前言
在游戏开发中经常会接触到各种物理引擎,虽然开源的引擎各种各样,但是基本原理是相通的。实质上物理引擎只是以时间为单位的刷新物理世界中的刚体的位置(其中运用了大量物理公式和知识),然后刷新刚体关联的物品(节点)的位置来达到模拟效果。其中的细节是我们开发者不需要知道,也不知道的。所以刚体轨迹预测成为了难题。
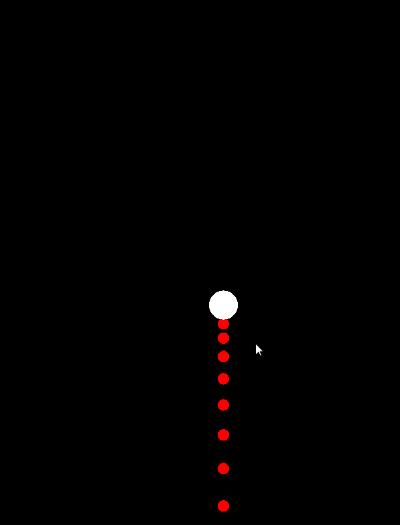
效果
物理公式
在开始之前先补一下高中基础物理公式(主要涉及匀加速直线运动):
- 速度公式
- 距离公式
- 阻尼公式
(比较贴近)
是指运动物体的
初始速度, 是指运动物体的
运动时间, 是指运动物体的
结束速度, 是指运动物体
运动距离, 是指运动物体的
运动加速度, 是指运动物体的
阻尼系数(模拟的空气阻尼等)。
即:
//速度公式
v(v0, a, t) {
return v0 + a * t;
}
//距离公式
s(v0, a, t) {
return v0 * t + (a * t * t) / 2;
}
//阻尼公式
let damping = -this.linear_Damping * this.v_y * dt;
this.v_y = this.v(this.v_y, this.a_y, dt) + damping;运动分解
运动比较复杂,但是可以简单的拆解为X轴运动和Y轴运动,把运动简单化。
- Y轴
阻尼系数:
typescript this.linear_Damping = this.RigidBody.linearDamping;
加速度为物理世界重力*刚体的重力缩放(PTM_RATIO为单位换算比):
typescript let world_y = cc.director.getPhysicsManager().gravity.y; this.a_y =(-this.RigidBody.gravityScale * world_y) /cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO;
速度为物体初始速度(PTM_RATIO为单位换算比):
typescript this.v_y =-this.RigidBody.linearVelocity.y / cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO;
刚体Y轴位置:
typescript this.y = this.RigidBody.node.y;
经过dt时间,物体Y轴运动为(PTM_RATIO为单位换算比):
typescript this.y -= this.s(this.v_y, this.a_y, dt)*cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO; let damping = -this.linear_Damping * this.v_y * dt; this.v_y = this.v(this.v_y, this.a_y, dt) + damping;
- X轴
同理...
关键代码
const { ccclass, property } = cc._decorator;
@ccclass
export default class RigidBodyaPrediction extends cc.Component {
@property(cc.RigidBody)
RigidBody: cc.RigidBody = null;
@property(cc.Prefab)
show_prefab: cc.Prefab = null;
@property(cc.Node)
result: cc.Node = null;
//米/秒^2
a_y = 0;
a_x = 0;
//米/秒
v_y = 0;
v_x = 0;
//位置
x = 0;
y = 0;
//阻尼
linear_Damping = 0;
status = true;
pool: cc.Node[] = new Array<cc.Node>();
onLoad() {
for (let index = 0; index < 25; index++) {
let tmp = cc.instantiate(this.show_prefab);
this.pool.push(tmp);
this.result.addChild(tmp);
}
}
init() {
let world_y = cc.director.getPhysicsManager().gravity.y;
let world_x = cc.director.getPhysicsManager().gravity.x;
this.a_y =
(-this.RigidBody.gravityScale * world_y) /
cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO;
this.a_x =
(this.RigidBody.gravityScale * world_x) /
cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO;
this.v_y =
-this.RigidBody.linearVelocity.y / cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO;
this.v_x =
this.RigidBody.linearVelocity.x / cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO;
this.x = this.RigidBody.node.x;
this.y = this.RigidBody.node.y;
this.linear_Damping = this.RigidBody.linearDamping;
}
start() {
this.RigidBody.node.on(
cc.Node.EventType.TOUCH_CANCEL,
function() {
this.RigidBody.type = cc.RigidBodyType.Dynamic;
this.status = false;
},
this
);
this.RigidBody.node.on(
cc.Node.EventType.TOUCH_MOVE,
function(event: cc.Touch) {
let vec2 = this.RigidBody.node.convertToNodeSpaceAR(
event.getLocation()
);
this.RigidBody.linearVelocity = new cc.Vec2(
-vec2.x,
-vec2.y * 2
);
},
this
);
}
show() {
this.init();
this.node.removeChild(this.RigidBody.node, false);
this.node.addChild(this.RigidBody.node, 9999);
for (let index = 0; index < 25; index++) {
let tmp = this.pool[index];
tmp.x = this.x;
tmp.y = this.y;
this.updatePostion(0.15);
}
}
updateX(dt) {
this.x += this.s(this.v_x, this.a_x, dt) * cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO;
let damping = -this.linear_Damping * this.v_x * dt;
this.v_x = this.v(this.v_x, this.a_x, dt) + damping;
}
updateY(dt) {
this.y -= this.s(this.v_y, this.a_y, dt) * cc.PhysicsManager.PTM_RATIO;
let damping = -this.linear_Damping * this.v_y * dt;
this.v_y = this.v(this.v_y, this.a_y, dt) + damping;
}
updatePostion(dt) {
this.updateX(dt);
this.updateY(dt);
}
v(v0, a, t) {
return v0 + a * t;
}
s(v0, a, t) {
return v0 * t + (a * t * t) / 2;
}
update() {
if (this.status) {
this.show();
}
}
}