最近使用了Dictionary,出现了意想不到的错误,先记录一下自己遇到的问题以及目前我的解决方法,然后温习一下Dictionary的基础用法。
一、自己遇到的问题
1、代码如下:

namespace DictionaryExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] pedlarArray = {"小明","小王","小红"};
Dictionary<Apple, string[]> appleMessageDict = new Dictionary<Apple, string[]>();
appleMessageDict.Add(new Apple() {
Quantity = 20,
Price = 5
}, pedlarArray);
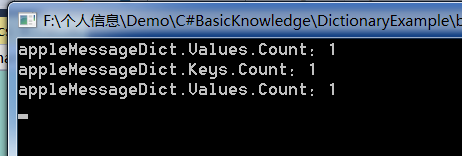
Console.WriteLine("appleMessageDict.Values.Count:{0}", appleMessageDict.Count);
Console.WriteLine("appleMessageDict.Keys.Count:{0}", appleMessageDict.Keys.Count);
Console.WriteLine("appleMessageDict.Values.Count:{0}", appleMessageDict.Values.Count);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Apple
{
private int _quantity;
private float _price;
public int Quantity
{
get { return _quantity; }
set
{
_quantity = value;
}
}
public float Price
{
get { return _price; }
set
{
_price = value;
}
}
public Apple()
{
}
}
}
运行结果:
2、原因分析
代码里面的字典AppleMessageDict的value是字符串数组类型,key是一个类类型。为什么数量都是1呢?通过分析我发现appleMessageDict.Count、appleMessageDict.Keys.Count、appleMessageDict.Values.Count这三个统计count的方式仅仅是针对于字典本身的统计,无关key/value是什么类型,仅仅是统计字典包含多少键值对。如果每个键值对中的key或者value是集合,想要知道key或者value的数量,需要另外处理。
3、目前我的解决方法

static void Main(string[] args)
{
int length = 0;
string[] pedlarArray = { "小明", "小王", "小红" };
Dictionary<Apple, string[]> appleMessageDict = new Dictionary<Apple, string[]>();
appleMessageDict.Add(new Apple()
{
Quantity = 20,
Price = 5
}, pedlarArray);
foreach (KeyValuePair<Apple, string[]> pair in appleMessageDict)//目前只能循环统计字典的数量
{
length += pair.Value.Length;
}
Console.WriteLine("appleMessageDict的数量:{0}", length);
//Console.WriteLine("appleMessageDict.Values.Count:{0}", appleMessageDict.Count);
//Console.WriteLine("appleMessageDict.Keys.Count:{0}", appleMessageDict.Keys.Count);
//Console.WriteLine("appleMessageDict.Values.Count:{0}", appleMessageDict.Values.Count);
Console.ReadKey();
}
二、Dictionary的基础知识
1、Dictionary的概念
Dictionary<[key], [value]>是一个泛型,Dictionary是一种变种的HashTable,是一个表示键和值的集合。
2、Dictionary的特点
键必须是唯一的,而值不需要唯一的 。键和值都可以是任何类型。通过一个键读取一个值的时间是接近O(1) 。
3、Dictionary的构造函数

(1)Dictionary<TKey,TValue>()构造函数:初始化 Dictionary<TKey,TValue> 类的新实例,该实例为空,具有默认的初始容量(Dictionary的默认大小为3)并为键类型使用默认的相等比较器。key不可重复,区分大小写

static void Main(string[] args) { #region Dictionary构造函数 (key不可重复,区分大小写) Console.WriteLine("==========Dictionary普通构造函数! key不可重复,区分大小写==========="); Dictionary<string, string> dict =new Dictionary<string, string>(); dict.Add("a","1"); try { dict.Add("A", "1"); foreach (KeyValuePair<string,string> item in dict) { Console.WriteLine("Key:{0},Value:{1}", item.Key,item.Value); } } catch (ArgumentException) { Console.WriteLine("键A已经存在!"); } Console.WriteLine("输入任意值,执行下一个构造函数:"); Console.ReadKey(); }
运行结果

