一. 哈希变量(相当于Python中的字典)
详情参看:https://www.runoob.com/ruby/ruby-hash.html
1.值得注意的
(1). 创建Hash时需注意
# 创建一个空的Hash months = Hash.new puts months print(months[1]) # 创建一个具有默认值得Hash months = Hash.new( "month" ) # 或 months = Hash.new "month" puts months print(months[1]) 输出结果: {} 报错 {} month
(2).Ruby创建一个有数据的Hash时与Python创建一个有数据的dict时的区别
Python: a = dict(a=1, b=2) # 正确 print(a) b = dict[a=1, b=2] # 错误 print(b) c = {["a", "b"]: 1} # 错误 print(c)
Ruby: a = Hash(a=1, b=2) # 错误 puts a a = Hash["a" => 1, "b" => 2] # 正确 puts a b = Hash("a" => 1, "b" => 2) # 正确 puts b c = Hash("a": 1, "b": 2) # 正确 puts c d = Hash([1, "he"] => "hai") # 正确 puts d 输出结果: error {"a"=>1, "b"=>2} {"a"=>1, "b"=>2} {:a=>1, :b=>2} {[1, "he"]=>"hai"}
(3).Ruby调用hash中的数据与Python调用dict中的数据时的区别
Python: a = {"a": 1, "b": 2} print(a["a"])
Ruby: game = {"疾风剑豪" => "亚索", "流影之主" => "劫", "刀锋之影" => "泰隆"} puts game puts game["疾风剑豪"] user = {name: "进不去啊", age: 18, gender: "男"} puts user puts user["name"] # nil puts user[name] # 报错 puts user[:name] 输出结果: {"疾风剑豪"=>"亚索", "流影之主"=>"劫", "刀锋之影"=>"泰隆"} 亚索 {:name=>"进不去啊", :age=>18, :gender=>"男"} error 进不去啊
注:Ruby关于字典中的方法大体与Python类似,请放心使用
二. 简单的类型转换
str = "12345" puts str str1 = str.to_i # 转整型 puts str1 str2 = str1.to_s # 转字符串 puts str2 str3 = str1.to_f # 转浮点 puts str3
注:这些转换方法与Python有很大的不同
str = "12345hei" str1 = str.to_i str2 = str.to_f puts str1, str2 puts str1.class, str2.class 输出结果: 12345 12345.0 Integer Float
str = "hei12345hei" str1 = str.to_i str2 = str.to_f puts str1, str2 puts str1.class, str2.class 输出结果: 0 0.0 Integer Float
str = "12345hei6789" str1 = str.to_i str2 = str.to_f puts str1, str2 puts str1.class, str2.class 输出结果: 12345 12345.0 Integer Float
str = "hei12345hei6789" str1 = str.to_i str2 = str.to_f puts str1, str2 puts str1.class, str2.class 输出结果: 0 0.0 Integer Float
注:经过to_i, to_f转换的字符串如果没有对应的值就会输出0或0.0,并且只会去字符串从首字符向后的所有的连续的数字,有且只取一次
三. 类(class)的再深入
详情参看:https://www.runoob.com/ruby/ruby-class.html
1.值得注意的
(1).Ruby类中的变量

注:Ruby中的类变量看的我有点懵逼(介是嘛呀),所以不推荐使用(别问为什么)
(2).静态类方法
Python: class Foo(object): def foo1(self): print("0") @staticmethod def foo2(): print("1") foo = Foo() Foo.foo2() # 正确 foo.foo2() # 正确
Ruby: class Game def initialize(id, title, price) # 构造方法 @id = id @title = title @price = price end def show_game puts @id + " " + @title + " " + @price end def self.to_str puts "I Love This Game" end end one = Game.new("one", "LOL", "0") one.show_game one.to_str # 错误 Game.to_str Game::to_str 输出结果: one LOL 0 error I Love This Game I Love This Game
注:类的静态方法,直属此类,不能被其它类所引用调用(具体稍后解释)
(3).Ruby 类的继承
class Game def initialize(id, title, price) @id = id @title = title @price = price end def show_game puts @id + " " + @title + " " + @price end def self.to_str puts "I Love This Game" end end class SteamGame < Game # 关于继承,与Python最大的区别 def steam_info puts "G胖无敌" end end SteamGame.to_str my_game = SteamGame.new("new", "城市:天际线", "100") my_game.show_game my_game.steam_info 输出结果: I Love This Game new 城市:天际线 100 G胖无敌
四. Ruby中的模块
详情参见:https://www.runoob.com/ruby/ruby-module.html
注:Python中也有模块这个概念,但和Ruby中模块的概念不相同
Python:
Python中的模块是以文件.py,且包含了 Python 对象定义和Python语句
Ruby:
模块(Module)是一种把方法、类和常量组合在一起的方式,具体就像是写一个类,只不过把class改为module(简单理解),和Python最大的区别就是Python是以文件作为区分,Ruby是以module作为区分
1.Ruby与Python的最大区别
Ruby中没有多继承!!!
