一、需求:
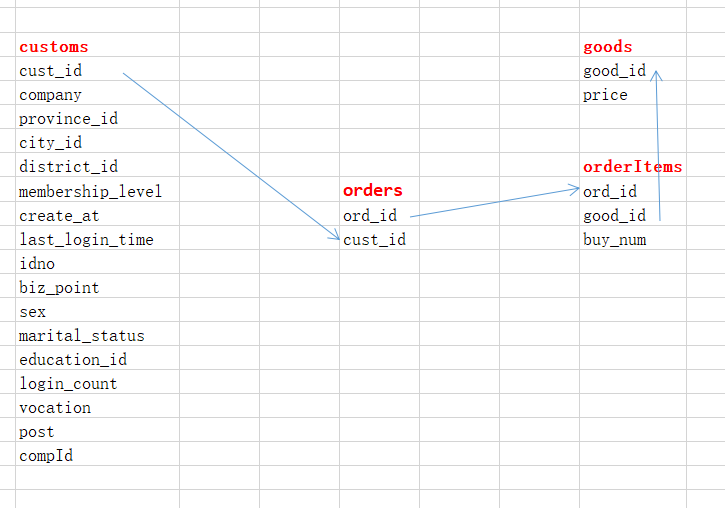
现有customers,orders,orderItems,goods表,记录电商相关信息,需要给每类customers推荐他们最感兴趣的商品
表表关系为:
二、思路:
- 获得特征:组成代表顾客消费特征的DataFrame(如用户年龄,用户会员等级)
- 归一化特征:除了ID标识,所有特征归一化成feature一列,训练成模型model
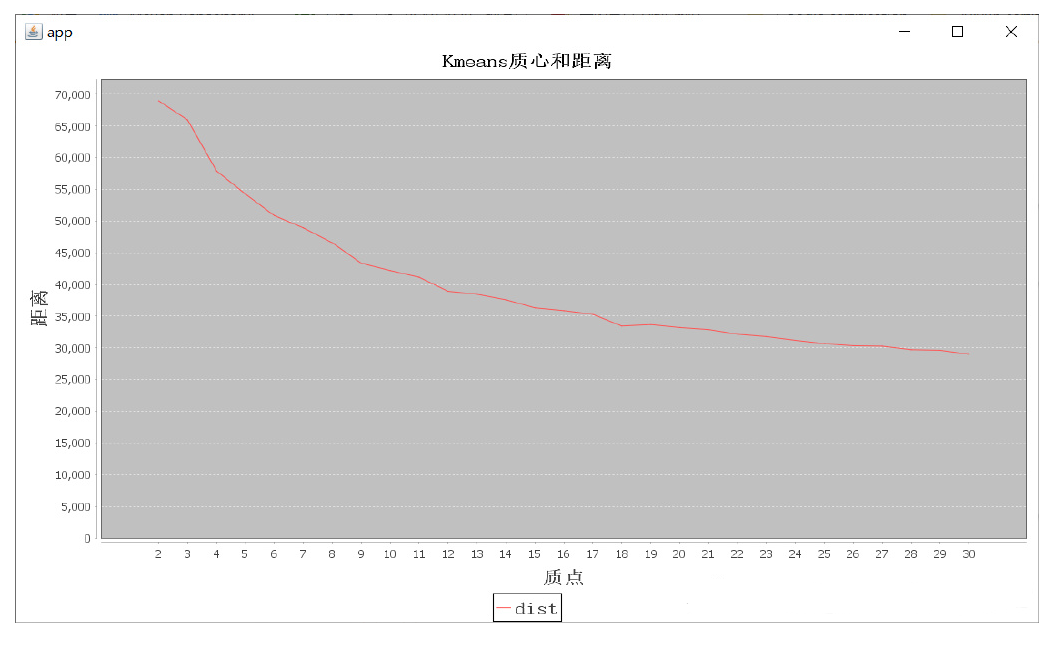
- 确定K值:针对每个K值(2,3,4,5...),计算每个K值对应的SSD(sum of squared distance)大小,K值越大SSD越小,取K-SSD曲线平稳的最小K值
- 使用Jfreechart画图,手动确定K
- 训练model,产生prediction(分组)
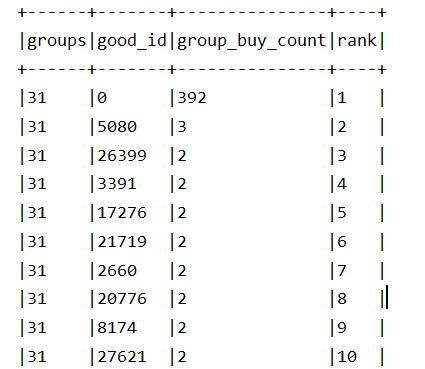
- 分组后,使用DF 获取每组用户购买的前30名商品
三、具体实现:
1.获得特征
数据清洗:
- 文字 => 数字,通过StringIndexer
- 使用自定义UDF函数确定每一类属于什么分级
- 拼接有效的列
- 所有列转换成DoubleType
辅助def:
def readMySQL(spark: SparkSession,tableName:String) = { val map: Map[String, String] = Map[String, String]( elems = "url" -> "jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.111:3306/myshops2", "driver" -> "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver", "user" -> "root", "password" -> "root", "dbtable" -> tableName ) spark.read.format("jdbc").options(map).load() } val func_membership = udf { (score: Int) => { score match { case i if i < 100 => 1 case i if i < 500 => 2 case i if i < 1000 => 3 case _ => 4 } } } val func_bir = udf { (idno: String, now: String) => { val year = idno.substring(6, 10).toInt val month = idno.substring(10, 12).toInt val day = idno.substring(12, 14).toInt val dts = now.split("-") val nowYear = dts(0).toInt val nowMonth = dts(1).toInt val nowDay = dts(2).toInt if (nowMonth > month) { nowYear - year } else if (nowMonth < month) { nowYear - 1 - year } else { if (nowDay >= day) { nowYear - year } else { nowYear - 1 - year } } } } val func_age = udf { (num: Int) => { num match { case n if n < 10 => 1 case n if n < 18 => 2 case n if n < 23 => 3 case n if n < 35 => 4 case n if n < 50 => 5 case n if n < 70 => 6 case _ => 7 } } } val func_userscore = udf { (sc: Int) => { sc match { case s if s < 100 => 1 case s if s < 500 => 2 case _ => 3 } } } val func_logincount = udf { (sc: Int) => { sc match { case s if s < 500 => 1 case _ => 2 } } }
main方法:
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("db").master("local[*]").getOrCreate()
val featureDataTable = readMySQL(spark,"customs").filter("active!=0").select("cust_id", "company", "province_id", "city_id", "district_id"
, "membership_level", "create_at", "last_login_time", "idno", "biz_point", "sex", "marital_status", "education_id"
, "login_count", "vocation", "post")
//商品表
val goodTable=readMySQL(spark,"goods").select("good_id","price")
//订单表
val orderTable=readMySQL(spark,"orders").select("ord_id","cust_id")
//订单明细表
val orddetailTable=readMySQL(spark,"orderItems").select("ord_id","good_id","buy_num")
//先将公司名通过StringIndex转为数字
val compIndex = new StringIndexer().setInputCol("company").setOutputCol("compId")
//使用自定义UDF函数
import spark.implicits._
//计算每个用户购买的次数
val tmp_bc=orderTable.groupBy("cust_id").agg(count($"ord_id").as("buycount"))
//计算每个用户在网站上花费了多少钱
val tmp_pay=orderTable.join(orddetailTable,Seq("ord_id"),"inner").join(goodTable,Seq("good_id"),"inner").groupBy("cust_id").