(2)Dictionary<TKey,TValue>(IEqualityComparer<TKey>)构造函数:初始化 Dictionary<TKey,TValue> 类的新实例,该实例为空,具有默认的初始容量(Dictionary的默认大小为3)并使用指定的 IEqualityComparer<T>。key不可重复,不区分大小写

#region Dictionary 构造函数,key不可重复,不区分大小写 Console.WriteLine("==========Dictionary构造函数! key不可重复,不区分大小写==========="); Dictionary<string, string> dict1 = new Dictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase); dict1.Add("a", "1"); try { dict1.Add("A", "1"); } catch (ArgumentException) { Console.WriteLine("键A已经存在!"); } Console.WriteLine("输入任意值,执行下一个构造函数:"); Console.ReadKey(); #endregion
运行结果

(3)Dictionary<TKey,TValue>(IDictionary<TKey,TValue>)构造函数:初始化 Dictionary<TKey,TValue> 类的新实例,该实例包含从指定的 IDictionary<TKey,TValue> 复制的元素并为键类型使用默认的相等比较器。

#region Dictionary构造函数 通过SortedDictionary初始化Dictionary Console.WriteLine("==========Dictionary构造函数!通过SortedDictionary初始化Dictionary==========="); SortedDictionary<string, string> sortDict =new SortedDictionary<string, string>(); sortDict.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); sortDict.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); sortDict.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); sortDict.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); Dictionary<string, string> copyDict = new Dictionary<string, string>(sortDict); foreach (KeyValuePair<string,string> item in copyDict) { Console.WriteLine("key:{0},value:{1}",item.Key,item.Value); } Console.WriteLine("输入任意值,执行下一个构造函数:"); Console.ReadKey(); #endregion
运行结果

(4)Dictionary<TKey,TValue>(Int32)构造函数:初始化 Dictionary<TKey,TValue> 类的新实例,该实例为空,具有指定的初始容量并为键类型使用默认的相等比较器。
字典默认容量是3,可以初始化字典容量,如果初始化的容量不满足实际需求,将自动增加容量(自动扩容的规则将在下边专门介绍)。如果可以估计集合的大小,指定的初始容量,则无需要执行多个大小调整操作

#region Dictionary 构造函数 初始化Dictionary的大小容量 //字典默认容量是3,可以初始化字典容量,如果初始化的容量不满足实际需求,将自动增加容量。如果可以估计集合的大小,指定的初始容量,则无需要执行多个大小调整操作 Console.WriteLine("==========Dictionary 构造函数 初始化Dictionary的大小容量==========="); Dictionary<string, string> capacityDict = new Dictionary<string, string>(2); capacityDict.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); capacityDict.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); capacityDict.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); capacityDict.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); foreach (KeyValuePair<string, string> item in copyDict) { Console.WriteLine("key:{0},value:{1}", item.Key, item.Value); } Console.WriteLine("输入任意值,执行下一个构造函数:"); Console.ReadKey(); #endregion
运行结果

(5)Dictionary<TKey,TValue>(IDictionary<TKey,TValue>, IEqualityComparer<TKey>)构造函数:使用不区分大小写的比较器创建一个新的字典和填充从一个字典,其中使用区分大小写的比较器,如本示例所示的条目时如果输入的字典具有仅大小写不同的键,则会发生异常。

