三元运算符:
三元运算又叫三目运算,是对简单的条件语句的缩写。
书写格式:
n1 = 值1 if 条件 else 值2 # 如果条件成立,那么将 “值1” 赋值给n1变量,否则,将“值2”赋值给n1变量
基本数据类型之set:
set集合,是一个无序且不重复的元素集合。
set和dict类似,也是一组key的集合,但是它不存储value,由于key不能重复,所以在set中没有重复的key。
要创建一个set,需要提供一个list作为输入集合:
s = set([1, 2, 3])
print(s)
{1, 2, 3}

class set(object): """ set() -> new empty set object set(iterable) -> new set object Build an unordered collection of unique elements. """ def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Add an element to a set,添加元素 This has no effect if the element is already present. """ pass def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements from this set. 清楚内容""" pass def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a shallow copy of a set. 浅拷贝 """ pass def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. A中存在,B中不存在 (i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.) """ pass def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove all elements of another set from this set. 从当前集合中删除和B中相同的元素""" pass def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove an element from a set if it is a member. If the element is not a member, do nothing. 移除指定元素,不存在不保错 """ pass def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the intersection of two sets as a new set. 交集 (i.e. all elements that are in both sets.) """ pass def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. 取交集并更更新到A中 """ pass def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return True if two sets have a null intersection. 如果没有交集,返回True,否则返回False""" pass def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Report whether another set contains this set. 