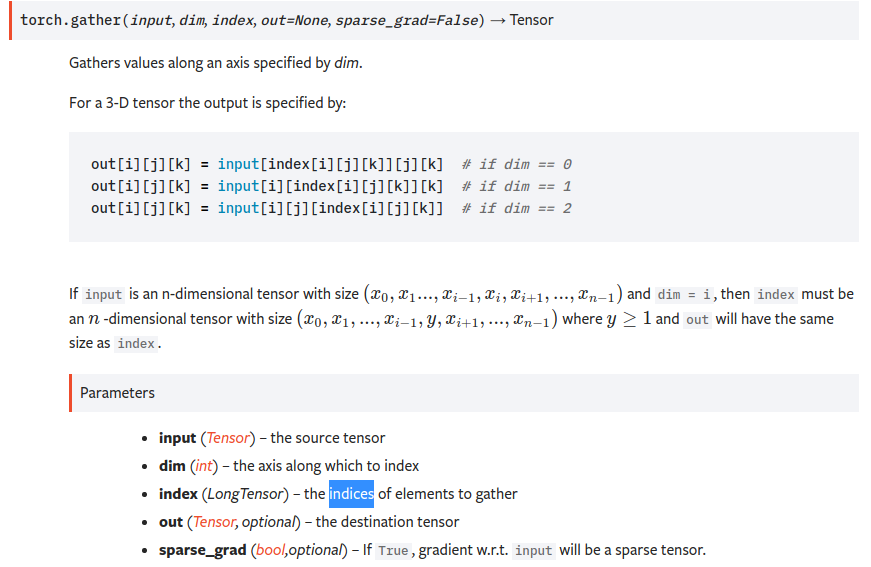
torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None, sparse_grad=False) → Tensor
即dim维度的下标由index替换.input是n维的,index也得是n维的,tensor在第dim维度上的size可以和input不一致. 最终的output和index的shape是一致的.
即对dim维度的数据按照index来索引.
比如
import torch
t = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
index=torch.tensor([[0,0],[1,0]])
torch.gather(t,1,index)
输出
tensor([[1, 1],
[4, 3]])
gather(t,1,index)替换第1维度的数据(即列方向),替换成哪些列的值呢?[[0,0],[1,0]],对第一行,分别为第0列,第0列,对第二行,分别为第1列,第0列.
从而得到tensor([[1, 1],[4, 3]])
sum

沿着第n维度,求和.keepdim表示是否保持维度数目不变.
import torch
t = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
a=torch.sum(t,0)
b=torch.sum(t,1,keepdim=True)
print(a.shape,b.shape)
print(a)
print(b)

sort
沿着第n个维度的方向排序
import torch
t = torch.tensor([[1,9,7],[8,5,6]])
_sorted,_index = t.sort(1)
print(_sorted)
print(_index)
_sorted,_index = t.sort(0)
print(_sorted)
print(_index)

clamp
import torch
print()
t = torch.tensor([[1,2,7],[3,4,8]])
res = t.clamp(3,7) #<3的变为3,>7的变为7 中间范围的不变
print(res)
res2 = torch.clamp(t,max=5) #所有大于5的都改为5
print(res2)

各种损失函数
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangxb35/article/details/72464152
有用link: