最近负责AD账户同步,遇到证书问题。
搜索后都说从AD服务器拿下证书,导入到java的cacerts中,尝试多次后无效。
绝望之际,看到 https://www.iteye.com/blog/chnic-2065877 的一篇文章,想起请求https接口时做的绕过证书操作,发现基本一个原理。
以下为大神的原文:
前两天工作遇到一个基于C/S结构的LDAP+SSL访问的问题,由于LDAP的服务器都是内网服务器,所以不需要去进行certificate。在网上搜了一下,找到了个solution分享给大家。
由于默认的Java over SSL是需要certificate,对于一些不需要证书的case,如果只是简简单单的在初始化Context的时候加上如下的语句
1 props.put(Context.SECURITY_PROTOCOL, "ssl");
你就会收到如下的异常:
1 Caused by: javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target 2 at sun.security.ssl.Alerts.getSSLException(Alerts.java:192) 3 at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.fatal(SSLSocketImpl.java:1884) 4 at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.fatalSE(Handshaker.java:276) 5 at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.fatalSE(Handshaker.java:270) 6 at sun.security.ssl.ClientHandshaker.serverCertificate(ClientHandshaker.java:1341) 7 at sun.security.ssl.ClientHandshaker.processMessage(ClientHandshaker.java:153) 8 at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.processLoop(Handshaker.java:868) 9 at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.process_record(Handshaker.java:804) 10 at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.readRecord(SSLSocketImpl.java:1016) 11 at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.performInitialHandshake(SSLSocketImpl.java:1312) 12 at sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl.readDataRecord(SSLSocketImpl.java:882) 13 at sun.security.ssl.AppInputStream.read(AppInputStream.java:102) 14 at java.io.BufferedInputStream.fill(BufferedInputStream.java:235) 15 at java.io.BufferedInputStream.read1(BufferedInputStream.java:275) 16 at java.io.BufferedInputStream.read(BufferedInputStream.java:334) 17 at com.sun.jndi.ldap.Connection.run(Connection.java:853) 18 at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:744) 19 Caused by: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target 20 at sun.security.validator.PKIXValidator.doBuild(PKIXValidator.java:385) 21 at sun.security.validator.PKIXValidator.engineValidate(PKIXValidator.java:292) 22 at sun.security.validator.Validator.validate(Validator.java:260) 23 at sun.security.ssl.X509TrustManagerImpl.validate(X509TrustManagerImpl.java:326) 24 at sun.security.ssl.X509TrustManagerImpl.checkTrusted(X509TrustManagerImpl.java:231) 25 at sun.security.ssl.X509TrustManagerImpl.checkServerTrusted(X509TrustManagerImpl.java:126) 26 at sun.security.ssl.ClientHandshaker.serverCertificate(ClientHandshaker.java:1323) 27 ... 12 more 28 Caused by: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target 29 at sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilder.engineBuild(SunCertPathBuilder.java:196) 30 at java.security.cert.CertPathBuilder.build(CertPathBuilder.java:268) 31 at sun.security.validator.PKIXValidator.doBuild(PKIXValidator.java:380) 32 ... 18 more
这一大串的异常信息用一句简单的话来概括就是你的Java client通过SSL来访问LADP server的时候,需要证书来做certificate,但是在我们本地并没有这样的东西,所以创建连接失败。
如何在建立连接的时候忽略certificate这一步呢?在我们的Java代码里需要做如下的事情,首先我们需要创建一个我们自己的TrustManagerh和SSLSocketFactory来替代默认的SSLSocketFactory
import java.security.cert.CertificateException; import java.security.cert.X509Certificate; import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager; public class LTSTrustmanager implements X509TrustManager { @Override public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] arg0, String arg1) throws CertificateException { } @Override public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] arg0, String arg1) throws CertificateException { } @Override public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() { return new java.security.cert.X509Certificate[0]; } }
