图的常用储存结构之一。邻接表由表头结点和表结点两部分组成,其中图中每个顶点均对应一个存储在数组中的表头结点。
http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=356SEBUQpBZT2E2M0Hssd5benLxbyMWd13ZF-DbZi-mvyQEoyssk4eBweeTpfIqZdLN9-g9cTwwqpPVC1WiM5K
除了克鲁斯卡尔和floyd,像广搜,普里姆,Bellman-Ford,迪杰斯特拉,SPFA,拓扑排序等等,都可以用到图的邻接表形式。
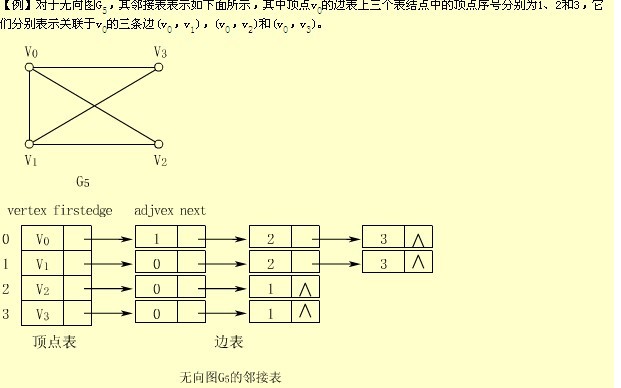
数据结构书上的邻接表是这样的:
借用一下这张图
http://blog.csdn.net/linxinyuluo/article/details/6847851
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #define MaxVertexNum 20 5 6 typedef char VertexType; 7 8 typedef struct node 9 { 10 int adjvex; 11 node* next; 12 }EdgeNode; 13 14 typedef struct 15 { 16 VertexType data; 17 EdgeNode* firstedge; 18 }VertexNode,AdjList[MaxVertexNum]; 19 20 typedef struct 21 { 22 AdjList adjlist; 23 int n,e; 24 }ALGraph; 25 26 void CreateG(ALGraph *G) 27 { 28 cout<<"Input vex and edge "; 29 cin>>G->n>>G->e; 30 EdgeNode *p; 31 32 //建立顶点表 33 for(int i = 0;i<G->n;i++) 34 { 35 cout<<"create vex table "<<i<<endl; 36 cin>>G->adjlist[i].data; 37 G->adjlist[i].firstedge = NULL; 38 } 39 40 //建立边表 41 for(int k = 0;k<G->e;k++) 42 { 43 cout<<"create edge table "<<k<<endl; 44 int a,b; 45 cin>>a>>b; 46 p = new EdgeNode; 47 p->adjvex = b; 48 p->next = G->adjlist[a].firstedge; 49 G->adjlist[a].firstedge = p; 50 p = new EdgeNode; 51 p->adjvex = a; 52 p->next = G->adjlist[b].firstedge; 53 G->adjlist[b].firstedge = p; 54 } 55 } 56 57 int main() 58 { 59 ALGraph *G = new ALGraph; 60 CreateG(G); 61 for(int i = 0;i<G->n;i++) 62 { 63 cout<<i; 64 while(G->adjlist[i].firstedge!=NULL) 65 { 66 cout<<" -> "<<G->adjlist[i].firstedge->adjvex; 67 G->adjlist[i].firstedge = G->adjlist[i].firstedge->next; 68 } 69 cout<<endl; 70 } 71 }
http://www.cnblogs.com/g0feng/archive/2012/09/18/2690913.html
数组实现:
http://bbs.ahalei.com/thread-4612-1-1.html
思路是先用e[i]保存所有的边,再用pre[i]保存i最后一个边的位置,最后用e[i].next实现跳转
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #define MaxVertexNum 20 5 6 typedef char VertexType; 7 8 typedef struct 9 { 10 int to; 11 int w; 12 int next; 13 }Edge; 14 15 Edge e[MaxVertexNum]; 16 int pre[MaxVertexNum]; 17 18 void CreateG(int n,int ed) 19 { 20 for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) 21 pre[i] = -1; 22 for(int i = 1;i<=ed;i++) 23 { 24 int from,to,wg; 25 cin>>from>>to>>wg; 26 e[i].to = to; 27 e[i].w = wg; 28 e[i].next = pre[from]; 29 pre[from] = i; 30 } 31 } 32 33 int main() 34 { 35 cout<<"Input vex and edge "; 36 int n,ed; 37 cin>>n>>ed; 38 CreateG(n,ed); 39 /*now为弧尾结点序号,i为now所发出的边序号,adj为弧头结点序号,w为now-->adj这条边的权值*/ 40 for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) 41 { 42 for(int j = pre[i]; j != -1; j = e[j].next) 43 { 44 int adj = e[j].to; 45 int w = e[j].w; 46 cout<<adj<<" -> "<<i<<" weight: "<<w<<endl; 47 } 48 } 49 return 0; 50 } 51 /* 52 4 5 53 1 4 9 54 4 3 8 55 1 2 5 56 2 4 6 57 1 3 7 58 */