#region Dictionary 构造函数 使用不区分大小写的比较器创建一个新的字典和填充从一个字典 //使用不区分大小写的比较器创建一个新的字典和填充从一个字典,其中使用区分大小写的比较器,如本示例所示的条目时如果输入的字典具有仅大小写不同的键,则会发生异常。 Console.WriteLine("==========Dictionary 构造函数 使用不区分大小写的比较器创建一个新的字典和填充从一个字典==========="); SortedDictionary<string, string> sortDict1 = new SortedDictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase); sortDict1.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); sortDict1.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); sortDict1.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); sortDict1.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); Dictionary<string, string> copyDict1 = new Dictionary<string, string>(sortDict1,StringComparer.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase); foreach (KeyValuePair<string, string> item in copyDict1) { Console.WriteLine("key:{0},value:{1}", item.Key, item.Value); } Console.WriteLine("输入任意值,执行下一个构造函数:"); Console.ReadKey(); #endregion #region Dictionary 构造函数 使用不区分大小写的比较器创建一个新的字典和填充从一个字典 //使用不区分大小写的比较器创建一个新的字典和填充从一个字典,其中使用区分大小写的比较器,如本示例所示的条目时如果输入的字典具有仅大小写不同的键,则会发生异常。 Console.WriteLine("==========Dictionary 构造函数 使用不区分大小写的比较器创建一个新的字典和填充从一个字典==========="); SortedDictionary<string, string> sortDict1 = new SortedDictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase); sortDict1.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); sortDict1.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); sortDict1.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); sortDict1.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); Dictionary<string, string> copyDict1 = new Dictionary<string, string>(sortDict1,StringComparer.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase); foreach (KeyValuePair<string, string> item in copyDict1) { Console.WriteLine("key:{0},value:{1}", item.Key, item.Value); } Console.WriteLine("输入任意值,执行下一个构造函数:"); Console.ReadKey(); #endregion
运行结果

(6)Dictionary<TKey,TValue>(Int32, IEqualityComparer<TKey>)构造函数:初始化 Dictionary<TKey,TValue> 类的新实例,该实例为空,具有指定的初始容量并使用指定的 IEqualityComparer<T>。

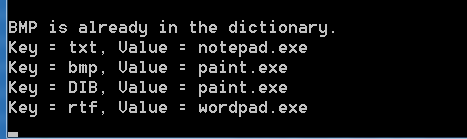
#region Dictionary<string, string> dict3 =new Dictionary<string, string>(5,StringComparer.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase); dict3.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); dict3.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); dict3.Add("DIB", "paint.exe"); dict3.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); try { dict3.Add("BMP", "paint.exe"); } catch (ArgumentException) { Console.WriteLine(" BMP is already in the dictionary."); } foreach (KeyValuePair<string, string> kvp in dict3) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", kvp.Key,kvp.Value); } #endregion
运行结果
(7)Dictionary<TKey,TValue>(SerializationInfo, StreamingContext)构造函数:用序列化数据初始化 Dictionary<TKey,TValue> 类的新实例。
===============List和Dictionary扩容规则======================
List和Dictionary的构造函数都有一个入参为int的构造函数:public Dictionary(int capacity);和public List(int capacity);capacity用来指定List和Dictionary的初始容量。List和Dictionary的内部实现方式都是使用数组,因为数组的容量是固定的,所以初始化的时候就会对其申请内存,List的默认大小为4,Dictionary的默认大小为3。如果不指定初始化容量,系统会默认创建。当往容器里Add数据时,如果当前数组已满,就会新创建一块两倍于当前数组长度的内存,把原有数据copy到新内存中,再继续往里添加。
举个例子,创建一个没指定初始容量的List后,依次往里面添加了12个元素,内存是这样分配的:首先默认分配了一块长度为4个List元素的内存给List数组,当添加到第五个时,发现长度不足,所以会分配4*2=8的内存,把原有的4个数据拷贝到新内存块中并把第五个元素添加到末尾;当添加到第九个时,也会重新分配一个8*2=16的内存,把原有的8个数据拷贝到新内存块中并把第9个元素添加到末尾;所以最终List数组的长度为16,里面存放了12个元素,共分配了三次内存,进行了两次的内存拷贝。
Dictionary容量分配规则也是如此。
所以合理的指定初始容量,可以减少内存的分配和拷贝次数,甚至还能节省内存空间。
================================================================
4、Dictionary的常用属性
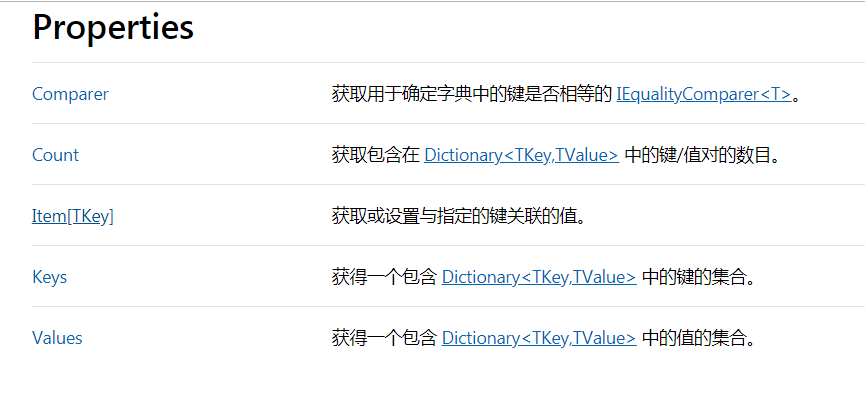
5、Dictionary的方法