import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.UnknownHostException; import java.security.SecureRandom; import javax.net.SocketFactory; import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext; import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory; import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager; public class LTSSSLSocketFactory extends SSLSocketFactory { private SSLSocketFactory socketFactory; public LTSSSLSocketFactory() { try { SSLContext ctx = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS"); ctx.init(null, new TrustManager[]{ new LTSTrustmanager()}, new SecureRandom()); socketFactory = ctx.getSocketFactory(); } catch ( Exception ex ) { ex.printStackTrace(System.err); } } public static SocketFactory getDefault(){ return new LTSSSLSocketFactory(); } @Override public Socket createSocket(Socket arg0, String arg1, int arg2, boolean arg3) throws IOException { return null; } @Override public String[] getDefaultCipherSuites() { return socketFactory.getDefaultCipherSuites(); } @Override public String[] getSupportedCipherSuites() { return socketFactory.getSupportedCipherSuites(); } @Override public Socket createSocket(String arg0, int arg1) throws IOException, UnknownHostException { return socketFactory.createSocket(arg0, arg1); } @Override public Socket createSocket(InetAddress arg0, int arg1) throws IOException { return socketFactory.createSocket(arg0, arg1); } @Override public Socket createSocket(String arg0, int arg1, InetAddress arg2, int arg3) throws IOException, UnknownHostException { return socketFactory.createSocket(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3); } @Override public Socket createSocket(InetAddress arg0, int arg1, InetAddress arg2, int arg3) throws IOException { return socketFactory.createSocket(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3); } }
这两个类里有几句代码要解释一下。
SSLContext ctx = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
ctx.init(null, new TrustManager[]{ new LTSTrustmanager()}, new SecureRandom());
socketFactory = ctx.getSocketFactory();
这里的TLS其实是一个protocol。TLS的全称是Transport Layer Security Protocol,至于这个协议具体是干嘛用的,自己google啦。 接下来的两句就是通过自己dummy的TrustManager来初始化我们的SSLSocketFactory。值得多提的一句就是getDefault方法一定要有,因为在SSL建立连接的时候他需要通过这个方法来获取SSLSocketFactory的实例。
接下来的两句就是通过自己dummy的TrustManager来初始化我们的SSLSocketFactory。值得多提的一句就是getDefault方法一定要有,因为在SSL建立连接的时候他需要通过这个方法来获取SSLSocketFactory的实例。
至于我们自己dummy的TrustManager我们只需要实现getAcceptedIssuers这个方法,让他返回一个X509Certificate的数组即可。
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() { return new java.security.cert.X509Certificate[0]; }
上述的一切都做好之后,我们需要把我们dummy的class配置到LdapContextt当中。
Properties props = new Properties(); props.setProperty(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory"); props.setProperty(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "ldap.provider.url=ldap://XXXXXX:636"); props.put("java.naming.ldap.factory.socket", "LTSSSLSocketFactory"); props.put(Context.SECURITY_PROTOCOL, "ssl"); props.setProperty(Context.URL_PKG_PREFIXES, "com.sun.jndi.url"); props.setProperty(Context.REFERRAL, "ignore"); props.setProperty(Context.SECURITY_AUTHENTICATION, "simple"); props.setProperty(Context.SECURITY_PRINCIPAL, "xxxxx"); props.setProperty(Context.SECURITY_CREDENTIALS, "xxxxxxx"); LdapContext ctx = new InitialLdapContext(props, null);
这里注意我们新配置的java.naming.ldap.factory.socket是需要包名+类名的,比如
props.put("java.naming.ldap.factory.socket", "com.xxx.LTSSSLSocketFactory");
就此我们完成了全部的工作,Java over SSL再也不需要certificate。
我是这样用的
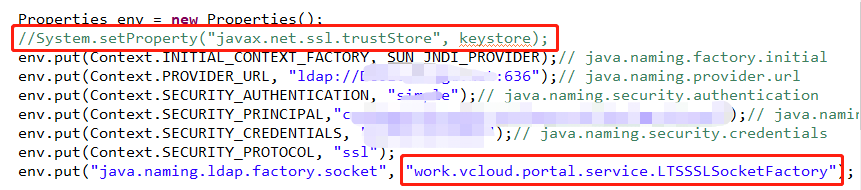
原来引用的keystore注释掉了,加上自定义的ssl类
另外: ladp 进行批量同步时,25个左右会报一次错,停留3S左右,继续进行就不会报错了。