栈结构具有后进先出的特点,是程序设计中的有用工具
我们先来看看进制转换的过程 如图:
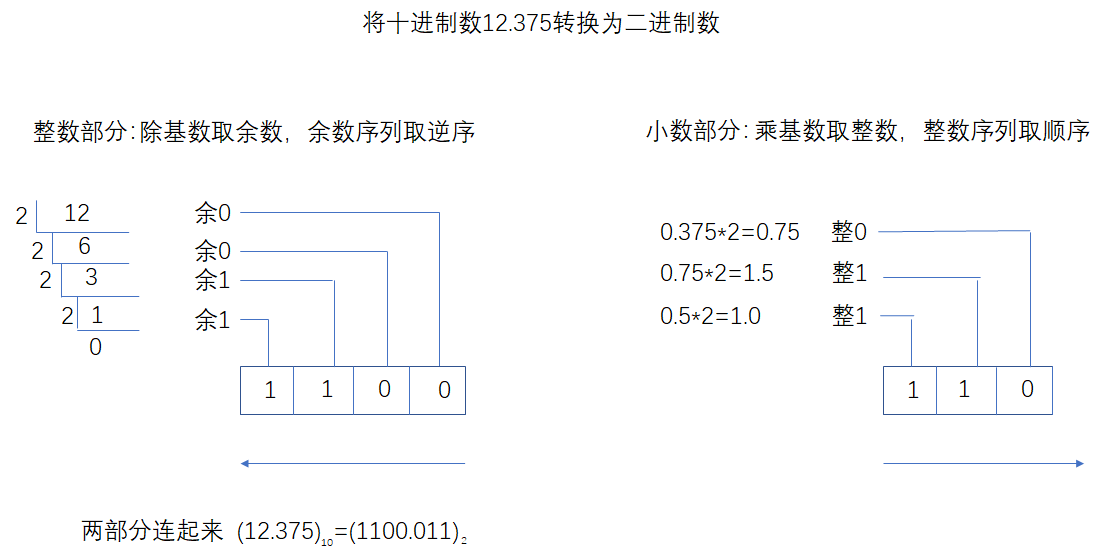
可以看出 整数部分符合后进先出的特点,可以应用栈结构
小数部分先进先出,可以应用线性表
栈的头文件 sqstack.h
1 #pragma once 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #define STACK_INIT_SIZE 100//储存空间初始分配量 5 #define STACKINCREMENT 10//存储空间分配增量 6 #define OK 1 7 #define ERROR 0 8 typedef int StackType; //栈元素类型 9 10 typedef struct { 11 StackType *base; //在构造之前和销毁之后,base的值为NULL 12 StackType *top; //栈顶指针 13 int stacksize; //当前已分配的存储空间,以元素为单位 14 }SqStack; //顺序栈 15 16 //栈的初始化 17 int InitStack(SqStack *p) { 18 19 20 p->base = (StackType*)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(StackType)); 21 if (p->base == NULL) return ERROR; //内存分配失败 22 p->top = p->base; //栈顶与栈底相同表示一个空栈 23 p->stacksize = STACK_INIT_SIZE; 24 return OK; 25 26 } 27 //判断栈是否为空 28 int EmptyStack(SqStack *p) { 29 //若为空栈 则返回OK,否则返回ERROR 30 if (p->top == p->base) return OK; 31 else return ERROR; 32 } 33 //顺序栈的压入 34 int Push(SqStack *p, StackType e) { 35 //插入元素e为新的栈顶元素 36 if ((p->top - p->base) >= p->stacksize) //栈满,追加储存空间 37 { 38 p->base = (StackType*)realloc(p->base, (p->stacksize + STACKINCREMENT) * sizeof(StackType)); 39 if (p->base == NULL) return ERROR;// 储存空间分配失败 40 p->top = p->base + p->stacksize; 41 p->stacksize += STACKINCREMENT; 42 } 43 *(p->top) = e; 44 (p->top)++; 45 return OK; 46 } 47 // 顺序栈的弹出 48 int Pop(SqStack *p, StackType *e) { 49 //若栈不空,则删除p的栈顶元素,用e返回其值 50 if (p->top == p->base) return ERROR; 51 --(p->top); 52 *e = *(p->top); 53 return OK; 54 55 56 } 57 //顺序栈的销毁 58 int DestroyStack(SqStack *p) { 59 //释放栈底空间并置空 60 free(p->base); 61 p->base = NULL; 62 p->top = NULL; 63 p->stacksize = 0; 64 65 return OK; 66 }
线性表的头文件 sqlist.h
#pragma once //顺序线性表 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define LIST_INIT_SIZE 100 //线性表储存空间的初始分配量 #define LISTINCREMENT 10 //线性表储存空间的分配增量 #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 typedef double ElemType; typedef struct { ElemType *elem; //储存空间基地址 int length; //当前长度 int listsize; //当前分配的储存容量(以sizeof(ElemType))为单位 }SqList; //顺序表的初始化 void InitList(SqList *L) { L->elem = (ElemType*)malloc(LIST_INIT_SIZE); if (!L->elem) //储存分配失败 exit(-1); L->length = 0; //空表长度为0 L->listsize = LIST_INIT_SIZE; //初始储存容量 } //判断表是否为空 int EmptyList(SqList *L) { if (L->length == 0) { return OK; } return ERROR; } //尾插 int BackInsert(SqList *L,ElemType e) { ElemType *newbase, *p; if (L->length >= L->listsize) //当前储存空间已满,增加分配 { newbase = (ElemType*)realloc(L->elem, (L->listsize + LISTINCREMENT) * sizeof(ElemType)); if (!newbase) exit(-1); L->elem = newbase; //新基地址 L->listsize += LISTINCREMENT; //增加储存容量 } p = L->elem + L->length; //p指向最后一个元素的后一个地址 *p = e; //插入e L->length++; //表长加1 return OK; } //打印表中元素 void PrintList(SqList *L) { int i; if (EmptyList(L)==OK) { printf("表为空! "); exit(-1); } for (i = 0; i< L->length; i++) { printf("%d ",*( L->elem+i)); } printf(" "); } //销毁表 int DestoryList(SqList *L) { free(L->elem); return OK; }
源代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <math.h> 4 #include "sqstack.h" //引入顺序栈储存结构及其基本操作 5 #include "sqlist.h" //引入顺序表储存结构及其基本操作 6 #define OK 1 7 #define ERROR 0 8 9 //对于输入任意一个非负的十进制数,打印与其等值的N进制数 10 void Conversion(int N) { 11 double x, decimal; 12 int integer; 13 scanf("%lf", &x); 14 integer =(int)floor(x); //整数部分 15 decimal = x - integer; //小数部分 16 //处理整数部分 17 18 StackType *e; 19 SqStack *ps, s; 20 ps = &s; 21 e = (StackType*)malloc(sizeof(StackType)); //为指针e分配内存地址 22 InitStack(ps); //初始化栈 23 while (integer) //当integer不等于0 24 { 25 Push(ps, integer % N); //压入integer 除以N的余数 26 integer = integer / N; 27 } 28 while (EmptyStack(ps) != OK) //当栈不为空 29 { 30 Pop(ps, e); //弹出的栈顶元素,并让e指向其地址 31 printf("%d ", *e); // 输出e 每一个数码间用空格隔开 32 } 33 //处理小数部分 34 if (decimal) { //小数部分不为0 才处理 35 SqList *L; 36 ElemType m; 37 L = (SqList*)malloc(sizeof(SqList)); //为指针L分配内存地址 38 InitList(L); //初始化顺序表 39 while (decimal) //当decimal不为0 40 { 41 m = (ElemType)floor(decimal*N); 42 BackInsert(L, m); //插入decimal*N的整数 43 decimal = decimal * N - m; 44 } 45 printf(". "); 46 PrintList(L); //每一个数码之间用空格隔开 47 } 48 } 49 int main() { 50 int N; 51 printf("请输入目标进制:"); 52 scanf("%d", &N); 53 printf("将十进制数n转换为%d进制数,请输入:n(>=0)=", N); 54 Conversion(N); 55 return 0; 56 57 }
合理的使用数据结构可以使代码跟易读,易懂。栈的引入
简化了程序设计的问题,划分了不同的关注层次,逻辑思路清晰。