(1)添加元素
第一种方式:通过Add()添加元素
Dictionary<string, string> messageDict = new Dictionary<string, string>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
messageDict.Add("key"+i,"value"+i);
}
第二种方式(推荐):通过中括号添加元素
Dictionary<string, string> messageDict = new Dictionary<string, string>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
messageDict["key" + i]="value"+i;
}
为什么我们推荐第二种方式呢?我们知道字典的键值不可重复(不使用StringComparer.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase指定的情况下),使用Add()方式,如果存在相同的键,会直接抛出ArgumentException异常。而使用第二种方式,如果存在相同的键,只要key不是null,就会进行改写,就不会出现异常。
(2)查找元素:第一种方式:通过key查找元素

static void Main(string[] args) { Dictionary<string, string> messageDict = new Dictionary<string, string>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { messageDict["key" + i]="value"+i; } if (messageDict.ContainsKey("key4")) { Console.WriteLine("key是{0},value是{1}","key4",messageDict["key4"]); } Console.ReadKey(); }
(3)遍历字典:通过KeyValuePair遍历元素

static void Main(string[] args) { Dictionary<string, string> messageDict = new Dictionary<string, string>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { messageDict["key" + i]="value"+i; } foreach (KeyValuePair<string,string> item in messageDict) { Console.WriteLine("key是{0},value是{1}", item.Key,item.Value); } Console.ReadKey(); }
(4)仅遍历所有的values

static void Main(string[] args) { Dictionary<string, string> messageDict = new Dictionary<string, string>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { messageDict["key" + i]="value"+i; } Dictionary<string, string>.ValueCollection valueCollection =messageDict.Values; if (valueCollection!= null&&valueCollection.Count>0) { foreach (string item in valueCollection) { Console.WriteLine("value是{0}", item); } } Console.ReadKey(); }
(5)仅遍历所有的keys

static void Main(string[] args) { Dictionary<string, string> messageDict = new Dictionary<string, string>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { messageDict["key" + i]="value"+i; } Dictionary<string, string>.KeyCollection keyCollection =messageDict.Keys; if (keyCollection != null&& keyCollection.Count>0) { foreach (string item in keyCollection) { Console.WriteLine("key是{0}", item); } } Console.ReadKey(); }
(6)通过Remove移除元素

static void Main(string[] args) { Dictionary<string, string> messageDict = new Dictionary<string, string>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { messageDict["key" + i]="value"+i; } messageDict.Remove("key0"); foreach (KeyValuePair<string,string> item in messageDict) { Console.WriteLine("key是{0},value是{1}", item.Key,item.Value); } Console.ReadKey(); }
