十五、contextMap
1、动作类的生命周期
明确:动作类是多例的,每次动作访问,动作类都会实例化。所以是线程安全的。与Struts1的区别是,struts1的动作类是单例的。
2、请求动作的数据存放
问题:
每次请求时,都会产生一些请求数据,这些数据存放到哪里去了?
明确:
在每次动作执行前,核心控制器StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter都会创建一个ActionContext和ValueStack对象。且每次动作访问都会创建。
这两个对象存储了整个动作访问期间用到的数据。并且把数据绑定到了线程局部变量(ThreadLocal)上了。所以是线程安全的。

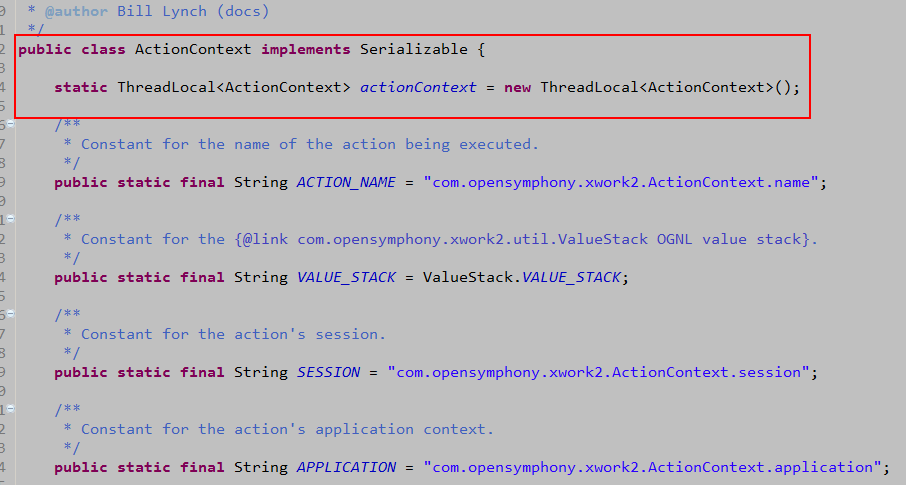
3、contextMap:存储数据
Struts2的官方文档对contextMap的说明:

|
contextMap中存放的主要内容 |
||
|
Key |
Value |
说明 |
|
value stack (root) |
java.util.List |
没有root这个key。contextMap中它有key,但是我们不用。它是一个list。(com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack是它的key)。 |
|
application |
java.util.Map<String,Object> |
ServletContext中的所有属性。 |
|
session |
java.util.Map<String,Object> |
HttpSession中的所有属性。 |
|
request |
java.util.Map<String,Object> |
ServletRequest中的所有属性。 |
|
parameters |
java.util.Map |
参数 |
|
attr |
java.util.Map |
把页面、请求、会话、应用范围内的所有属性放到一起。 |
注意:
除了value stack之外,全是map,而contextMap也是一个map。其实就是Map中又封装的Map。(很像dbutils中KeyedHandler封装数据的结构,只是封装数据的结构)
查看contextMap中的数据:
在页面上使用<s:debug/>



