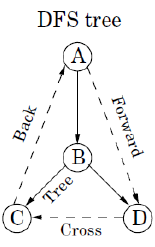
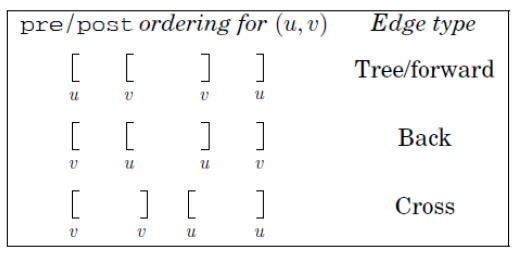
DFS算法:
explore(G, v) visited(v) = true
previsit(v) for each edge(v, u) in E: if not visited(u): explore(u) postvisit(v)
dfs(G) for all v in V: visited(v) = false for all v in V: if not visited(v): explore(v)
应用:
1) 判断顶点u与v之间是否存在路径
2) 判断一个无向图是否连通
112. Path Sum
Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.

解题思路:
深度优先。使用递归的方式写。直接贴代码,简单易懂。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if (root == NULL)
return false;
if (root->val == sum && root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return true;
return hasPathSum(root->left, sum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, sum - root->val);
}
};
类似的一道题:
129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers

解题思路:走到叶子节点的时候加上cur值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumNumbers(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
sum = 0;
dfs(root, 0);
return sum;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int curSum) {
int cur = curSum * 10 + root->val;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
sum += cur;
if (root->left != NULL)
dfs(root->left, cur);
if (root->right != NULL)
dfs(root->right, cur);
}
private:
int sum;
};
类似的题:
257. Binary Tree Paths

解题思路:
在叶子节点时将nums转换为string放入path中。注意,因为每个节点的值都压栈了,所以每个压入nums的值,最后都要出栈,不然打印路径时会有重复。
数字转字符串:sprintf
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return path;
vector<int> nums;
dfs(root,nums);
return path;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<int> nums) {
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
nums.push_back(root->val);
string str="";
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (i != 0)
str += "->";
char arr[10];
sprintf(arr, "%d", nums[i]);
str += arr;
}
path.push_back(str);
nums.pop_back();
}
if (root->left != NULL) {
nums.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->left, nums);
nums.pop_back();
}
if (root->right != NULL) {
nums.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->right, nums);
nums.pop_back();
}
}
private:
vector<string> path;
};
拓扑排序:
1) Find a source, output it, and delete it from the graph. Repeat until the graph is empty.
2) dfs and sort with post[u] in descending order: TOPOLOGICAL-SORT(G)
1 call DFS(G) to compute finishing times post[v] for each vertex v
2 as each vertex is finished, insert it onto the front of a linked list
3 return the linked list of vertices