gate
这是一道虚树的模板题。首先来介绍一下什么是虚树。
虚树,顾名思义,是一棵原本不存在的树。
虚树DP的标志是:一棵(n)个点的树,给出(k)个关键点((sum k<frac{n}{2})),求使这些点互不连通的最小代价。
可以发现,答案只与这些点和他们的(LCA)有关。
所以,可以通过建一棵只有这些点和他们的(LCA)的树,就可以大幅度降低DP的时间复杂度。
例如,我们只保留这张图上的关键点和它们的(LCA):
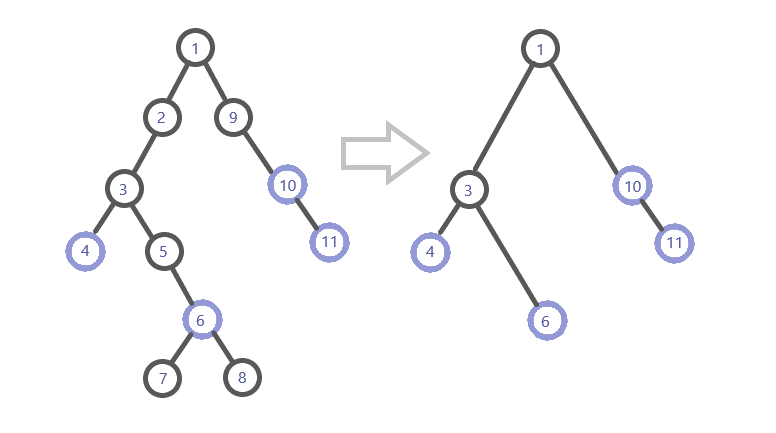
那么,如何建出这个虚树呢?
将关键点按dfs序排序,以符合遍历这棵树的顺序。
维护一个栈,栈中的元素表示从根节点到这个节点的一条链。(处理完所有关键点后,将栈中元素依次连边。)
元素入栈前,要清空这个元素所连的边。
第一个关键点在初始时直接入栈。
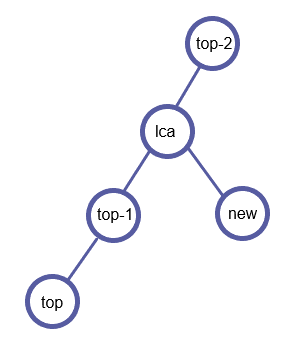
假设当前要加入的关键点为new,栈顶元素为top,第二个为top-1,首先求出它们的LCA。
因为按dfs序遍历,因此LCA一定不是new
此时可以分为两种情况:
- (LCA = top):即
new在top的子树中(new可以直接入栈); - (LCA
ot= top):即
new和top分别在LCA的两棵子树中。此时要继续讨论:
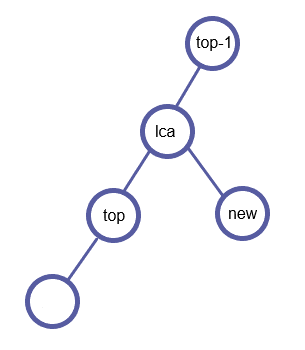
检查是否(dfn[top-1] > dfn[LCA]):如果栈顶第二个元素top-1也在LCA的下面,那么top和top-1之间一定需要连边,连完就可以从栈中将top弹出了。
重复这个过程,直到(dfn[top-1] ≤ dfn[LCA])为止。
检查LCA是否已在栈中。- (LCA = top-1):即
LCA已在栈中;则同上连边top和top-1,将top弹出。 - (LCA
ot= top-1):即
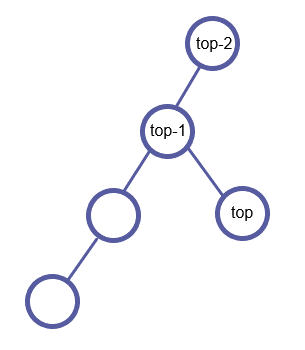
LCA不在栈中;LCA是为了为了连接top和new的一个新点。因此连接top和LCA,并将LCA入栈。LCA成为了新的top。
- (LCA = top-1):即
处理完这些后,再将new入栈。
(new和LCA入栈前,都不要忘记把边清空!)
