逻辑斯谛回归模型是研究因变量为二分类或多分类观察结果与影响因素之间的关系的一种概率型非线性回归模型。逻辑斯谛回归系数通过最大似然估计得到。Logistic函数如下:

式中x为

这里 是输入变量的n个特征,然后按照Logistic函数形式求出。
是输入变量的n个特征,然后按照Logistic函数形式求出。
假设有n个独立变量的向量 ,设条件概率
,设条件概率 在x条件下y发生的概率(假设y=1为y发生)。则Logistic函数表示为:
在x条件下y发生的概率(假设y=1为y发生)。则Logistic函数表示为:


同理,在x条件下y不发生的概率为:

Logistic回归都是围绕Logistic函数展开的,如何求解 是Logistic回归模型的主要问题,采用的最大似然估计来求解这组参数。
是Logistic回归模型的主要问题,采用的最大似然估计来求解这组参数。
假设有m个观测样本,观测值分别为 ,设
,设 为给定条件下
为给定条件下 的概率,同理
的概率,同理 的概率为
的概率为 ,得到一个观测值得概率为:
,得到一个观测值得概率为:


因为各观测样本间相互独立,于是得到似然函数:


对似然函数取对数:


现要求向量 使的
使的 最大,其中:
最大,其中:


要求的最大似然估计,我们需要确定似然函数存在局部极大值。因此,对似然函数求偏导后得:

由多元函数极值的必要条件可知,若多元函数在一点取得极值,且一阶偏导存在,则该点处所有一阶偏导为0。由此,可以得出n+1个方程,如下:

由此方程解出的 不一定是似然函数的极值,需要通过Hessian矩阵来判断得出的解是否为似然函数的极值。
不一定是似然函数的极值,需要通过Hessian矩阵来判断得出的解是否为似然函数的极值。
Hessian矩阵是一个多元函数的二阶偏导构成的方阵,描述了函数的局部曲率。对一个多元函数 ,如果他的二阶偏导都存在,那么Hessian矩阵如下:
,如果他的二阶偏导都存在,那么Hessian矩阵如下:

通过Hessian矩阵,我们可以判断一点M处极值的三种情况:
-
如果
 是正定矩阵,则临界点M处是一个局部极小值;
是正定矩阵,则临界点M处是一个局部极小值; -
如果
 是负定矩阵,则临界点M处是一个局部极大值;
是负定矩阵,则临界点M处是一个局部极大值; -
如果
 是不定矩阵,则临界点M处不是极值。
是不定矩阵,则临界点M处不是极值。
对于中的n+1个方程,要求Hessian矩阵,先要求似然函数的二阶偏导,即:

则似然函数的Hessian矩阵为

设有矩阵X、A:


则似然函数的Hessian矩阵可表示为:

显然,矩阵A是负定的,则可以证明H也是负定的,说明似然函数存在局部极大值。因此,可以使用牛顿迭代法(Newton's Method)来求 。
。
对一元函数,使用牛顿迭代法来求零点。假设要求 的解,首先选取一个点
的解,首先选取一个点 作为迭代起点,通过下面的式子进行迭代,直到达到指定精度为止。
作为迭代起点,通过下面的式子进行迭代,直到达到指定精度为止。

由此,有时起始点选择很关键,如果函数只存在一个零点,那么这个起始点选取就无关重要。对已Logistic回归问题,Hessian矩阵对于任意数据都是负定的,所以说极值点只有一个,初始点的选取无关紧要。
因此,对于上述Logistic回归的似然函数, 令:

则由可以得到如下的迭代式子:

由于Hessian矩阵是负定的,将矩阵A提取一个负号,得:

然后Hessian矩阵变为

这样,Hessian矩阵就是对称正定的了。那么牛顿迭代式变为:

现在,关键是如何快速并有效的计算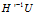 ,即解方程组
,即解方程组 。由于
。由于 是对称正定的,可以使用Cholesky矩阵分解法来解。
是对称正定的,可以使用Cholesky矩阵分解法来解。
若 对称正定,则存在一个对角元为正数的下三角矩阵
对称正定,则存在一个对角元为正数的下三角矩阵 ,使得
,使得 成立。对于
成立。对于 ,可以通过以下步骤求解:
,可以通过以下步骤求解:
-
求
 的Cholesky分解,得到
的Cholesky分解,得到
-
求解
 ,得到
,得到
-
求解
 ,得到
,得到
现在的关键问题是对 进行Cholesky分解。假设:
进行Cholesky分解。假设:

通过 比较两边的关系,首先由
比较两边的关系,首先由

再由

这样,得到了矩阵 的第一列元素。假设,已经算出了
的第一列元素。假设,已经算出了 的前
的前 列元素,通过
列元素,通过

可以得出

进一步由

最终:

这样便通过 的前
的前 列求出了第
列求出了第 列,一直递推下去即可求出
列,一直递推下去即可求出 。这种方法称为平方根法。
。这种方法称为平方根法。
利用上述方法需要进行开方,这有可能损失精度和增加运算量,为了避免开方,将Cholesky分解进行改进,即:

