For a permutation P[1... N] of integers from 1 to N, function f is defined as follows:
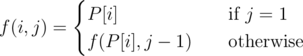
Let g(i) be the minimum positive integer j such that f(i, j) = i. We can show such j always exists.
For given N, A, B, find a permutation P of integers from 1 to N such that for 1 ≤ i ≤ N, g(i) equals either A or B.
Input
The only line contains three integers N, A, B (1 ≤ N ≤ 106, 1 ≤ A, B ≤ N).
Output
If no such permutation exists, output -1. Otherwise, output a permutation of integers from 1 to N.
Examples
input
Copy
9 2 5
output
6 5 8 3 4 1 9 2 7
input
Copy
3 2 1
output
1 2 3
Note
In the first example, g(1) = g(6) = g(7) = g(9) = 2 and g(2) = g(3) = g(4) = g(5) = g(8) = 5
In the second example, g(1) = g(2) = g(3) = 1
这题就是求 Ax+By=N 是否存在非负解,且 x,y解就是A,B的组数,每组将最前面的数丢到最后即可
扩展欧几里得求不定方程
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; #define inf 2147483647 const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fll; #define ri register int template <class T> inline T min(T a, T b, T c) { return min(min(a, b), c); } template <class T> inline T max(T a, T b, T c) { return max(max(a, b), c); } template <class T> inline T min(T a, T b, T c, T d) { return min(min(a, b), min(c, d)); } template <class T> inline T max(T a, T b, T c, T d) { return max(max(a, b), max(c, d)); } #define scanf1(x) scanf("%d", &x) #define scanf2(x, y) scanf("%d%d", &x, &y) #define scanf3(x, y, z) scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z) #define scanf4(x, y, z, X) scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z, &X) #define pi acos(-1) #define me(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x)); #define For(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++) #define FFor(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i >= b; i--) #define bug printf("*********** "); #define mp make_pair #define pb push_back const int N = 1000005; // name******************************* ll n,a,b; ll x0,y0; // function****************************** ll exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll &y) { if(b==0) { x=1; y=0; return a; } ll g=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y); ll t=x; x=y; y=t-(a/b)*y; return g; } //*************************************** int main() { // ios::sync_with_stdio(0); // cin.tie(0); // freopen("test.txt", "r", stdin); // freopen("outout.txt","w",stdout); cin>>n>>a>>b; ll g=exgcd(a,b,x0,y0); ll k1=x0*n/g,k2=y0*n/g; ll t=1; ll a1=a,b1=b; a/=g; //求通解时这里的a,b一定要除以最大公约数!!! b/=g; if(n%g) { cout<<-1; return 0; } if(k1<0) { t=(-k1)/b; if((-k1)%b)t++; if(k2-a*t<0) { cout<<-1; return 0; } k1+=b*t; k2-=a*t; } if(k2<0) { t=(-k2)/a; if((-k2)%a)t++; if(k1-b*t<0) { cout<<-1; return 0; } k2+=a*t; k1-=b*t; } queue<ll>q; For(i,1,n) { q.push(i); } For(i,1,k1) { ll x=q.front(); q.pop(); For(j,1,a1-1) { cout<<q.front()<<" "; q.pop(); } cout<<x<<" "; } For(i,1,k2) { ll x=q.front(); q.pop(); For(j,1,b1-1) { cout<<q.front()<<" "; q.pop(); } cout<<x<<" "; } return 0; }