but...
Ruby通过module实现了与多继承相同的思路
module BaseFunc Version = "0.1.1" def v return Version end def add(a, b) return a + b end def self.show_version return Version end # 讲v方法定义范围静态方法 module_function :v end puts BaseFunc::Version puts BaseFunc.show_version puts BaseFunc::show_version puts BaseFunc.v # puts BaseFunc.add(20 + 30) # 错误 class BaseClass include BaseFunc end puts "++++++++++++++++++++" # puts BaseClass.show_version # 错误 # puts BaseClass.v # 错误 puts BaseClass::Version my_cls = BaseClass.new puts my_cls.add(20, 30) # puts my_cls.show_version # 错误

module A def a1 end def a2 end end module B def b1 end def b2 end end class Sample include A include B def s1 end end samp=Sample.new samp.a1 samp.a2 samp.b1 samp.b2 samp.s1
2.Ruby关于模块的引用
(1).文件中引用
Ruby require 语句
语法:require filename
注:相当于Python中的import引入模块
实例: require 'trig.rb' require 'moral'
注:可以引入文件.rb或直接引入模块中的方法
(2).类中引用
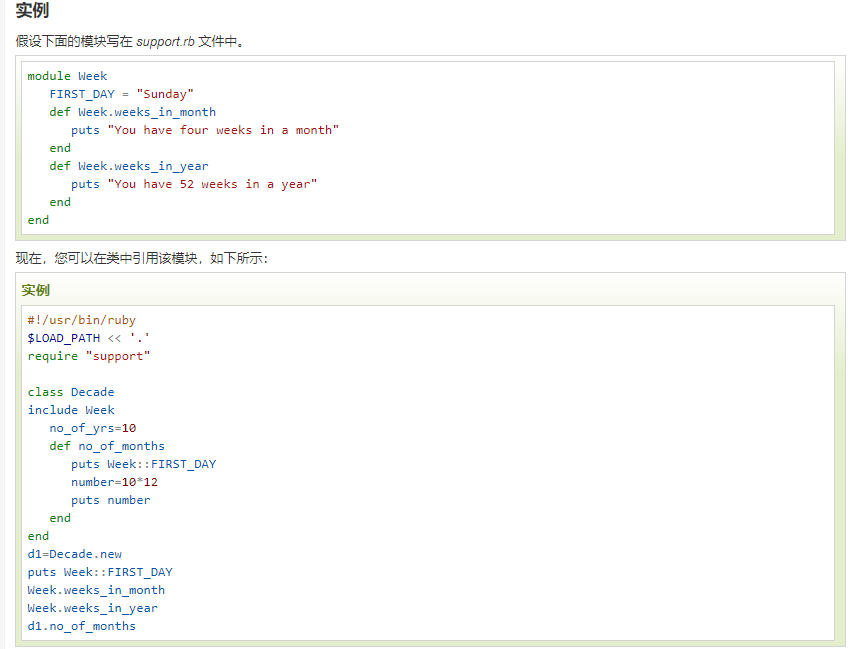
。。。
未完待续