其中: 是单位下三角矩阵,
是单位下三角矩阵, 为对角均为正数的对角矩阵。把这一分解叫
为对角均为正数的对角矩阵。把这一分解叫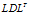 分解。设:
分解。设:

则对于 ,求解步骤变为:
,求解步骤变为:
-
求
 的
的 分解,得到
分解,得到
-
求解
 ,得到
,得到
-
求解
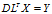 ,得到
,得到
对比两边元素,可以得到:

由此可以确定 和
和 的公式如下:
的公式如下:



牛顿迭代法
-
using System;
-
using System.Collections.Generic;
-
using System.Text;
-
using Model.MatrixDecomposition;
-
using Model.Matrix;
-
using System.IO;
-
-
namespace Model.NewtonRaphson
-
{
-
internal class NewtonRaphsonIterate
-
{
-
Cholesky_LDL_Decomposition decompositionMatrixByLDL = new Cholesky_LDL_Decomposition();
-
-
private double[,] matrix_Hessian = null;
-
private double[,] matrix_X = null;
-
private double[,] matrix_A = null;
-
-
-
private double[,] vector_HU = null;
-
private double[,] vector_U = null;
-
private double[,] vector_Y = null;
-
private double[,] vector_Omega = null;
-
private double[,] vector_PI = null;
-
private double[,] old_VectorOmega = null;
-
-
#region 属性
-
public double[,] MatrixL
-
{
-
get
-
{
-
return decompositionMatrixByLDL.MatrixL;
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
public double[,] MatrixD
-
{
-
get
-
{
-
return decompositionMatrixByLDL.MatrixD;
-
}
-
}
-
-
public double[,] Hessian
-
{
-
get
-
{
-
return this.matrix_Hessian;
-
}
-
}
-
#endregion
-
-
/// <summary>
-
/// 执行牛顿迭代法
-
/// </summary>
-
/// <param name="matrix_X">输入矩阵</param>
-
/// <param name="vector_Y">输出向量</param>
-
/// <param name="error_Threashold">迭代停止阈值</param>
-
/// <param name="omega">计算完成的参数</param>
-
internal void Run(double[,] matrix_X, double[,] vector_Y, double error_Threashold, ref double[,] omega)
-
{
-
double error = 1;
-
this.matrix_X = matrix_X;
-
this.vector_Y = vector_Y;
-
this.vector_Omega = omega;
-
InitializeParameter(matrix_X.GetLength(0));
-
int i = 0;
-
while (error > error_Threashold)
-
{
-
i++;
-
error = 0;
-
old_VectorOmega = (double[,])vector_Omega.Clone();
-
GetMatrixAAndVectorPI();
-
matrix_Hessian = MatrixOperation.MultipleMatrix(
-
MatrixOperation.MatrixMultiDiagMatrix(
-
MatrixOperation.TransportMatrix(matrix_X), matrix_A),
-
matrix_X);
-
GetMatrixU();
-
decompositionMatrixByLDL.Cholesky((double[,])matrix_Hessian.Clone(), vector_U, ref vector_HU);
-
vector_Omega = MatrixOperation.AddMatrix(vector_Omega, vector_HU);
-
GetIterationError(ref error);
-
//TODO:迭代计算
-
}
-
omega = (double[,])vector_Omega.Clone();
-
}
-
-
private void InitializeParameter(int rowNumber)
-
{
-
matrix_A = new double[rowNumber, 1];
-
vector_PI = new double[rowNumber, 1];
-
}
-
-
/// <summary>
-
/// 获取H=X^TAX的A以及PI(Xi)
-
/// </summary>
-
private void GetMatrixAAndVectorPI()
-
{
-
for (int i = 0; i < matrix_X.GetLength(0); i++)
-
{
-
double temp_A = 0;
-
//matrix_A[i, 0] += vector_Omega[0, 0];
-
for (int j = 0; j < matrix_X.GetLength(1); j++)
-
{
-
temp_A += matrix_X[i, j] * vector_Omega[j, 0];
-
}//for2
-
matrix_A[i, 0] = (1.0) / (1 + Math.Exp(-temp_A));
-
vector_PI[i, 0] = matrix_A[i, 0];
-
matrix_A[i, 0] *= (1 - matrix_A[i, 0]);
-
-
}//for1
-
}
-
-
//计算HU中的U
-
//U=X^T(Y-PI)
-
private void GetMatrixU()
-
{
-
vector_U = MatrixOperation.MultipleMatrix(MatrixOperation.TransportMatrix(matrix_X),
-
MatrixOperation.SubtracteMatrix(vector_Y, vector_PI));
-
}
-
-
/// <summary>
-
/// 计算每次迭代完成后的误差
-
/// </summary>
-
/// <param name="error">误差</param>
-
private void GetIterationError(ref double error)
-
{
-
for (int i = 0; i < vector_Omega.GetLength(0); i++)
