unit3 流
1.File类:java.io.File包,Serializable和Comparable接口。与系统无关的类。
file:文件 directory:文件夹、目录 path:路径
静态成员变量:

绝对路径,相对路径:
![]()
构造方法:
File parent1 = new File("C:\");
File file = new File("hello.java");
File f = new File(parent,child);
File f = new File("F:\test\only.txt");
获取方法:

判断功能:

创建删除:


File c = new File("F:\test\sjw.txt");
try {
boolean d = c.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(c);
删除直接在硬盘删除,不走回收站,所以慎重。可以删除文件和文件夹。
文件遍历:

File c = new File("F:\test");
String[] arr = c.list();
for (String fileName : arr) {
System.out.println(fileName);
File c = new File("F:\test");
File[] files = c.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file);
递归概念:

//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.StackOverflowError
例子,求和:
public static int sum(int n) {
if(n == 1){
return 1;
}
return n + sum(n-1);
}
例子,递归打印多级目录:
public static void getAllFile(File dir){
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file);
}
}
例子,文件搜索:文件过滤器:
private static void getAllFile(File dir) {
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for(File f:files){
if(f.isDirectory()){
getAllFile(f);
}else{
f.getName();
System.out.println(f);
}
}
}
文件过滤器具体运用:FileFilterImpl过滤器实现类,,,,FileNameFilter匿名内部类

2.IO概述:java.io包下
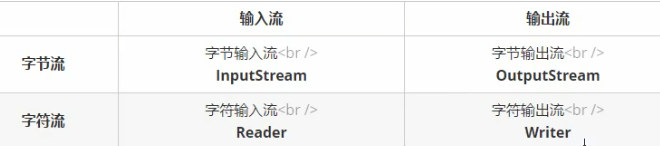
字节流:字节输出流,字节输入流
A:字节输出流:把内存数据写入硬盘文件中去



public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建对象,构造方法传递写入数据目的地
FileOutputStream f = new FileOutputStream("F:\test\only.txt");
//2.调用write方法
f.write(Integer.parseInt("22"));
//3.释放资源
f.close();
}
B:字节输入流:读取出内存数据


//1.创建对象,绑定数据源
FileInputStream f = new FileInputStream("F:\\test\\only.txt");
//2.read方法读取
int len = f.read();
System.out.println(len);
//循环遍历读取
int len1 = 0;
while( (len1 = f.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)len1);
}
//3.释放资源
f.close();
复制粘贴文件:
//创建对象
FileInputStream f = new FileInputStream("F:\test\only.txt");
FileOutputStream f1 = new FileOutputStream("F:\test\onlycopy.txt");
//读取
int len = 0;
while ((len = f.read()) != -1 ) {
//打印输出
f1.write(len);
}
//资源释放:先关闭写的,后关闭读的
f.close();
f1.close();
字符流:字节流读取中文产生乱码,所以改用字符流读写中文
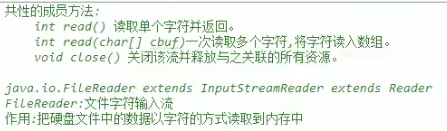
A,字符输入流:java.io.Reader

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader f = new FileReader("F:\test\onlycopy.txt");
int len = 0;
while ((len = f.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char)len);
}
f.close();
}
B,字符输出流:java.io.Writer


public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
FileWriter f = new FileWriter("F:\test\new.txt");
f.write(97);
//f.flush();
f.close();
//flush和close,都可以刷新写入字符
}
使用try--catch,finally处理异常,不用 throw exception
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter f = null;
try {
//可能产生异常的代码
f = new FileWriter
("F:\test\only.txt", true);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
f.write("hello,sjw" + i + " ");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
//异常处理逻辑
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//一定执行的代码
try {
//申明抛出异常对象
f.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.字节输出流
4.字节输入流
5.缓冲流:高效读写
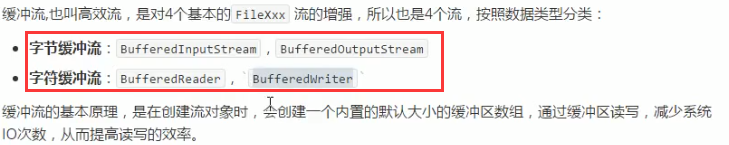
都是继承关系,也继承成员方法和构造方法
BufferedWriter:字符缓冲输出流