十六、contextMap中的数据操作
1、存数据:
需要熟悉ActionContext和valueStack的API。框架为我们存数据。
1.1、利用ActionContext存数据
1 public String demo1(){ 2 //1.获取到ActionContext对象 3 ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();//从当前线程上获取 4 //2.往大map中存入数据 5 context.put("contextMap", "hello context map"); 6 7 //3.往指定的小Map中存入数据(request,session,application) 8 //Map<String,Object> sessionMap = (Map<String, Object>) context.get("session"); 9 //第一种方式:使用map操作 10 Map<String,Object> sessionMap = context.getSession(); 11 sessionMap.put("sessionMap", "hello session map"); 12 //第二种方式:使用原始ServletAPI存入数据 13 HttpSession session = ServletActionContext.getRequest().getSession(); 14 session.setAttribute("sessionAttr","hello session attribute"); 15 16 //4.往application的map中存入数据 17 //第一种方式:使用map操作 18 Map<String,Object> applicationMap = context.getApplication(); 19 applicationMap.put("applicationMap", "hello application map"); 20 //第二种方式:使用原始ServletAPI对象 21 ServletContext application = ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); 22 application.setAttribute("applicationAttr", "hello application attribute"); 23 return SUCCESS; 24 }
1.2、利用ValueStack存数据
a、如何获取ValueStack
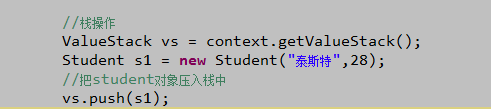
1 /** 2 * 利用ValueStack存取数据操作 3 * 明确: 4 * 1、它本身是一个List结构,同时具备了栈的特点。 5 * 2、它里面只能存放对象,没有key,value的概念。 6 * @author zhy 7 * 8 */ 9 public class Demo2Action extends ActionSupport { 10 11 private String name = "泰斯特"; 12 13 public String demo2(){ 14 //1.获取valueStack 15 //先获取ActionContext 16 ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext(); 17 context.put("contextMap", "hello context map"); 18 //再使用ActionContext中的getValueStack方法获取 19 ValueStack vs = context.getValueStack(); 20 /* 21 * 压栈操作 22 */ 23 Student s1 = new Student("test",18,"male"); 24 vs.push(s1); 25 26 Student s2 = new Student("test1",20,"female"); 27 vs.push(s2); 28 29 return SUCCESS; 30 } 31 32 public String getName() { 33 return name; 34 } 35 36 public void setName(String name) { 37 this.name = name; 38 } 39 40 }
b、ValueStack中的getRoot()方法:
c、CompoundRoot是什么:

d、栈操作:
2、取数据:用Struts2的标签(OGNL表达式)在JSP上
使用OGNL表达式来去,struts2的OGNL表达式必须写在struts2标签中。
2.1、使用s:property取数据
a、取contextMap中的数据,需使用#
1 <body> 2 <%--1.获取ValueStack中的数据 : 3 当我们使用s:property不指定value属性时,默认获取的是栈顶元素(对象) 4 注意:获取的是一个对象。 5 只有不使用value属性时,才获取的是对象。 6 剩余的情况全是: 7 根据属性名称获取属性值!!!!!!!! 8 --%> 9 <s:property/> 10 <hr/> 11 <%--2.获取指定属性的值 12 当s:property标签的value属性没有使用#号时,是从ValueStack中获取数据 13 把value的取值当做property name,从栈顶逐个元素往下寻找,找和value取值一样的属性, 14 找到了,把值获取回来。只要找到了,就不再继续寻找。 15 16 17 获取valueStack中的数据,不用写#号。并且直接写属性名称即可。 18 --%> 19 <s:property value="name"/> 20 <hr/> 21 <%--3.获取指定位置指定属性的值 22 [1]表示的不是属性名称出现的索引位置。 23 而是指的集合中元素(对象)的索引位置。 24 25 当我们使用[n].propertyname方式获取值时,它就是把栈中下标为n的元素看成是栈顶元素,逐个往下寻找。 26 --%> 27 <s:property value="[1].name"/> 28 <hr/> 29 <%--4.ValueStack中的findValue方法 --%> 30 <% ActionContext ac = ActionContext.getContext(); 31 ValueStack vs = ac.getValueStack(); 32 Object obj = vs.findValue("name"); 33 Object obj1 = vs.findValue("[2].name"); 34 out.print(obj); 35 out.print("<hr/>"); 36 out.print(obj1); 37 out.print("<hr/>"); 38 Object obj2 = vs.findValue("#contextMap"); 39 out.print("aaaa:"+obj2); 40 %> 41 <%-- <s:property value="#contextMap"/> --%> 42 <s:debug/> 43 </body>

b、取contextMap里面ValueStack中对象的属性:直接写属性名
1 <tr> 2 <td><s:property value="name"/></td> 3 <td><s:property value="age"/></td> 4 <td><s:property value="gender"/></td> 5 </tr>