-
{
-
error += Math.Abs(vector_Omega[i, 0] - old_VectorOmega[i, 0]);
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}
Cholesky分解
-
using System;
-
using System.Collections.Generic;
-
using System.Text;
-
using Model.Matrix;
-
-
namespace Model.MatrixDecomposition
-
{
-
internal class Cholesky_LDL_Decomposition
-
{
-
private double[,] matrix_L = null;
-
private double[,] matrix_D = null;
-
-
public double[,] MatrixL
-
{
-
get
-
{
-
return this.matrix_L;
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
public double[,] MatrixD
-
{
-
get
-
{
-
return this.matrix_D;
-
}
-
}
-
private int matrix_Dimension = 0;
-
-
#region Decomposition Matrix
-
/// <summary>
-
/// 方程AX=B
-
/// 利用Cholesky LDL^T分解法,求方程的解
-
/// </summary>
-
/// <param name="m_A">系数矩阵A</param>
-
/// <param name="v_B">列向量,B</param>
-
/// <param name="v_X">求得方程的解</param>
-
public void Cholesky(double[,] m_A, double[,] v_B, ref double[,] v_X)
-
{
-
this.matrix_Dimension = m_A.GetLength(0);
-
matrix_L = new double[matrix_Dimension, matrix_Dimension];
-
matrix_D = new double[matrix_Dimension, matrix_Dimension];
-
//为了计算方便,将L的严格下三角存储在A的对应位置上,
-
//而将D的对角元素存储A的对应对角位置上
-
//double[,] q = (double[,])m_A.Clone();
-
for (int i = 0; i < matrix_Dimension; i++)
-
{
-
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
-
{
-
m_A[i, i] -= m_A[j, j] * m_A[i, j] * m_A[i, j];
-
}//for
-
for (int k = i + 1; k < matrix_Dimension; k++)
-
{
-
for (int n = 0; n < i; n++)
-
{
-
m_A[k, i] -= m_A[k, n] * m_A[n, n] * m_A[i, n];
-
}//for
-
m_A[k, i] /= m_A[i, i];
-
}//for
-
}//for
-
-
this.GetLDMatrix(m_A);
-
this.SolveEquation(v_B,ref v_X);
-
//double[,] resut = MatrixOperation.MultipleMatrix(MatrixOperation.MultipleMatrix(MatrixL, MatrixD), MatrixOperation.TransportMatrix(MatrixL));
-
}
-
-
/// <summary>
-
/// 将L和D矩阵分别赋值
-
/// </summary>
-
/// <param name="m_A">经过Cholesky分解后的矩阵</param>
-
private void GetLDMatrix(double[,] m_A)
-
{
-
for (int i = 0; i < matrix_Dimension; i++)
-
{
-
matrix_L[i, i] = 1;
-
matrix_D[i, i] = m_A[i, i];
-
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
-
{
-
matrix_L[i, j] = m_A[i, j];
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
#endregion End Decomposition Matrix
-
-
#region Solve Equation
-
/// <summary>
-
/// 求解LY=B => Y
-
/// DL^TX=Y => X
-
/// </summary>
-
/// <param name="v_B">方程AX=B的列向量B</param>
-
/// <param name="v_X">求解结果</param>
-
private void SolveEquation(double[,] v_B, ref double[,] v_X)
-
{
-
v_X =(double[,])v_B.Clone();
-
//求解LY=B=>Y
-
for (int i = 0; i < matrix_Dimension; i++)
-
{
-
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
-
{
-
v_X[i,0] -= v_X[j,0] * matrix_L[i, j];
-
}
-
v_X[i,0] /= matrix_L[i, i];
-
}
-
-
//计算DL^T
-
double[,] dMultiLT = MatrixOperation.MultipleMatrix(matrix_D,
-
MatrixOperation.TransportMatrix(matrix_L));
-
//求解DL^TX=Y => X
-
for (int i = matrix_Dimension - 1; i >= 0; i--)
-
{
-
for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix_Dimension; j++)
-
{
-
v_X[i,0] -= v_X[j,0] * dMultiLT[i, j];
-
}
-
v_X[i,0] /= dMultiLT[i, i];
-
}
-
}//end Method
-
#endregion
-
}
-
}
MatrixOperation是一个有关矩阵加、减、乘以及特殊矩阵求逆的一个类。
 是正定矩阵,则临界点M处是一个局部极小值;
是正定矩阵,则临界点M处是一个局部极小值;  是负定矩阵,则临界点M处是一个局部极大值;
是负定矩阵,则临界点M处是一个局部极大值;  是不定矩阵,则临界点M处不是极值。
是不定矩阵,则临界点M处不是极值。  的Cholesky分解,得到
的Cholesky分解,得到
 ,得到
,得到
 ,得到
,得到
 的
的 分解,得到
分解,得到
 ,得到
,得到
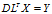 ,得到
,得到