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter b = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("F:\test\1.doc"));
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
b.write("writer");
b.newLine();//===b.write(" ");
}
b.flush();
b.close();
}
BufferedReader:字符缓冲输入流
特有方法:String readLine() 读一行文本
BufferedOutputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建文件输出流对象,确定写入的文件地址
FileOutputStream f = new FileOutputStream("F:\test\shuang.txt");
//创建数据缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream b = new BufferedOutputStream(f);
b.write("数据写入到内部缓冲区中".getBytes());//写入内容
b.flush();//刷新
b.close();//关闭
}
BufferedInputStream:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream f = new FileInputStream("F:\test\shuang.txt");
BufferedInputStream b = new BufferedInputStream(f);
// int len = 0;
// while((len = b.read()) != -1){
// System.out.println(len);
// } //逐个读取
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = b.read(bytes)) != -1){
System.out.println(len);
} //一起读取
b.close();
}
缓冲流效率测试:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
//创建字节缓冲输入流对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("F:\test\1.jpg"));
//创建字节缓冲输出流对象
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("F:\11.jpg"));
int len = 0;
//读出
while ((len = bis.read())!=-1){
//写入
bos.write(len);
}
//释放资源
bos.close();
bis.close();
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("复制文件耗时:" + (e-s) + "ms");
}
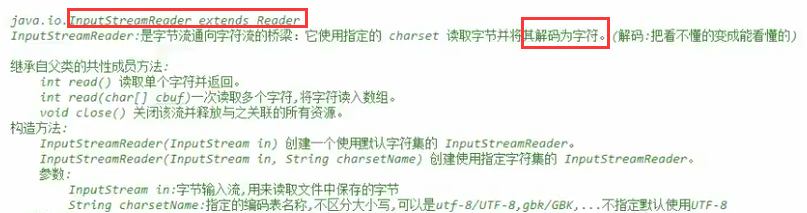
6.转换流:转换编码 ,可以指定编码表进行转换


编码的问题:只能读取UTF-8(默认格式)
A:文本txt----》字节输入流FileInpStream----》FileReader----》字节转换为字符:解码 乱码
B:文本txt----》字节输入流FileInpStream----》InpStreamReader----》字节转换为字符 不是乱码


private static void write_utf_8() throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter o = new OutputStreamWriter
(new FileOutputStream("F:\test\utf_8.txt"), "utf-8");
o.write("你好");
o.flush();
o.close();
}

private static void read_utf_8 () throws IOException {
InputStreamReader o = new InputStreamReader
(new FileInputStream("F:\test\utf_8.txt"), "utf-8");
int len = 0;
while((len = o.read()) != -1){
System.out.println(len);
}
o.close();
}
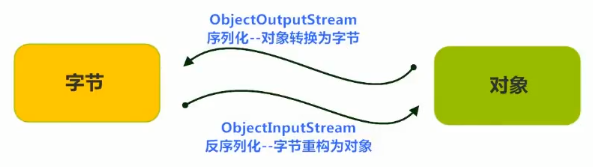
7.序列化流:对象以流的方式写入到文件中存储,也叫做对象的序列化
ObjectOutputStream:writeObject() 将对象写入文件中
ObjectInputStream:readObject() 读取对象,是对象的反序列化

public class Person implements Serializable
序列化:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream o = new ObjectOutputStream
(new FileOutputStream("F:\test\person.txt"));
o.writeObject(new Person("sjw",12));
o.close();
}
反序列化:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream o = new ObjectInputStream
((new FileInputStream("F:\test\person.txt")));
Object obj = o.readObject();
o.close();
System.out.println(obj);
//Person{name='sjw', age=12}
//结合ObjectOutputStream
}
瞬态关键字:不能被序列化

8.打印流:用来打印,java.io.PrintStream,只负责输出


PrintStream p = new PrintStream("F:\test\only.txt");
p.println("22");
p.close();
9.补充:Pproperties集合





Properties p = new Properties();
p.setProperty("sjw","11");
p.setProperty("linzi","15");
//取出键,存到set集合
Set<String> s = p.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : s) {
String value = p.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
=================================================
Properties p = new Properties();
p.setProperty("sjw","11");
p.setProperty("linzi","15");
FileWriter f = new FileWriter("F:\test\linzi.txt");
try {
p.store(f,"save data");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
f.close();
==================================================
Properties p = new Properties();
p.load(new FileReader("F:\test\linzi.txt"));
Set<String> s = p.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : s) {
String value = p.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}