1. Array & List
1.1Sort
Array的变更操作,好好运用尾指针:88题的end,75题的blueHead
- 88. Merge Sorted Array (Array)
- 75. Sort Colors
- 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
- 23. Merge k Sorted Lists
- 128. Longest Consecutive Sequence
- 147. Insertion Sort List
- 148. Sort List
Segment/project
- 56. Merge Intervals
- 57. Insert Interval
- 218. 天际线问题 (JAVA)
- <编程之美> P50-51
1.2 Rejust List
两种方法:
法I:改变结构
涉及的操作主要有:
- 子队列中逆序
- 子队列与前队列连接
- 子队列与后队列连接
在赋值的时候前后顺序是有讲究的,先备份到tmp,然后再给它赋值
法II: 只改变值,如:Delete a node in the middle of a single linked list, fiven only access to that node. -->Solution: 把下一个节点赋值给该节点,删除下一个节点,这样就省却了寻找上一个节点的麻烦。
注意特殊节点:(以防空指针)
- NULL
- head
- tail
比如上题
if(n==null || n->next == null) return false; ListNode* next = n->next; n->data = next->data; n->next = next->next;
- 86. Partition List
- 92. Reverse Linked List II
- 61. Rotate List
- 25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
- 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
- 143. Reorder List
- 27. Remove Element
- 26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
- 80. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
- 83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- 82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
- 146. LRU Cache
1.3 Search sorted array/list
搜索有序序列 - 二分法(对于Array,需要一头一尾两个指针;对于List,需要头指针及size)
- 35. Search Insert Position
- 34. Search for a Range
- 108.Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
- 109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
- 69. Sqrt(x)
- 4.Median of Two Sorted Arrays
- 167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted (Array)
1.4 Search unsorted array
- 135. Candy 使用贪心法
- 31. Next Permutation
- 350. 两个数组的交集 II (Java) 使用Hash Map查找
- 发帖水王 <编程之美> P130
1.5 Two Pointers
- 15. 3Sum
- 16. 3Sum Closest
- 125. Valid Palindrome
- 11.Container With Most Water
- 19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
- 141. Linked List Cycle
- 142. Linked List Cycle II
1.6 Shift
- 通过逆序移位 <编程之美> P201
- 字符串通过连接来代替移位 P103
2. Stack & Queue
2.1 Queue
- 三个队列排序 p195
- 实现带最大值查询的队列 <编程之美> P239
2.2 Stack
- 114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
- 144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
- 145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
- 71. Simplify Path
- 20. Valid Parentheses
- 32. Longest Valid Parentheses
- 150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
- 84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
- 85. Maximal Rectangle
- Implementation Stack by Array p111
- stack的实现(含min方法)p113
- Hanoi p118
3. Tree
前序遍历(Pre-order Traversal):自己->左->右
- 前序遍历用于,从上到下的遍历,左右子树的遍历依赖于根节点的数据
中序遍历(In-order Traversal):左->自己->右
后序遍历(Post-order Traversal):左->右->自己
- 后序遍历用于,从下到上的遍历,根节点的处理依赖于左右子树的遍历结果
3.1 递归实现前序遍历
- 112. Path Sum
- 113. Path Sum II
- 129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
- 101. Symmetric Tree
3.2 递归实现中序遍历
- 99. Recover Binary Search Tree
3.3 递归实现后序遍历
- 124. Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
- 111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
- 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
- 110. Balanced Binary Tree
- 96. Unique Binary Search Trees
- 95. Unique Binary Search Trees II
- 105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
- 106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
3.4“循环+栈”实现前序、中序、后序
- 114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List(2.2)
- 144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal(2.2)
- 145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal(2.2)
3.5 level search(wfs)
树是一种特殊的图,在树中,广度优先搜索又称为层次搜索;深度有限搜索又分为前序、中序、后序
- 107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