是否是子序列""" pass def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Report whether this set contains another set. 是否是父序列""" pass def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove and return an arbitrary set element. Raises KeyError if the set is empty. 移除元素 """ pass def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. 移除指定元素,不存在保错 """ pass def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. 对称交集 (i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.) """ pass def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. 对称交集,并更新到a中 """ pass def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return the union of sets as a new set. 并集 (i.e. all elements that are in either set.) """ pass def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Update a set with the union of itself and others. 更新 """ pass
深浅拷贝:
1.数字和字符串
对于数字和字符串 而言,赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址。
import copy # ######### 数字、字符串 ######### n1 = 123 # n1 = "i am alex age 10" print(id(n1)) # ## 赋值 ## n2 = n1 print(id(n2)) # ## 浅拷贝 ## n2 = copy.copy(n1) print(id(n2)) # ## 深拷贝 ## n3 = copy.deepcopy(n1) print(id(n3))
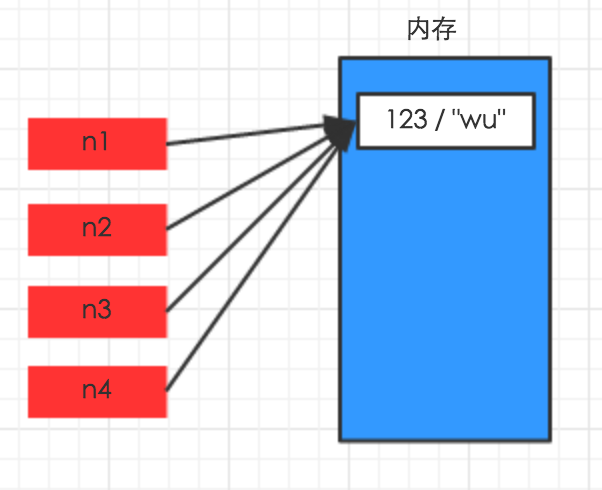
2.其他基本数据类型
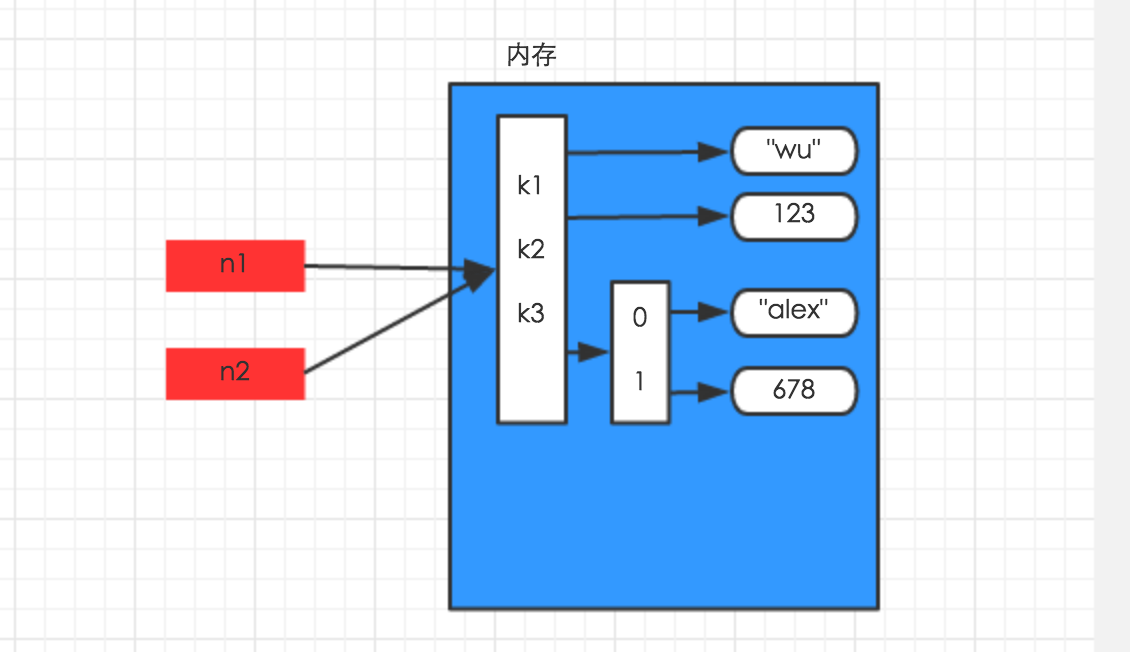
对于字典、元祖、列表而言,进行赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝时,其内存地址的变化是不同的。
- 赋值
n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]}
n2 = n1
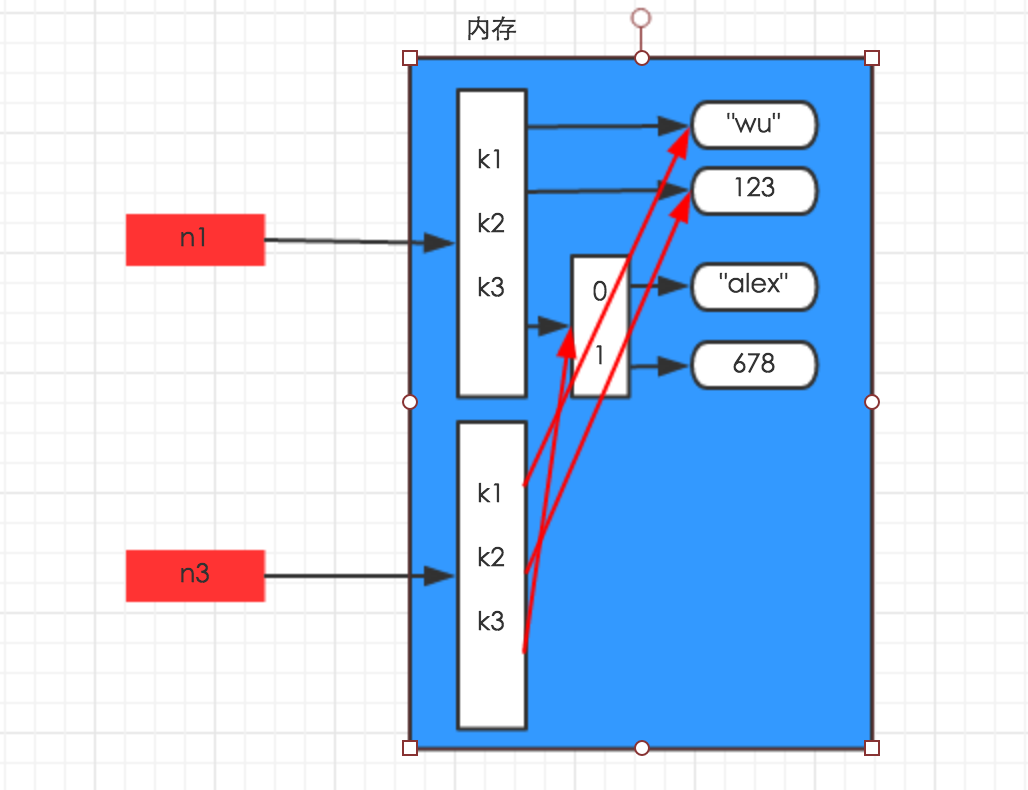
- 浅拷贝
浅拷贝:在内存中只额外创建第一层数据(其他的不考虑)
import copy
n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]}
n3 = copy.copy(n1)
