https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+Select
查询语句语法:
[WITH CommonTableExpression (, CommonTableExpression)*] (Note: Only available starting with Hive 0.13.0) SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ... FROM table_reference [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY col_list] [ORDER BY col_list] [CLUSTER BY col_list | [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] [SORT BY col_list] ] [LIMIT number]
1 基本查询(Select…From)
1.1 全表和特定列查询
0)数据准备
(0)原始数据
dept:
10 ACCOUNTING 1700 20 RESEARCH 1800 30 SALES 1900 40 OPERATIONS 1700
emp:
7369 SMITH CLERK 7902 1980-12-17 800.00 20 7499 ALLEN SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-20 1600.00 300.00 30 7521 WARD SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-22 1250.00 500.00 30 7566 JONES MANAGER 7839 1981-4-2 2975.00 20 7654 MARTIN SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-28 1250.00 1400.00 30 7698 BLAKE MANAGER 7839 1981-5-1 2850.00 30 7782 CLARK MANAGER 7839 1981-6-9 2450.00 10 7788 SCOTT ANALYST 7566 1987-4-19 3000.00 20 7839 KING PRESIDENT 1981-11-17 5000.00 10 7844 TURNER SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-8 1500.00 0.00 30 7876 ADAMS CLERK 7788 1987-5-23 1100.00 20 7900 JAMES CLERK 7698 1981-12-3 950.00 30 7902 FORD ANALYST 7566 1981-12-3 3000.00 20 7934 MILLER CLERK 7782 1982-1-23 1300.00 10
创建部门表
create table if not exists dept( deptno int, dname string, loc int ) row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
创建员工表
create table if not exists emp( empno int, ename string, job string, mgr int, hiredate string, sal double, comm double, deptno int) row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
导入数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table dept; hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/emp.txt' into table emp;
1.全表查询
hive (default)> select * from emp;
2.选择特定列查询
hive (default)> select empno, ename from emp;
注意:
(1)SQL 语言大小写不敏感。
(2)SQL 可以写在一行或者多行
(3)关键字不能被缩写也不能分行
(4)各子句一般要分行写。
(5)使用缩进提高语句的可读性。
1.2 列别名
1.重命名一个列
2.便于计算
3.紧跟列名,也可以在列名和别名之间加入关键字‘AS’
4.案例实操
查询名称和部门
hive (default)> select ename AS name, deptno dn from emp;
1.3 算术运算符
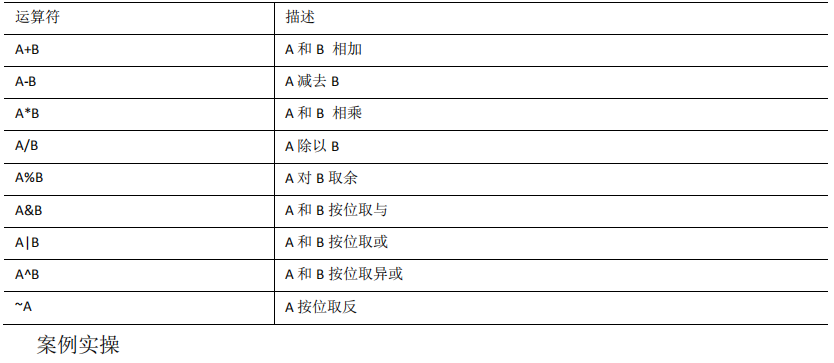
查询出所有员工的薪水后加 1 显示。
hive (default)> select sal +1 from emp;
1.4 常用函数
1.求总行数(count)