- 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
- 117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
- 127. Word Ladder
- 126. Word Ladder II (unordered_map,map,set的使用)
3.6 字典树/前缀树
适用于单词的搜索
- 面试题 17.13. 恢复空格 (JAVA)
- 208. 实现 Trie (前缀树) (JAVA)
- 212. 单词搜索 II (JAVA)
- 28. Implement strStr()
4. Graph
注意:对于不能重复遍历的情况,需要为每个节点标记是否已访问过。
4.1 遍历所有节点,两个for循环
- 118. Pascal's Triangle
- 119. Pascal's Triangle II
- 120. Triangle
- 48. Rotate Image
- 74. Search a 2D Matrix
- 36. Valid Sudoku
4.2 设定遍历方向,按照该方向遍历
- 54. Spiral Matrix
- 59. Spiral Matrix II
4.3 DFS/WFS
- 79. Word Search
- 73. Set Matrix Zeroes
- 133. Clone Graph
- 138. Copy List with Random Pointer
- 130. Surrounded Regions
- 51. N-Queens
- 52. N-Queens II
- 37. Sudoku Solver
- 210. 课程表 II (JAVA) (拓扑排序)
4.4 数据结构
- bfs在大数据时通过hash表代替node marking p199
- 稀疏矩阵的表示方法(链表、数组、三元组) <珠玑>p97 p209
4.5 着色问题
- 点图&区间图 <编程之美> P58-60
5. Hash table, map
看到数组与是否包含,首先想到的是Hashmap,否则每次的查找时间都是O(n)
- 1. Two Sum
- 3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters (KMP)
- 76. Minimum Window Substring (两个Hashmap的比较)
- 49. Group Anagrams (字母异位字符串的判定)
- 30. Substring with Concatenation of All Words
- 41. First Missing Positive
- 18. 4Sum (Hash table时间复杂度)
6. recursion
递归剪枝:
法I:最优剪枝。如果目前的结果已经差于之前得到的最优值,那么返回。
法II: 可行性剪枝。举个简单的例子,如图,问作者能否在正好第11秒的时候避过各种障碍物最终取得爱心,作者每秒能且只能移动一格,允许走重复的格子。
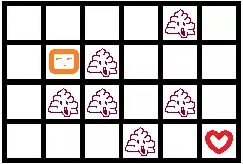
答案是永远不可能。因为无论怎么走,都只能在第偶数秒到达爱心,这是由他们的曼哈顿距离(两点的XY坐标差的绝对值之和)的奇偶性决定的。
6.1Recursion with backtracking
有重复元素,如何在结果集中避免重复?
法I:递归情况是包括当前元素和不包括当前元素。
那么在不包括当前元素的递归中,要忽略之后与当前元素相等的元素。如:Subsets II、Combination Sum II、4Sum
法II:递归情况涉及当前元素以及其后的元素,即递归时带有for循环
那么得通过额外设置flag来判断某元素是否已出现过(因为当前位置的值不限于当前元素)。如:Permutations II
- 131. Palindrome Partitioning
- 78. Subsets
- 90. Subsets II (no duplicates)
- 77. Combinations
- 46. Permutations
- 47. Permutations II (no duplicates)
- 39. Combination Sum
- 40. Combination Sum II (no duplicates)
- 17.Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
- 22. Generate Parentheses (两个递归函数互相调用)
- 93. Restore IP Addresses
- 44. Wildcard Matching
- 10.Regular Expression Matching
6.2 Divide and Conquer, 二分法
- 50. Pow(x, n)
- 29. Divide Two Integers
7. Dynamique programming
连续元素最值问题:只需要O(1)的空间复杂度。一个INT存储目前为止的最值,一个INT存储以当前元素结尾的和的最大值。
- 53. Maximum Subarray
- 134. Gas Station
- 45. Jump Game II
线性模型:状态的排布呈线性
- 42. Trapping Rain Water
- 60. Permutation Sequence
- 121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
- 122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
- 123. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
- 70. Climbing Stairs
- 91. Decode Ways
- 面试题 08.11. 硬币 (Java)
区间模型:
二维状态数组状态转移顺序:
1. 如果i、j标识同一个String,那么遍历顺序类似插入排序,内部for遍历至i结束;
2. 如果i、j标识两个String,那么内部for要遍历到S2结尾。
- 5. Longest Palindromic Substring (KMP)
- 132. Palindrome Partitioning II
- <编程之美> P44, 191-193
- 139. Word Break
- 140. Word Break II
- 97. Interleaving String
- 72. Edit Distance
- 115. Distinct Subsequences
-
87. Scramble String
- KMP
GRAPH:
- 64. Minimum Path Sum
- 62. Unique Paths(为什么DP优于DFS)
- 63. Unique Paths II
8. Greedy
- 55. Jump Game
- 149. Max Points on a Line
- 14. Longest Common Prefix
9. Numerique analysis
- 65. Valid Number
- 66. Plus One
- 2. Add Two Numbers
- 67. Add Binary
- 13. Roman to Integer
- 12. Integer to Roman (用减法代替除法)
- 8. String to Integer (atoi)
- 7. Reverse Integer
- 9 Palindrome Number
10. Bit Operation
- 89. Gray Code
- 136. Single Number
- 137. Single Number II
- p95,p140, p141,p172
- Permutations p173
- Parenthese p174
- pennies p176
- Queen 177
11. optimization <珠玑>
- malloc的优化 <珠玑>p92
- string连接的优化p100
- 数据压缩 <珠玑>p100-101
- 哨兵(一元数组、链表、箱、BST)<珠玑>p137
- 随机数 <珠玑>p120(减少生成次数P125/9 未知n p125/10)