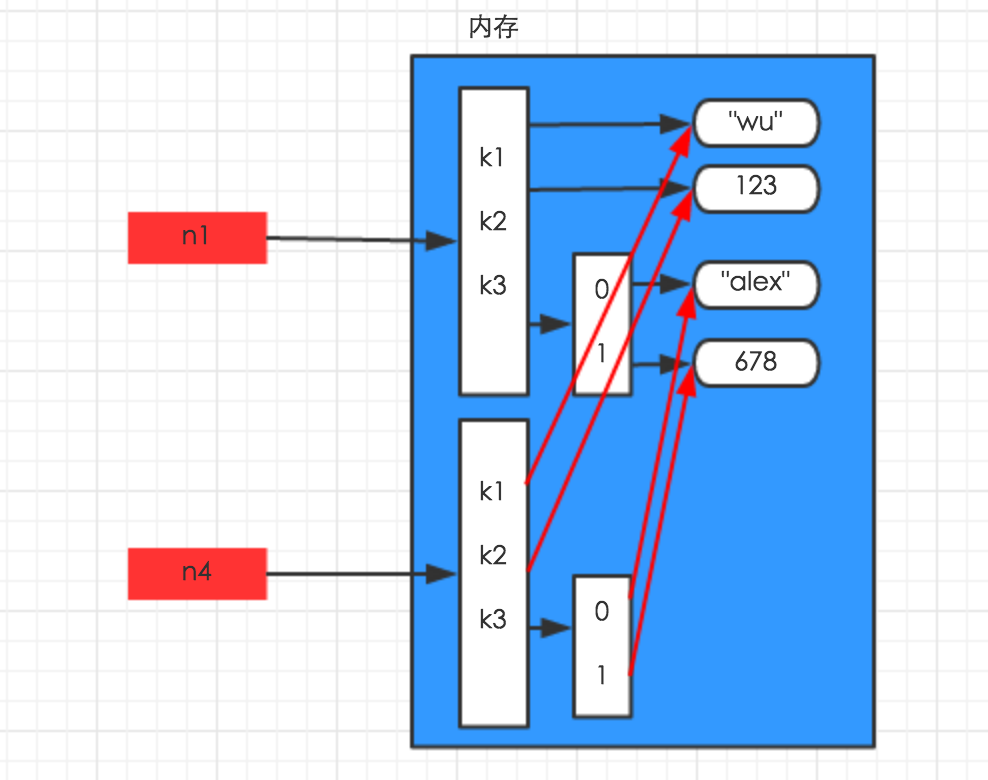
- 深拷贝
深拷贝,在内存中将所有的数据重新创建一份(排除最后一层,即:python内部对字符串和数字的优化),除了底层不一样其他的都一样。
import copy
n1 = {"k1": "wu", "k2": 123, "k3": ["alex", 456]}
n4 = copy.deepcopy(n1)
函数
函数是组织好的,可以重复使用的,用来实现单一、或者有关联功能的代码块。
函数能提高应用的模块性,和代码的重复利用率。
一、定义一个函数
你可以定义一个有自己想要功能的函数,定义函数的规则:
- 函数代码以def关键字开头,后接函数的标识符名称和():
- 所有出现的符号都是英文的符号
- 任何传入参数和自变量必须放在括号内,圆括号之间可以用于定义参数
- 函数的第一行语句可以选择性的使用文档字符串---用于存放函数说明
- 函数内容以冒号起始并且缩进
1、语法

2、实例
def printme( str ): "打印传入的字符串到标准显示设备上" print str return
3、函数调用
定义一个函数只给了函数一个名称,指定了函数里面的参数、代码块结构
这个函数的基本结构完成之后,你可以通过另一个函数进行调用。
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# 定义函数
def printme( str ):
"打印任何传入的字符串"
print str;
return;
# 调用函数
printme("我要调用用户自定义函数!");
printme("再次调用同一函数");
结果:
我要调用用户自定义函数! 再次调用同一函数
4、按值传递参数和按引用传递参数:
所有参数(自变量)在python里都是按引用传递,如果你在函数里修改了参数,那么在调用这个函数时,原始的参数也被改变。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 可写函数说明 def changeme( mylist ): "修改传入的列表" mylist.append([1,2,3,4]); print "函数内取值: ", mylist return # 调用changeme函数 mylist = [10,20,30]; changeme( mylist ); print "函数外取值: ", mylist
传入函数的和在末尾添加新内容的对象用的是同一个引用
函数内取值: [10, 20, 30, [1, 2, 3, 4]] 函数外取值: [10, 20, 30, [1, 2, 3, 4]]
5、参数
调用函数时可以使用的正式参数类型
- 必备参数
- 关键字参数
- 默认参数
- 不定长参数
必备参数:
必备参数以正确的顺序传入函数,调用时数量必须和声明的一样。
调用printme()函数,你必须传入一个参数否则报错
关键字参数:
关键字参数和函数调用关系密切,函数调用使用使用关键字参数来确定传入的参数值
使用关键字参数允许函数调用时参数的顺序和声明时不一致。
缺省参数:
调用函数时缺省参数的值如果没有传入,则被认为是默认值
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- #可写函数说明 def printinfo( name, age = 35 ): "打印任何传入的字符串" print "Name: ", name; print "Age ", age; return; #调用printinfo函数 printinfo( age=50, name="miki" ); printinfo( name="miki" );
