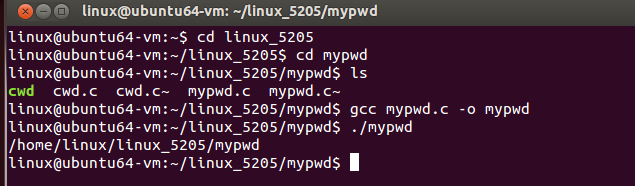
mypwd
学习pwd命令
- pwd的作用:以绝对路径显示当前目录,目录使用/分隔,第一个/表示根目录,最后一个/表示当前目录
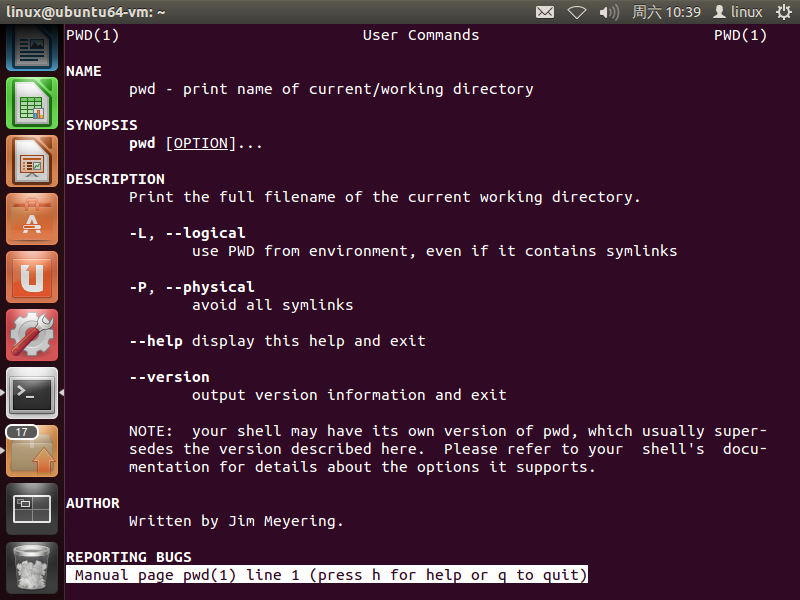
通过man学习pwd
mypwd的实现
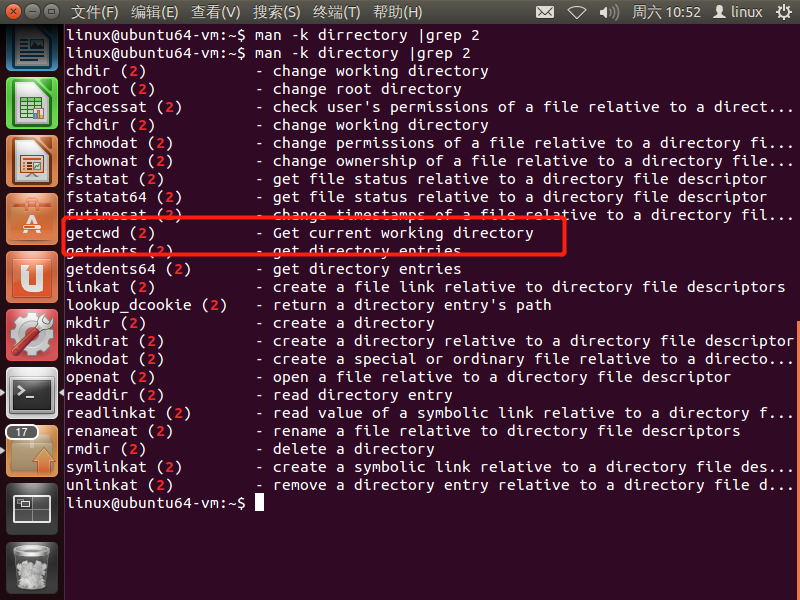
通过(man -k;grep)查看需要的系统调用
-
找到getcwd函数
-
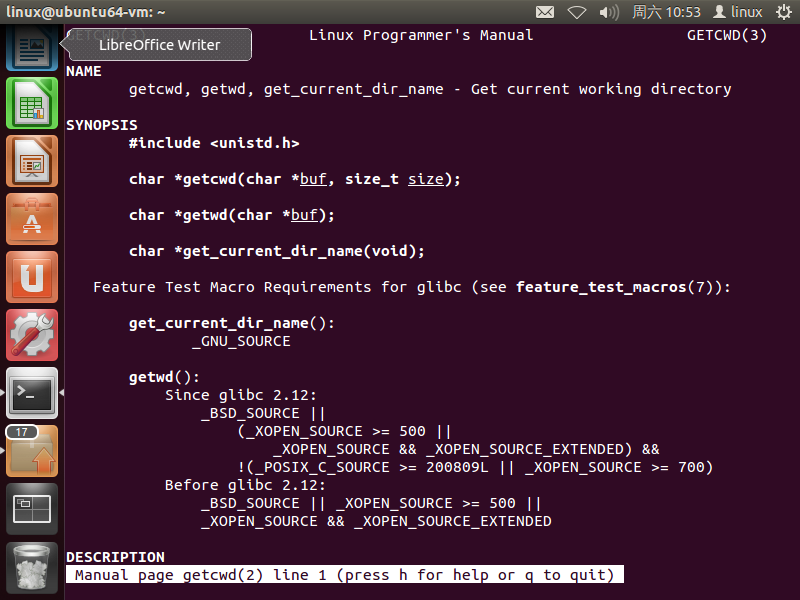
通过man 2 getcwd查看函数结构
-
根据
getcwd函数的功能发现,这个函数可以直接得到当前路径,若直接使用这个函数,则只要getcwd的返回值不为空,就输出返回值 -
代码
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define MAX 2048 int main() { char buf[MAX],*a=getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf)); if(a==NULL) printf("Error!"); else printf("%s ",a); return 0; } -
测试
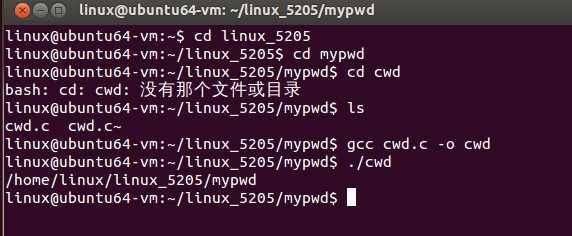
但是根据老师上课讲的i节点来做这一题又是不一样的写法
-
通过man -k directory | grep 3查看相关库函数
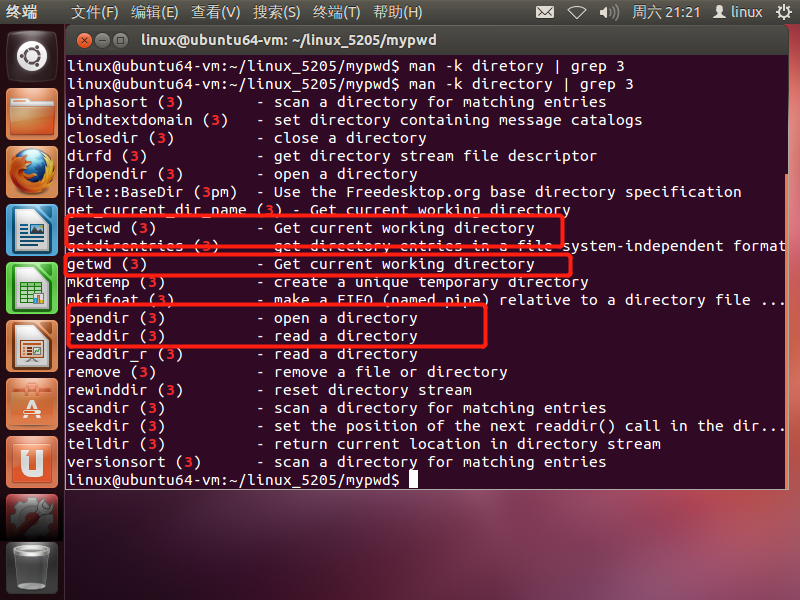
-
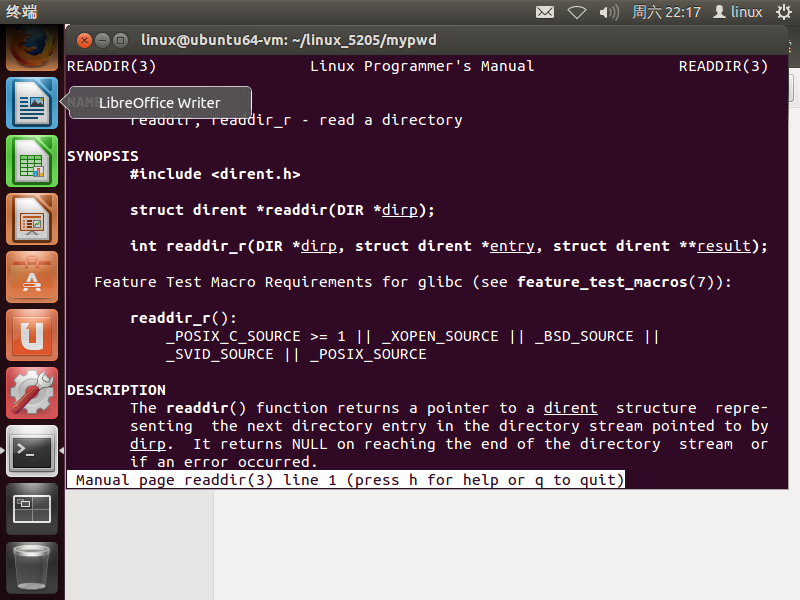
getwd和getcwd功能相同不再查看。学习一下opendir()和readdir()函数
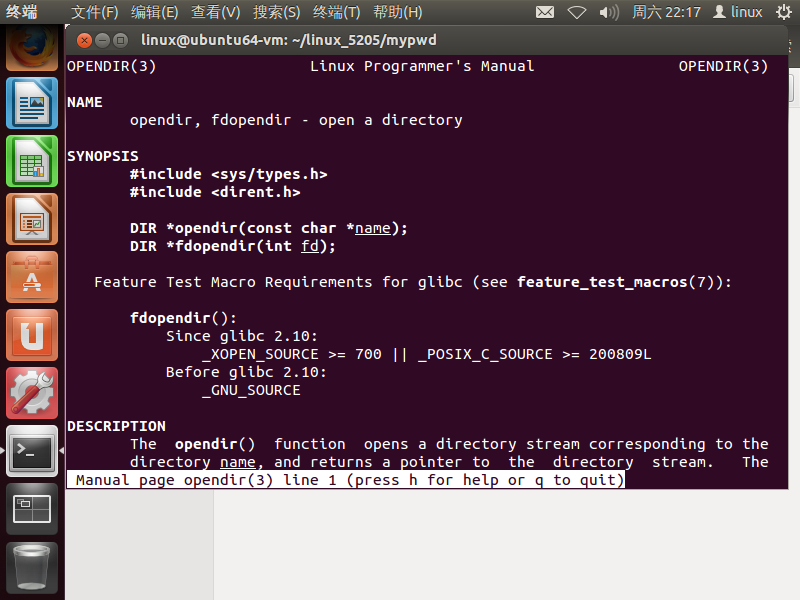
- opendir()函数
- readdir()函数
- 其中可以看到`readdir()`中的结构体
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */
off_t d_off; /* not an offset; see NOTES */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported
by all filesystem types */
char d_name[256]; /* filename */
};
- 可见需要得到`i-node`才能得到文件名,通过百度知道需要使用`stat`函数
- 准备工作结束,通过上课,知道需要当前目录的上一级目录是`..`才能结束寻找上一级目录的路径,写出伪代码:
设置一个char型数组(或指针)用于保存当前绝对路径内容,无符号数用于记录绝对路径的深度;
while(1)
{
分别获取"."(当前目录)和".."(当前目录的上一级目录)i-node;
if("."i-node==".."i-noode)
输出目录信息;
else
{
切换至父级目录获取i-node
在父级目录中搜索对应的文件名并记录下来
}
}
-
完整代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <dirent.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> //获取文件的inode-number ino_t get_ino_byname(char *filename) { struct stat file_stat; if(0 != stat(filename, &file_stat)) //stat()通过文件名filename获取文件信息,并保存在buf所指的结构体stat中 { perror("stat"); exit(-1); } return file_stat.st_ino; } //根据inode-number, 在当前目录中查找对应文件名 char *find_name_byino(ino_t ino) { DIR *dp = NULL; struct dirent *dptr = NULL; char *filename = NULL; if(NULL == (dp = opendir("."))) //opendir()打开一个目录,在失败的时候返回一个空的指针,成返回DIR结构体 { fprintf(stderr, "Can not open Current Directory "); exit(-1); } else { while(NULL != (dptr = readdir(dp))) //readdir()用来读取目录。返回是dirent结构体指针 { if(dptr->d_ino == ino) { filename = strdup(dptr->d_name); //strdup()将串拷贝到新建的位置处,返回一个指针,指向为复制字符串分配的空间;如果分配空间失败,则返回NULL值. break; } } closedir(dp); } return filename; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { //记录目名的栈 char *dir_stack[256]; unsigned current_depth = 0; while(1) { ino_t current_ino = get_ino_byname("."); //通过"."获取当期目录inode ino_t parent_ino = get_ino_byname(".."); //通过".."获取当前目录的父目录的inode if(current_ino == parent_ino) break; //达到根目录,推出循环 /*若两个inode不一样*/ chdir(".."); //更改当前工作目录,变为当前目录的父目录 dir_stack[current_depth++] = find_name_byino(current_ino); //"文件名"地址存放 } int i = current_depth - 1; for(i = current_depth - 1; i >= 0; i--) //打印路径 { fprintf(stdout, "/%s", dir_stack[i]); } fprintf(stdout, "%s ", current_depth == 0 ? "/" : ""); return 0; } -
运行结果