如图所示为一个可能的入栈过程:

处理完每一个关键点后,将栈中元素依次(i和i+1)连边。
View code
void build(int n) {
st[top = 1] = 1;
e[1].clear();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(po[i] == 1) continue;
int lca = getlca(po[i],st[top]);
if(lca != st[top]) {
while(dfn[st[top-1]] > dfn[lca])
add(st[top-1],st[top]),top--;
if(st[top-1] == lca)
add(st[top-1],st[top]),top--;
else {
e[lca].clear();
add(lca,st[top]);
st[top] = lca;
}
}
st[++top] = po[i];
e[po[i]].clear();
}
for(int i = 1; i < top; i++)
add(st[i],st[i+1]);
}
建树完成后就可以开始(dp)了。
回到这道题上:求删除最少非关键点使关键点互不连通。
若父子均为关键点,则无解;这里用一个(vis)记录该点是不是关键点,检查每个关键点的父亲是否被标记了(vis)即可。
设(f[u])表示(u)的子树的最小花费,(g[u])表示(u)的子树内有多少未断开的关键点。
首先,有(f[u]=sum f[v],g[u]=sum g[v])(不包括自己);
- 若(u)是关键点,则(u)需要跟它子树中的每个点断开,即(f[u]+=g[u]);
同时,(u)本身还没有处理,所以(g[u] = 1). - 若(u)不是关键点:
- 若(g[u] = 1),即(u)的子树中只有一个关键点,则没有现在必须处理的点,可以先不操作;
- 若(g[u] > 1),则去掉(u)就可以使子树中的关键点互不连通。此时(u)的子树已处理完毕。(f[u]+=1,g[u]=0)。
完整代码如下
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define MogeKo qwq
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5+10;
int n,q,k,now,top,x,y;
int po[maxn],f[maxn],g[maxn],st[maxn];
int dfn[maxn],dpth[maxn],p[maxn][25];
bool vis[maxn];
vector<int> e[maxn];
bool cmp(int x,int y) {
return dfn[x] < dfn[y];
}
void add(int x,int y) {
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
}
void dfs(int u,int fa) {
dfn[u] = ++now;
dpth[u] = dpth[fa]+1;
p[u][0] = fa;
for(int i = 1; (1<<i) <= dpth[u]; i++)
p[u][i] = p[p[u][i-1]][i-1];
for(int i = 0; i < e[u].size(); i++) {
int v = e[u][i];
if(v == fa) continue;
dfs(v,u);
}
}
int getlca(int a,int b) {
if(dpth[a] < dpth[b])
swap(a,b);
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--)
if(dpth[a]-(1<<i) >= dpth[b])
a = p[a][i];
if(a == b)return a;
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--)
if(p[a][i] != p[b][i]) {
a = p[a][i];
b = p[b][i];
}
return p[a][0];
}
void build(int n) {
st[top = 1] = 1;
e[1].clear();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(po[i] == 1) continue;
int lca = getlca(po[i],st[top]);
if(lca != st[top]) {
while(dfn[st[top-1]] > dfn[lca])
add(st[top-1],st[top]),top--;
if(st[top-1] == lca)
add(st[top-1],st[top]),top--;
else {
e[lca].clear();
add(lca,st[top]);
st[top] = lca;
}
}
st[++top] = po[i];
e[po[i]].clear();
}
for(int i = 1; i < top; i++)
add(st[i],st[i+1]);
}
void dp(int u,int fa) {
f[u] = g[u] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < e[u].size(); i++) {
int v = e[u][i];
if(v == fa) continue;
dp(v,u);
f[u] += f[v];
g[u] += g[v];
}
if(vis[u]) {
f[u] += g[u];
g[u] = 1;
} else if(g[u] > 1) {
f[u]++;
g[u] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
add(x,y);
}
dfs(1,0);
scanf("%d",&q);
while(q--) {
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
scanf("%d",&k);
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
scanf("%d",&po[i]);
vis[po[i]] = true;
}
bool flag = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
if(vis[p[po[i]][0]]) {
printf("-1
");
flag = true;
break;
}
if(flag) continue;
sort(po+1,po+k+1,cmp);
build(k);
dp(1,0);
printf("%d
",f[1]);
}
return 0;
}