hive (default)> select count(*) cnt from emp;
2.求工资的最大值(max)
hive (default)> select max(sal) max_sal from emp;
3.求工资的最小值(min)
hive (default)> select min(sal) min_sal from emp;
4.求工资的总和(sum)
hive (default)> select sum(sal) sum_sal from emp;
5.求工资的平均值(avg)
hive (default)> select avg(sal) avg_sal from emp;
1.5 Limit 语句
典型的查询会返回多行数据。LIMIT 子句用于限制返回的行数。
hive (default)> select * from emp limit 5;
2 Where 语句
1.使用 WHERE 子句,将不满足条件的行过滤掉
2.WHERE 子句紧随 FROM 子句
3.案例实操
查询出薪水大于 1000 的所有员工
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal >1000;
注意:where 子句中不能使用字段别名。
2.1 比较运算符(Between/In/ Is Null)
1)下面表中描述了谓词操作符,这些操作符同样可以用于 JOIN…ON 和 HAVING 语句中。
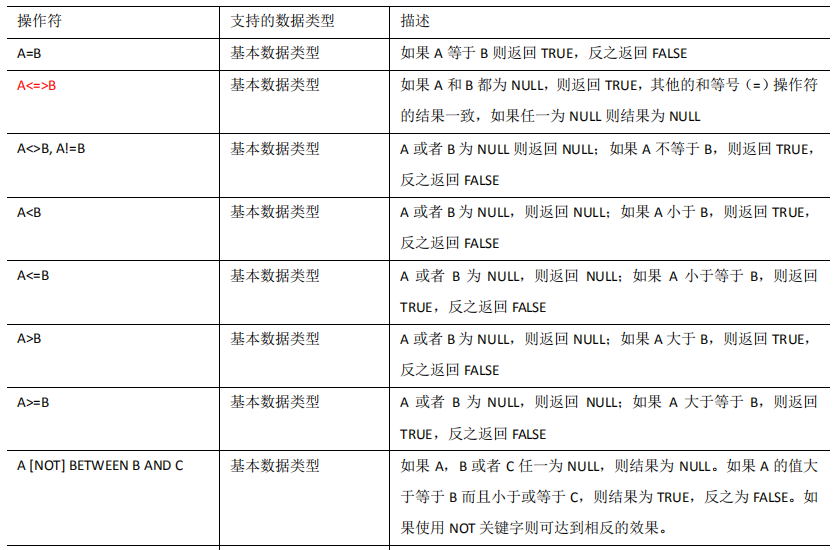

2)案例实操 (1)查询出薪水等于 5000 的所有员工 hive (default)> select * from emp where sal =5000; (2)查询工资在 500 到 1000 的员工信息 hive (default)> select * from emp where sal between 500 and 1000; (3)查询 comm 为空的所有员工信息 hive (default)> select * from emp where comm is null; (4)查询工资是 1500 或 5000 的员工信息 hive (default)> select * from emp where sal IN (1500, 5000);
2.2 Like 和 RLike
1)使用 LIKE 运算选择类似的值
2)选择条件可以包含字符或数字:
% 代表零个或多个字符(任意个字符)。
_ 代表一个字符。
3)RLIKE 子句是 Hive 中这个功能的一个扩展,其可以通过 Java 的正则表达式这个更
强大的语言来指定匹配条件。
4)案例实操
(1)查找以 2 开头薪水的员工信息 hive (default)> select * from emp where sal LIKE '2%'; (2)查找第二个数值为 2 的薪水的员工信息 hive (default)> select * from emp where sal LIKE '_2%'; (3)查找薪水中含有 2 的员工信息 hive (default)> select * from emp where sal RLIKE '[2]';
2.3 逻辑运算符(And/Or/Not)

案例实操
(1)查询薪水大于 1000,部门是 30 hive (default)> select * from emp where sal>1000 and deptno=30; (2)查询薪水大于 1000,或者部门是 30 hive (default)> select * from emp where sal>1000 or deptno=30; (3)查询除了 20 部门和 30 部门以外的员工信息 hive (default)> select * from emp where deptno not IN(30, 20);
3 分组
3.1 Group By 语句
GROUP BY 语句通常会和聚合函数一起使用,按照一个或者多个列队结果进行分组,
然后对每个组执行聚合操作。
案例实操:
(1)计算 emp 表每个部门的平均工资 hive (default)> select t.deptno, avg(t.sal) avg_sal from emp t group by t.deptno; (2)计算 emp 每个部门中每个岗位的最高薪水 hive (default)> select t.deptno, t.job, max(t.sal) max_sal from emp t group by t.deptno, t.job;
3.2 Having 语句
1.having 与 where 不同点
(1)where 后面不能写分组函数,而 having 后面可以使用分组函数。
(2)having 只用于 group by 分组统计语句。
2.案例实操
(1)求每个部门的平均薪水大于 2000 的部门
求每个部门的平均工资 hive (default)> select deptno, avg(sal) from emp group by deptno; 求每个部门的平均薪水大于 2000 的部门 hive (default)> select deptno, avg(sal) avg_sal from emp group by deptno having avg_sal > 2000;