agg(sum($"buy_num"*$"price").as("pay"))
val df=compIndex.fit(featureDataTable).transform(featureDataTable)
.withColumn("mslevel", func_membership($"membership_level"))
.withColumn("min_reg_date", min($"create_at") over())
.withColumn("reg_date", datediff($"create_at", $"min_reg_date"))
.withColumn("min_login_time", min("last_login_time") over()) // 窗口函数实现groupby的聚合函数功能,又能显示每行数据
.withColumn("lasttime", datediff($"last_login_time", $"min_login_time")) // 为什么每个时间要-最小时间?时间数字太大,减小数字收敛更快
.withColumn("age", func_age(func_bir($"idno", current_date()))) // 如何包装常量为Column?lit()函数
.withColumn("user_score", func_userscore($"biz_point"))
.withColumn("logincount", func_logincount($"login_count"))
// 右表:有的用户可能没有买/没花钱,所以是left join
.join(tmp_bc,Seq("cust_id"),"left").join(tmp_pay,Seq("cust_id"),"left")
.na.fill(0)
.drop("company", "membership_level", "create_at", "min_reg_date" // 使用withColumn方法需要drop列,select则选什么显示什么
, "last_login_time", "min_login_time", "idno", "biz_point", "login_count")
//将所有列换成数字
val columns=df.columns.map(f=>col(f).cast(DoubleType))
val num_fmt=df.select(columns:_*)
2.归一化特征
//将除了第一列的所有列都组装成一个向量列 val va=new VectorAssembler().setInputCols(Array("province_id","city_id","district_id","sex","marital_status","education_id","vocation","post","compId","mslevel","reg_date","lasttime","age","user_score","logincount","buycount","pay")) .setOutputCol("orign_feature") val ofdf=va.transform(num_fmt).select("cust_id","orign_feature") //将原始特征列归一化处理 val mmScaler:MinMaxScaler=new MinMaxScaler().setInputCol("orign_feature").setOutputCol("feature") //fit产生模型 把ofdf放到模型里使用 val resdf=mmScaler.fit(ofdf) // 训练模型 MinMaxScalerModel .transform(ofdf) // 设置进参数 .select("cust_id","feature").cache() // 归一成"feature" 一列
3.确定K值
//使用Kmeans算法进行分组 //计算根据不同的质心点计算所有的距离 //记录不同质心点距离的集合 val disList:ListBuffer[Double]=ListBuffer[Double]() for (i<-2 to 40){ // 计划K从2取到40 val kms=new KMeans().setFeaturesCol("feature").setK(i) val model=kms.fit(resdf) // 为什么不transform ?? // 目的不是产生df:cust_id,feature和对应的group(prediction) // 目的是用computeCost算K数量对应的[SSD] disList.append(model.computeCost(resdf)) } //调用绘图工具绘图 val chart=new LineGraph("app","Kmeans质心和距离",disList) chart.pack() RefineryUtilities.centerFrameOnScreen(chart) chart.setVisible(true)
等CPU烧15分钟可运行出:
4.分组,使用DF
//使用 Kmeans 进行分组:找一个稳定的 K 值 val kms = new KMeans().setFeaturesCol("feature").setK(40) val user_group_tab=kms.fit(resdf) .transform(resdf) // 产出 custId,feature,prediction .drop("feature") .withColumnRenamed("prediction","groups") // 获得 custId,groups // .show(false) //获取每组用户购买的前30名商品 // row_number 根据组分组,买的次数desc // groupby 组和商品,count买的次数order_id val rank=30 val wnd=Window.partitionBy("groups").orderBy(desc("group_buy_count")) user_group_tab.join(orderTable,Seq("cust_id"),"left").join(orddetailTable,Seq("ord_id"),"left"). na.fill(0) .groupBy("groups","good_id") .agg(count("ord_id").as("group_buy_count")) .withColumn("rank",row_number()over(wnd)) .filter($"rank"<=rank).show(false)
结果: