快速排序
原理是找出一个元素(理论上可以随便找一个)作为基准(pivot),然后对数组进行分区操作,使基准左边元素的值都不大于基准值,基准右边的元素值 都不小于基准值,如此作为基准的元素调整到排序后的正确位置。递归快速排序,将其他n-1个元素也调整到排序后的正确位置。最后每个元素都是在排序后的正 确位置,排序完成。所以快速排序算法的核心算法是分区操作,即如何调整基准的位置以及调整返回基准的最终位置以便分治递归。
冒泡排序算法
原理是临近的数字两两进行比较,按照从小到大或者从大到小的顺序进行交换,
这样一趟过去后,最大或最小的数字被交换到了最后一位,
然后再从头开始进行两两比较交换,直到倒数第二位时结束
双向冒泡排序算法
以整数升序排序为例来简单说明一下双向冒泡排序的过程:首先从前往后把最大数移到最后,然后反过来从后往前把最小的一个数移动到数组最前面,这一过程就是第一轮,然后重复这一过程,最终就会把整个数组从小到大排列好。双向冒泡排序要稍微优于传统的冒泡排序,因为双向排序时数组的两头都排序好了,我们只需要处理数组的中间部分即可,而单向即传统的冒泡排序只有尾部的元素是排好序的,这时每轮处理都需要从头一直处理到已经排好序元素的前面一个元素。虽然它在效率上有了点改进,但它也不能大幅度提高其排序的效率,这是由冒泡排序的基本过程所决定了的。在此基础上改进了一下,下面的代码可以实现对奇数偶数分别排序
源代码:

1 package com.zc.manythread; 2 3 public class Sort implements Runnable{ 4 int[] date; 5 public Sort (int[] date) { 6 super(); 7 this.date=date; 8 } 9 public void sort() { 10 throw new RuntimeException("please do it in subclass"); 11 } 12 @Override 13 public void run() { 14 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 15 long start=System.nanoTime(); 16 sort(); 17 long end=System.nanoTime(); 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行时间:"+(end-start)+"ns"); 19 } 20 21 }

package com.zc.manythread; /** * 快速排序 * @author Administrator * */ public class QSort extends Sort{ public void sort() { try { } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception e.printStackTrace(); } } public QSort(int[] date) { super(date); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } private void swap(int a[],int i,int j) { int T; T=a[i]; a[i]=a[j]; a[j]=T; } /******************* * * @param a * @param lo0 * @param hi0 * @return */ int[] QuickSort(int a[],int lo0,int hi0){ int lo=lo0; int hi=hi0; int mid; if (hi0>lo0) { mid=a[(hi0+lo0)/2]; while(lo<=hi){ while((lo<hi0)&&(a[lo]<mid)) ++lo; while((hi>lo0)&&(a[hi]>mid)) --hi; if (lo<=hi) { swap(a,lo,hi); ++lo; --hi; } } if (lo0<hi) { QuickSort(a, lo0, hi); } if (lo<hi0) { QuickSort(a, lo, hi0); } } return a; } /************** * * 创建数组数据 * *****************/ private static int[] createDate(int count) { int[] data=new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { data[i]=(int)(Math.random()*count); } return data; } /**************主函数*****************/ public static void main(String[] args) { final int count=100; int[] data=createDate(count); for (int n:data) { System.out.print(n+" "); } QSort data1=new QSort(data); System.out.println(); int[] a=data1.QuickSort(data,0, count-1); for (int n:a) { System.out.print(n+" "); } } }

1 package com.zc.manythread; 2 /** 3 * 冒泡排序 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 8 public class BSrot extends Sort{ 9 10 public void sort() { 11 try { 12 sort(date); 13 } catch (Exception e) { 14 // TODO: handle exception 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 public int[] sort(int[] a)throws Exception{ 19 for (int i = a.length; --i>=0;) { 20 boolean swapped=false; 21 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 22 if (a[j]>a[j+1]) { 23 int T=a[j]; 24 a[j]=a[j+1]; 25 a[j+1]=T; 26 swapped=true; 27 } 28 } 29 if (!swapped) { 30 return a; 31 } 32 } 33 return a; 34 } 35 public BSrot(int[] date) { 36 super(date); 37 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 38 } 39 40 }

1 package com.zc.manythread; 2 /** 3 * 双向冒泡排序 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class BBSort extends Sort{ 8 9 public BBSort(int[] date) { 10 super(date); 11 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 12 } 13 14 public void sort() { 15 try { 16 sort(date); 17 } catch (Exception e) { 18 // TODO: handle exception 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 22 } 23 24 void sort(int[] a)throws Exception{ 25 int j; 26 int limit=a.length; 27 int st=-1; 28 while(st<limit){ 29 st++; 30 limit--; 31 boolean swapped=false; 32 for (j = st ; j < limit; j++) { 33 if (a[j]>a[j+1]) { 34 int T=a[j]; 35 a[j]=a[j+1]; 36 a[j+1]=T; 37 swapped=true; 38 } 39 } 40 41 if (!swapped) { 42 return; 43 }else { 44 swapped=false; 45 for (j = limit; --j>=st;) { 46 if(a[j]>a[j+1]){ 47 int T=a[j]; 48 a[j]=a[j+1]; 49 a[j+1]=T; 50 swapped=true; 51 } 52 } 53 if (!swapped) { 54 return; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 60 }

1 package com.zc.manythread; 2 3 public class MainTest { 4 5 private static int[] createDate(int count) { 6 int[] data=new int[count]; 7 for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { 8 data[i]=(int)(Math.random()*count); 9 } 10 return data; 11 } 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 final int count=10000; 14 int[] data=createDate(count); 15 16 Thread qsort=new Thread(new QSort(data),"快速排序"); 17 int[] data2=new int[count]; 18 System.arraycopy(data,0,data2,0,count); 19 Thread bsort=new Thread(new BSrot(data2),"冒泡排序"); 20 int[] data3=new int[count]; 21 System.arraycopy(data,0,data3,0,count); 22 Thread bbsort=new Thread(new BBSort(data3),"双向排序"); 23 qsort.start(); 24 bsort.start(); 25 bbsort.start(); 26 } 27 }
运行结果:
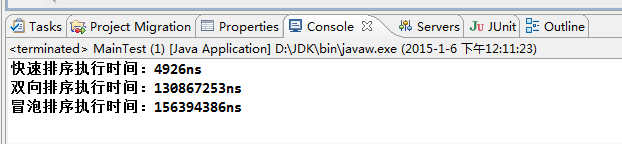
从结果来看 可以知道快速排序 效率更快!
