旋转模式用来解决三角函数,实现极坐标到直角坐标的转换,基础理论请参考Cordic算法——圆周系统之旋转模式。那么,向量模式则用来解决反三角函数的问题,体现的应用主要是直角坐标向极坐标转换,即已知一点的直角坐标(x,y),求其极坐标(α,γ),实际上是求arctan(y/x)。
旋转模式下,每次迭代使z趋近于α(α-z趋近于0),而向量模式下,则使y趋近于0,这一点很好理解,即从坐标位置,旋转到x正半轴,一共旋转了多少角度,则该角度即为α,从而知道了极角。

如图所示,在单位圆上,向量OP与X轴的正半轴夹角为α,故P点的坐标可表示为

根据开头描述,我们需要转动向量OP,先顺时针旋转θ角至向量OQ,Q点的坐标可表示为

这里定义θ为目标旋转角度。根据三角函数公式可将上式展开为

现在已经有点 Cordic 算法的样子了,但是我们看到每次旋转都要计算 4 次浮点数的乘法运算,运算量还是太大了。还需要进一步的改进,改进的切入点当然还是坐标变换的过程。
将式(1.1)代入到式(1.3)中可得

用矩阵形式表示为:

旋转了i次以后,可以得到:

最终需将y_Q_i+1转为0,先按45°的二分法查找来解释过程,用C语言描述过程为:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
double cordic_v(double x, double y);
int main(viod)
{
double alfa = cordic_v(120.0,200.0); //直角坐标(x,y)
printf("
极角为 = %f
",alfa);
return 0;
}
double cordic_v(double x, double y)
{
const double sine[] = {0.7071067811865,0.3826834323651,0.1950903220161,
0.09801714032956,0.04906767432742,0.02454122852291,0.01227153828572,
0.006135884649154,0.003067956762966,0.001533980186285,
7.669903187427045e-4,3.834951875713956e-4,1.917475973107033e-4,
9.587379909597735e-5,4.793689960306688e-5,2.396844980841822e-5
};
const double cosine[] = {0.7071067811865,0.9238795325113,0.9807852804032,0.9951847266722,
0.9987954562052,0.9996988186962,0.9999247018391,0.9999811752826,0.9999952938096,
0.9999988234517,0.9999997058629,0.9999999264657,0.9999999816164,0.9999999954041,
0.999999998851,0.9999999997128
};
int i = 0;
double x_new, y_new;
double angleSum = 0.0;
double angle = 45.0; //第一次旋转角度为45°
for( i=0; i<15;i++)
{
if(y > 0)
{
x_new = x * cosine[i] + y * sine[i];
y_new = y * cosine[i] - x * sine[i];
x = x_new;
y = y_new;
angleSum += angle;
}
else
{
x_new = x * cosine[i] - y * sine[i];
y_new = y * cosine[i] + x * sine[i];
x = x_new;
y = y_new;
angleSum -= angle;
}
printf("旋转次数: i = %2d 旋转角度 = %10f, 累计旋转角度 = %10f
", i+1, angle,angleSum );
angle /= 2;
}
return angleSum;
}

经过旋转模式的推导,向量模式的伪旋转公式,可表示为
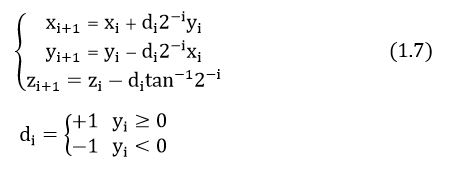
C语言描述过程,如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
double cordic_v(double x, double y);
double r = 0.0; //定义一个模长全局变量
int main(viod)
{
double alfa = cordic_v(120.0,200.0); //直角坐标(x,y)
printf("
极角 = %5f, 模长 = %5f
",alfa,r);
return 0;
}
double cordic_v(double x, double y)
{
const double theta[] = { 45.0, 26.56505118, 14.03624347, 7.125016349,
3.576334375, 1.789910608, 0.8951737102, 0.4476141709,
0.2238105004, 0.1119056771, 0.05595289189, 0.02797645262,
0.01398822714, 0.006994113675, 0.003497056851, 0.001748528427
}; //旋转角度
int i = 0;
double x_new, y_new;
double angleSum = 0.0;
r = sqrt(x*x+y*y);
for( i=0; i<16;i++)
{
if(y > 0)
{
x_new = x + y/(1<<i);
y_new = y - x/(1<<i);
x = x_new;
y = y_new;
angleSum += theta[i];
}
else
{
x_new = x - y/(1<<i);
y_new = y + x/(1<<i);
x = x_new;
y = y_new;
angleSum -= theta[i];
}
printf("旋转次数: i = %2d 旋转角度 = %10f, 累计旋转角度 = %10f, y = %5f
", i+1,theta[i],angleSum,y );
}
return angleSum;
}

同样,向量模式的cordic算法适用于第一、四象限的坐标变换,在第二、三象限的坐标需要进行预处理。
参考
-
《基于FPGA的数字信号处理(第2版)》——高亚军著