OGNL的使用总结:
1.取根中对象的属性,不使用#。
2.取contextMap中key的值,要使用#。
2.2、ValueStack的findValue方法(我们在Jsp上调用的都是findValue)

十七、Struts2对EL的改变
1、Struts2中使用EL的问题:
前提:
我们应该知道,如果我们没有往值栈(根)中放入数据的话,那么我们的动作类默认是在值栈的栈顶。


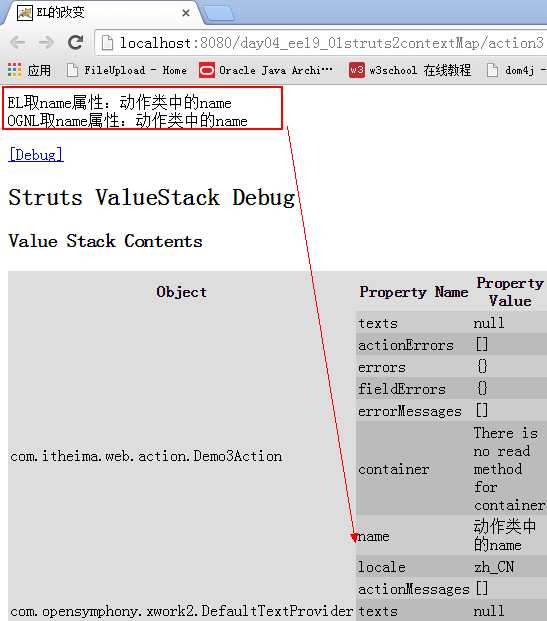
问题:
我们放到请求域中的属性,使用EL表达式取出来了。但是放到应用域中的属性,使用EL表达式没取出来。
2、关于EL问题的分析:
分析:
我们知道EL表达式是从四大域对象中依次查找属性。搜索范围是由小到大。page Scope————>request Scope————>sessionScope————>application Scope
但是通过测试发现,搜索完request范围后就没有继续搜索,而是返回了ValueStack中栈顶对象name属性的值。
3、Struts2中EL查找顺序改变总结:
EL表达式: page Scope————>request Scope————>sessionScope————>application Scope
OGNL表达式:page Scope————>request Scope————>valueStack(根中)————>contextMap————>sessionScope————>application Scope
4、OGNL的特殊说明:
1 public String demo3(){ 2 //1.获取HttpServletRequest的对象 3 HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); 4 //2.往请求域中存放一个name 5 //request.setAttribute("name", "请求域中的name"); 6 //3.获取HttpSession 7 HttpSession session = request.getSession(); 8 session.setAttribute("name", "会话域中的name"); 9 10 ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext(); 11 context.put("name", "大Map中的name"); 12 13 return SUCCESS; 14 }
十八、OGNL配合通用标签的其他使用
1、iterator标签
1 /** 2 * iterator标签的使用 3 * @author zhy 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Demo4Action extends ActionSupport { 7 8 private List<Student> students; 9 10 public String demo4(){ 11 //1.获取HttpServletRequest的对象 12 //HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); 13 //就相当于从数据库中获取学生列表 14 students = new ArrayList<Student>(); 15 students.add(new Student("test1",18,"male")); 16 students.add(new Student("test2",21,"female")); 17 students.add(new Student("test3",22,"male")); 18 //2.把查询出来的学生列表存入请求域中 19 //request.setAttribute("students", students); 20 21 return SUCCESS; 22 } 23 24 public List<Student> getStudents() { 25 return students; 26 } 27 28 public void setStudents(List<Student> students) { 29 this.students = students; 30 } 31 }
1 <s:iterator value="students"> 2 <tr> 3 <td><s:property value="name"/></td> 4 <td><s:property value="age"/></td> 5 <td><s:property value="gender"/></td> 6 </tr> 7 </s:iterator>
2、Struts2中#,$,%符号的使用
2.1、#
a、取ActionContext中key时使用,例如<s:property value="#name" />