结果:
Name: miki Age 50 Name: miki Age 35
注:如果age没有传入则打印默认值
不定长参数:
你可能需要一个函数能处理比当初声明时更多的参数,这些参数叫不定长参数
def functionname([formal_args,] *var_args_tuple ): "函数_文档字符串" function_suite return [expression]
加星号(*)的变量名会存放所有未命名的变量参数,
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# 可写函数说明
def printinfo( arg1, *vartuple ):
"打印任何传入的参数"
print "输出: "
print arg1
for var in vartuple:
print var
return;
# 调用printinfo 函数
printinfo( 10 );
printinfo( 70, 60, 50 );
结果:
输出: 10 输出: 70 60 50
匿名函数:
python使用lambda来创建匿名函数
- lambda只是一个表达式,函数体比def简单很多
- lambda的主体是一个表达式,而不是代码块,仅仅能在lambda表达式中封装有限的逻辑进去
- lambda函数拥有自己的命名空间,且不能访问自有参数之外或全局命名空间里的参数
- 虽然lambda函数看起来只能写一行,却不等同于C或者C++的内联函数
语法:
lambda函数的语法只包含一个语句,
lambda [arg1 [,arg2,.....argn]]:expression
例子:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 可写函数说明 sum = lambda arg1, arg2: arg1 + arg2; # 调用sum函数 print "相加后的值为 : ", sum( 10, 20 ) print "相加后的值为 : ", sum( 20, 20 )
结果:
相加后的值为 : 30 相加后的值为 : 40
return语句
return语句[表达式]退出函数,选择性的向调用方返回一个表达式。不带参数值的return语句返回None:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 可写函数说明 def sum( arg1, arg2 ): # 返回2个参数的和." total = arg1 + arg2 print "函数内 : ", total return total; # 调用sum函数 total = sum( 10, 20 ); print "函数外 : ", total
结果:
函数内 : 30 函数外 : 30
变量作用域
一个程序的所有的变量并不是在哪个位置都可以访问的,访问权限决定于这个变量是哪里赋值的。
变量的作用域决定了在哪一部分程序你可以访问哪一个特定的变量名称
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- total = 0; # 这是一个全局变量 # 可写函数说明 def sum( arg1, arg2 ): #返回2个参数的和." total = arg1 + arg2; # total在这里是局部变量. print "函数内是局部变量 : ", total return total; #调用sum函数 sum( 10, 20 ); print "函数外是全局变量 : ", total
结果:
函数内是局部变量 : 30 函数外是全局变量 : 0