b、OGNL中创建Map对象时使用,例如:<s:radio list="#{'male':'男','female':'女'}" />
2.2、$
a、在JSP中使用EL表达式时使用,例如${name}
b、在xml配置文件中,编写OGNL表达式时使用,例如文件下载时,文件名编码。struts.xml——>${@java.net.URLEncoder.encode(filename,"UTF-8")}
2.3、%
在struts2中,有些标签的value属性取值就是一个OGNL表达式,例如<s:property value="OGNL Expression" />
还有一部分标签,value属性的取值就是普通字符串,例如<s:textfield value="username"/>,如果想把一个普通的字符串强制看成时OGNL,就需要使用%{}把字符串套起来。
例如<s:textfield value="%{username}"/>。当然在<s:property value="%{OGNL Expression}" />也可以使用,但不会这么用。
3、其他标签
3.1、if标签,elseif标签 else标签
1 <%--1、s:if s:elseif s:else 2 作用: 3 进行条件判断。 4 属性: 5 test里面的内容是一个逻辑运算,返回的结果应该是一个布尔类型值。 6 可以使用常量运算,还可以是OGNL表达式的逻辑 运算 7 8 test的取值可以是OGNL表达式,但是只能在ValueStack中取值 9 10 --%> 11 <%--没有经过动作类 12 ActionContext ac = ActionContext.getContext(); 13 ac.put("name", "test"); 14 --%> 15 <s:if test="name == null"> 16 用户名没有了 17 </s:if> 18 <s:elseif test="#name == 'test'"> 19 是一个测试用户 20 </s:elseif>
3.2、url和a标签
1 <%--2、s:url 和 s:a 2 s:url标签: 3 作用:是把指定路径存入contextMap中 4 属性: 5 action:直接写动作名称。不用再写${pageContext.request.contextPath} 6 namespace:指定动作所在的名称空间,如果该动作是在默认名称空间下可以不写 7 var:取值是一个普通字符串。把var的取值当做key,把action的取值当做value,存入contextMap中 8 s:param标签: 9 作用:是给s:url或者s:a添加请求参数 10 属性: 11 name:参数的名称 12 value:参数的值.它的取值是一个OGNL表达式. 13 s:a标签: 14 作用:和超链接标签是一样的。并且可以和s:url互换 15 --%> 16 <s:url action="action1" var="action1_url"> 17 <s:param name="param1" value="'hello'"></s:param> 18 </s:url> 19 <a href="<s:property value="#action1_url"/>">let me see see</a> 20 21 22 <br/> 23 <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/action1.action">让我们看看</a> 24 <br/> 25 26 27 <s:a action="action1" namespace=""> 28 <s:param name="param1" value="'hello'"></s:param> 29 去action1 看看 30 </s:a>
3.3、date标签
1 <%--3、s:date --%> 2 <font color="red">我们想要的输出结果是:2016-05-30 或者是 2016年05月30日</font><br/> 3 <%--s:date标签: 4 作用:格式化输出日期 5 属性: 6 name:取值是一个OGNL表达式。指定的是要转换的日期对象 7 format:指定转换的格式 8 var:取值是一个普通的字符串。把var的值当做key,把转换好的日期当成value,存入contextMap中 9 --%> 10 <s:date name="birthday" format="yyyy-MM-dd" var="sbirthday"/> 11 <%-- 12 DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日"); 13 String date = format.format(birthday); 14 out.print(date); 15 --%> 16 17 18 <s:property value="#sbirthday"/>